Arduino Mega - Ultrasonic Sensor
This guide shows you how to use an ultrasonic sensor and an Arduino Mega to measure how far away an object is. Here’s what we will learn:
- How to connect an ultrasonic distance sensor to Arduino Mega
- How to write code for Arduino to read data from the ultrasonic sensor and turn it into distance
- How to reduce noise in the distance readings from the ultrasonic sensor on Arduino Mega
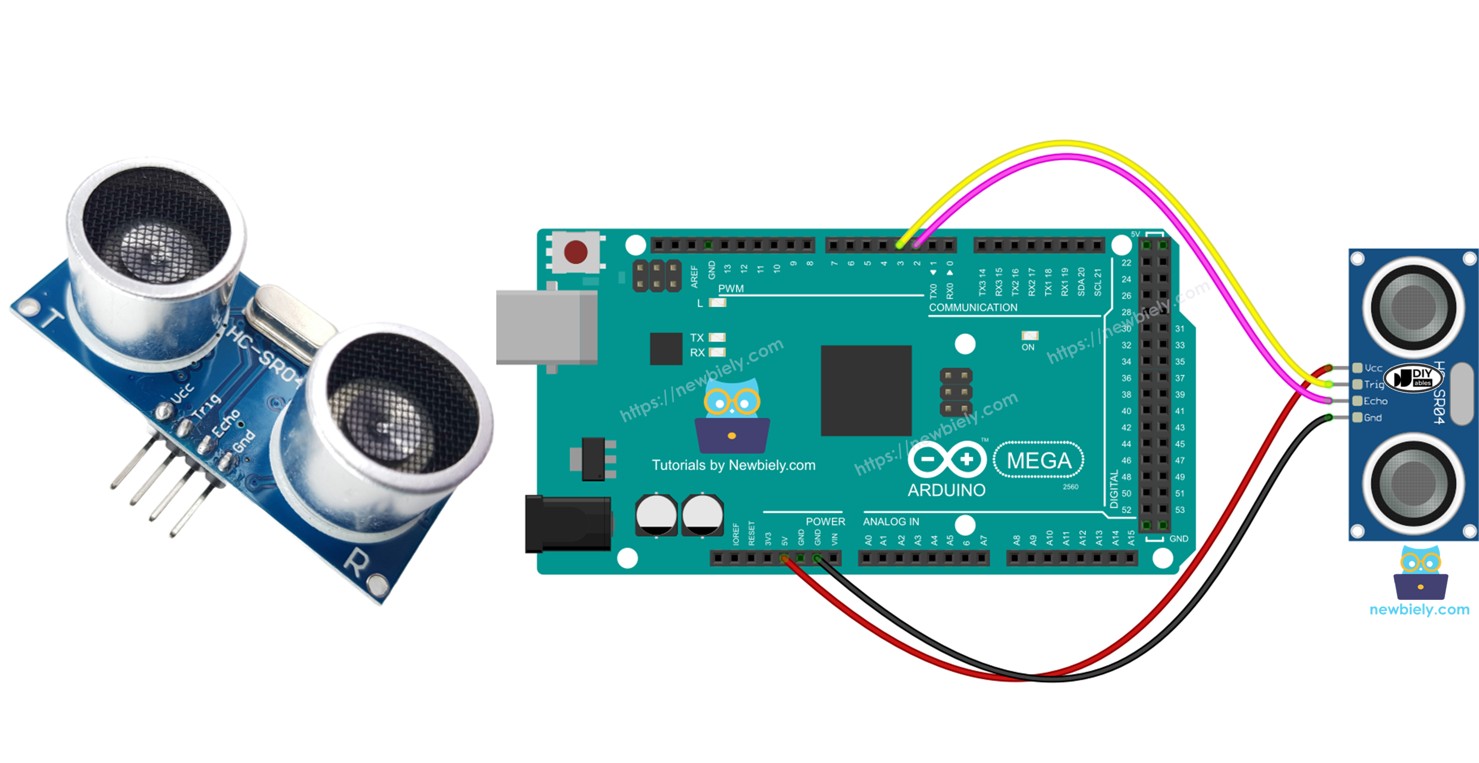
Hardware Preparation
| 1 | × | Arduino Mega | |
| 1 | × | USB 2.0 cable type A/B (for USB-A PC) | |
| 1 | × | USB 2.0 cable type C/B (for USB-C PC) | |
| 1 | × | Ultrasonic Sensor | |
| 1 | × | Jumper Wires |
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Ultrasonic Sensor
The HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor shows how far away things are by using sound waves. It sends out a sound wave that people can't hear, then waits for the echo when the sound wave bounces back from an object. By measuring how long the sound takes to come back, the sensor can figure out the distance.
