Arduino Mega - Control Fan
In this guide, we will show how to control a 12V or 5V fan with an Arduino Mega. We will explain it in more detail:
- How to connect a 12V or 5V fan to the Arduino Mega
- How to make the Arduino Mega turn the fan on and off
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of DC Fan
Pinout
A DC fan usually has two pins.
- Negative (-) pin (black): connect to the black wire of the DC power supply.
- Positive (+) pin (red): connect to the red wire of the DC power supply.
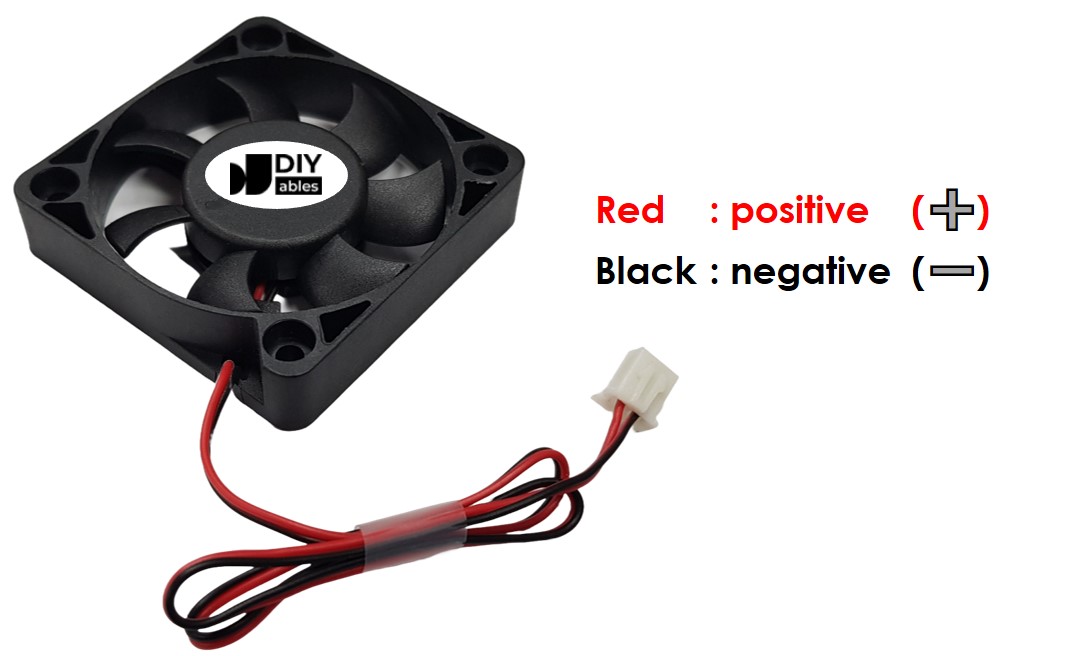

Make sure the DC power supply has the same voltage the fan needs. In this guide, we use fans that need 12 V DC and 5 V DC.
How to Control Fan
- A DC fan that gets power from a 12V or 5V power supply will run at full speed.
- A DC fan that gets a 12V or 5V PWM control signal can have its speed adjusted.