Pinout
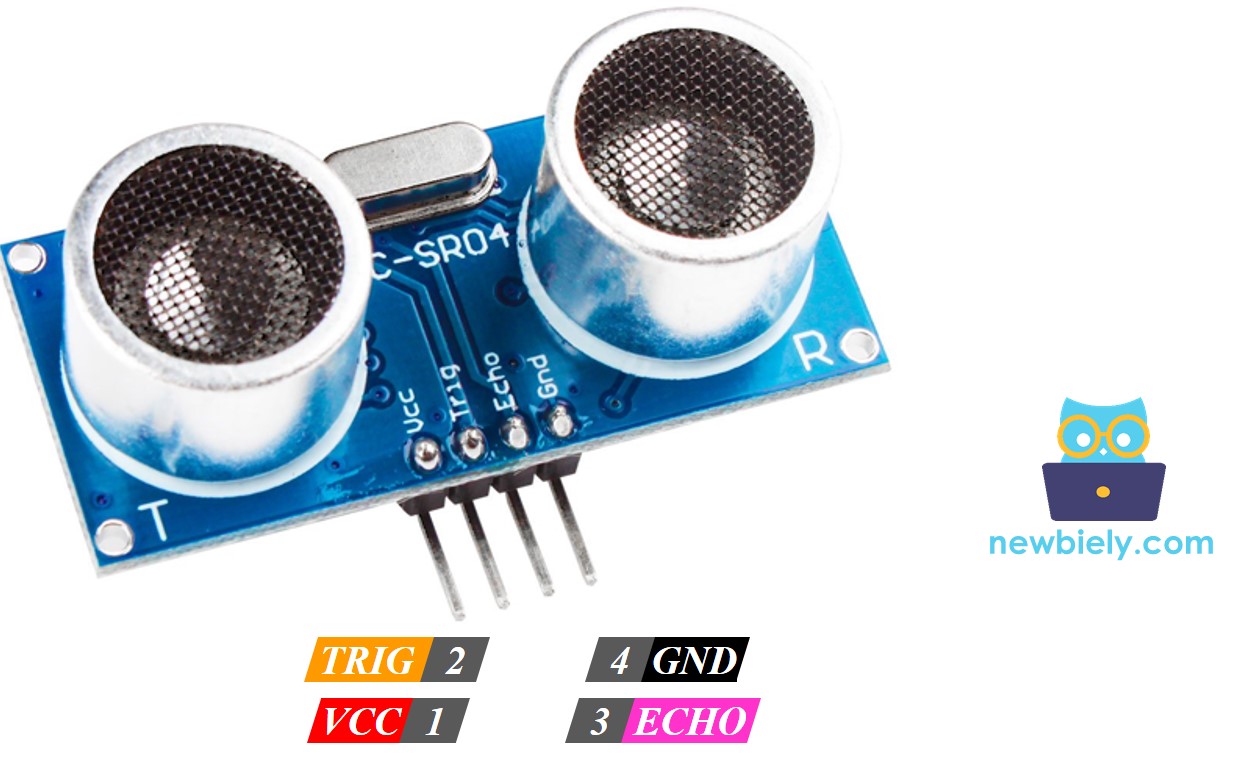
The HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor has four pins.
- VCC pin: connect to 5 volts.
- GND pin: connect to ground (0 volts).
- TRIG pin: connect to Arduino Mega to send control signals (pulses).
- ECHO pin: this pin sends pulses back to Arduino Mega. The Arduino Mega measures how long these pulses last to find distance.