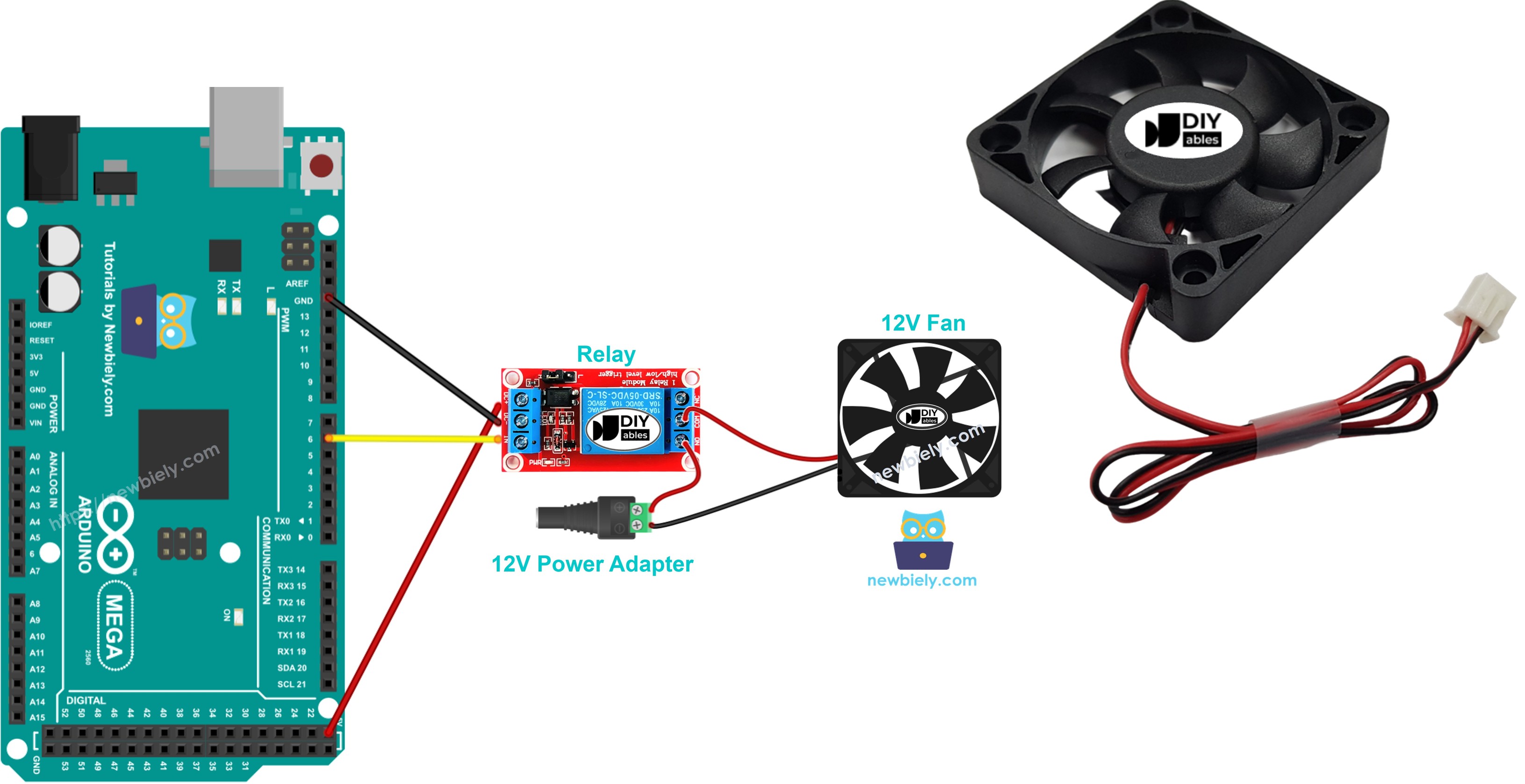
This guide shows how to turn a fan on and off with an Arduino Mega. The guide for controlling fan speed is in another guide. To control the fan, we use a relay between the Arduino Mega and the fan. The Arduino Mega controls the fan through the relay. If you are not familiar with relays (what they are, how they work, and how to program them), you can learn about them in the Arduino Mega - Relay tutorial.
Wiring Diagram
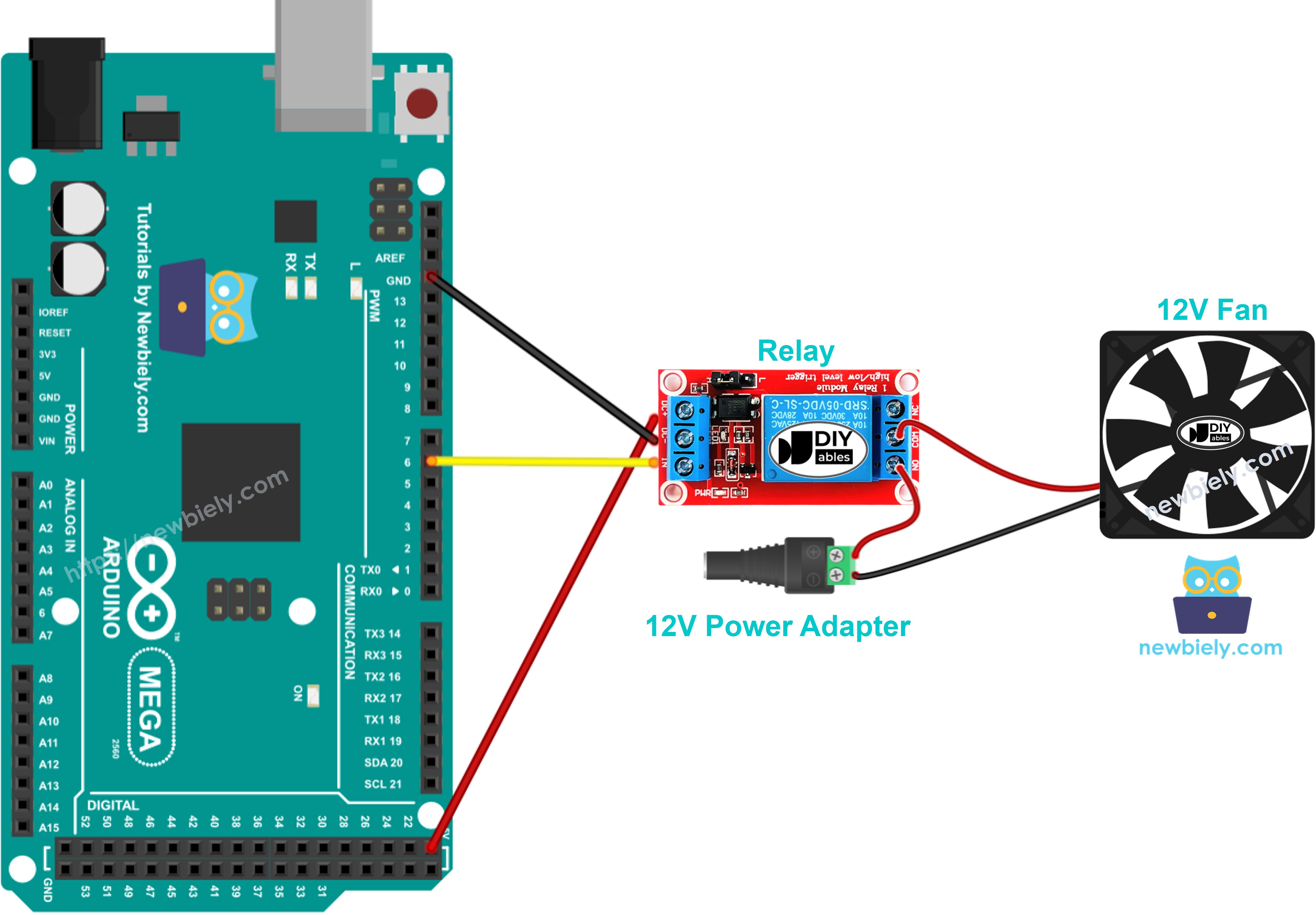
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino Mega Code
The following code keeps the fan on for five seconds and then off for five seconds.
Detailed Instructions
Do these steps one by one:
- Connect the Arduino Mega to the fan as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the Arduino Mega to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct board (Arduino Mega) and the right COM port.
- Copy and paste the given code into the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button to send the code to the Arduino Mega.
- Watch the fan to see how it works.
Code Explanation
The explanation is in the comments of the Arduino code shown above.