Wiring Diagram
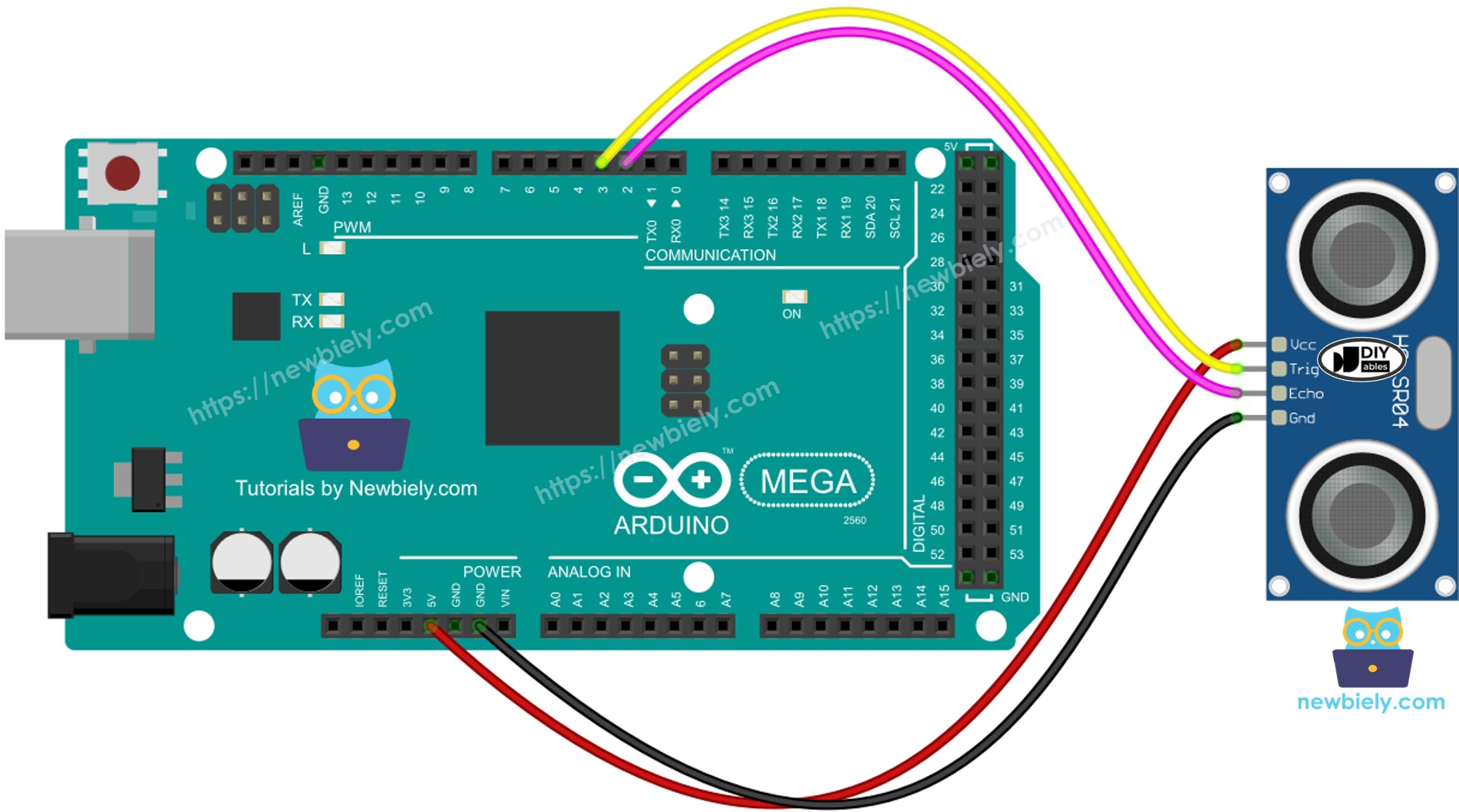
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino Mega Code
Detailed Instructions
Do these steps one by one.
- Connect the parts as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the Arduino Mega to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the Arduino Mega board and the correct COM port.
- Copy the code above and open it in the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to upload the code to the Arduino Mega.
- Open the Serial Monitor.
- Wave your hand in front of the ultrasonic sensor.
- See how far your hand is from the sensor on the Serial Monitor.
Code Explanation
The explanation is in the notes of the Arduino code shown above.
How to Filter Noise from Distance Measurements of Ultrasonic Sensor
The reading from the ultrasonic sensor has noise. Sometimes this noisy data can cause the system to work incorrectly. We can remove the noise with this method:
- Take several measurements and save them in a list.
- Sort the list from smallest to largest.
- Remove noise from the data:
- Ignore the smallest values as noise.
- Ignore the largest values as noise.
- Calculate the average using the remaining middle values.
- Skip the five smallest and the five largest samples because they are noise. Then find the average of the ten middle samples, from the 5th to the 14th.
The code below collects 20 measurements.
Video Tutorial
Ultrasonic Sensor Applications
- Preventing crashes
- Knowing when it's full
- Checking the level
- Seeing how close something is
