Arduino Mega - Water Sensor
This guide shows how to use a water sensor with the Arduino Mega. A water sensor can tell you if there is a water leak, measure rainfall, see if a tank is overflowing, or check the water level. Here is what we will learn:
- How to connect a water sensor to Arduino Mega
- How to program Arduino Mega to read the water sensor value
- How to detect water leaks, rain, or tank overflow with Arduino Mega
- How to measure water level with Arduino Mega
- How to calibrate the water sensor with Arduino Mega
Hardware Preparation
| 1 | × | Arduino Mega | |
| 1 | × | USB 2.0 cable type A/B (for USB-A PC) | |
| 1 | × | USB 2.0 cable type C/B (for USB-C PC) | |
| 1 | × | Water level sensor | |
| 1 | × | Jumper Wires |
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Water Level Sensor
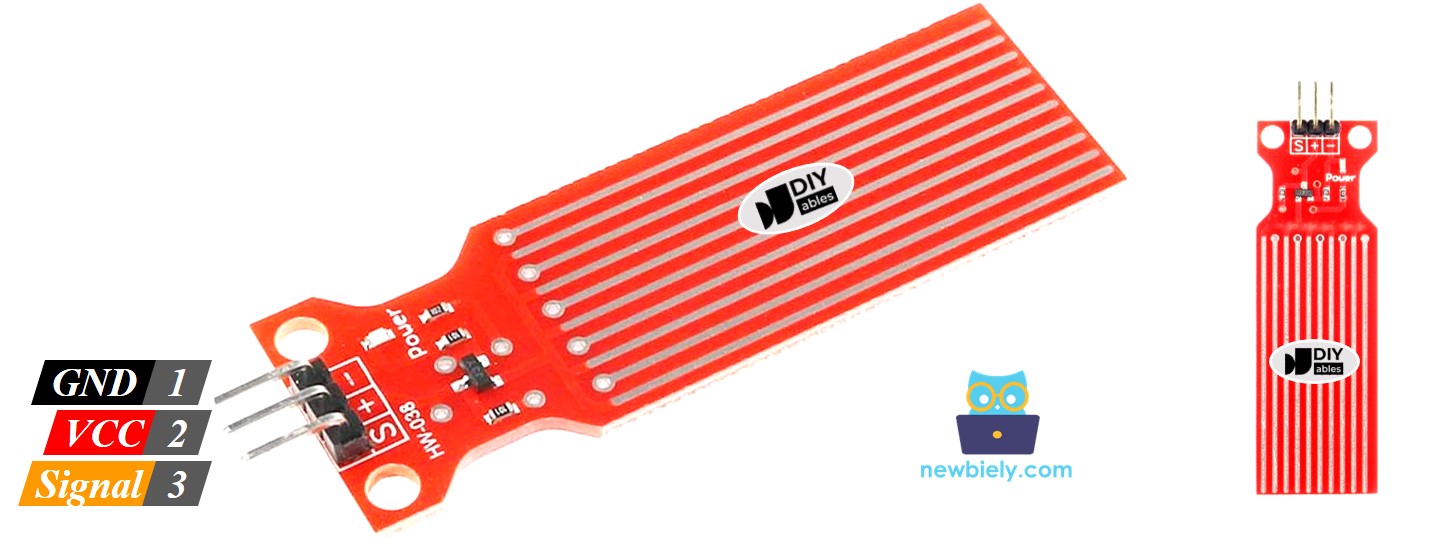
Water Level Sensor Pinout
The water level sensor has three pins:
- S (Signal) pin: It sends an analog signal. Connect it to an analog input on your Arduino Mega.
- + (VCC) pin: It powers the sensor. Use 3.3V to 5V.
- - (GND) pin: Ground connection.

※ NOTE THAT:
The sensor's signal pin output changes depending on the voltage you apply to its VCC pin.
How Water Level Sensor Works
When there is more water around the sensor, the voltage on the signal pin goes up.
Let's take a closer look.
The sensor has ten copper wires you can see. It has five power wires and five sensor wires. The wires are placed side by side, with one sensor wire between every two power wires. Normally the wires do not touch, but if the sensor is put in water, the water connects the wires.
The metal lines on the circuit board act like an adjustable resistor, like a potentiometer, and their resistance changes with the water level.
- The resistance changes to show how far the top of the sensor is from the water surface.
- Resistance goes down as the water level rises.
- When the sensor is deeper in the water, it conducts electricity better, so the resistance is lower.
- When the sensor is shallower in the water, it conducts electricity worse, so the resistance is higher.
- The sensor gives an output voltage that depends on the resistance.
We can tell the water level by measuring the voltage.
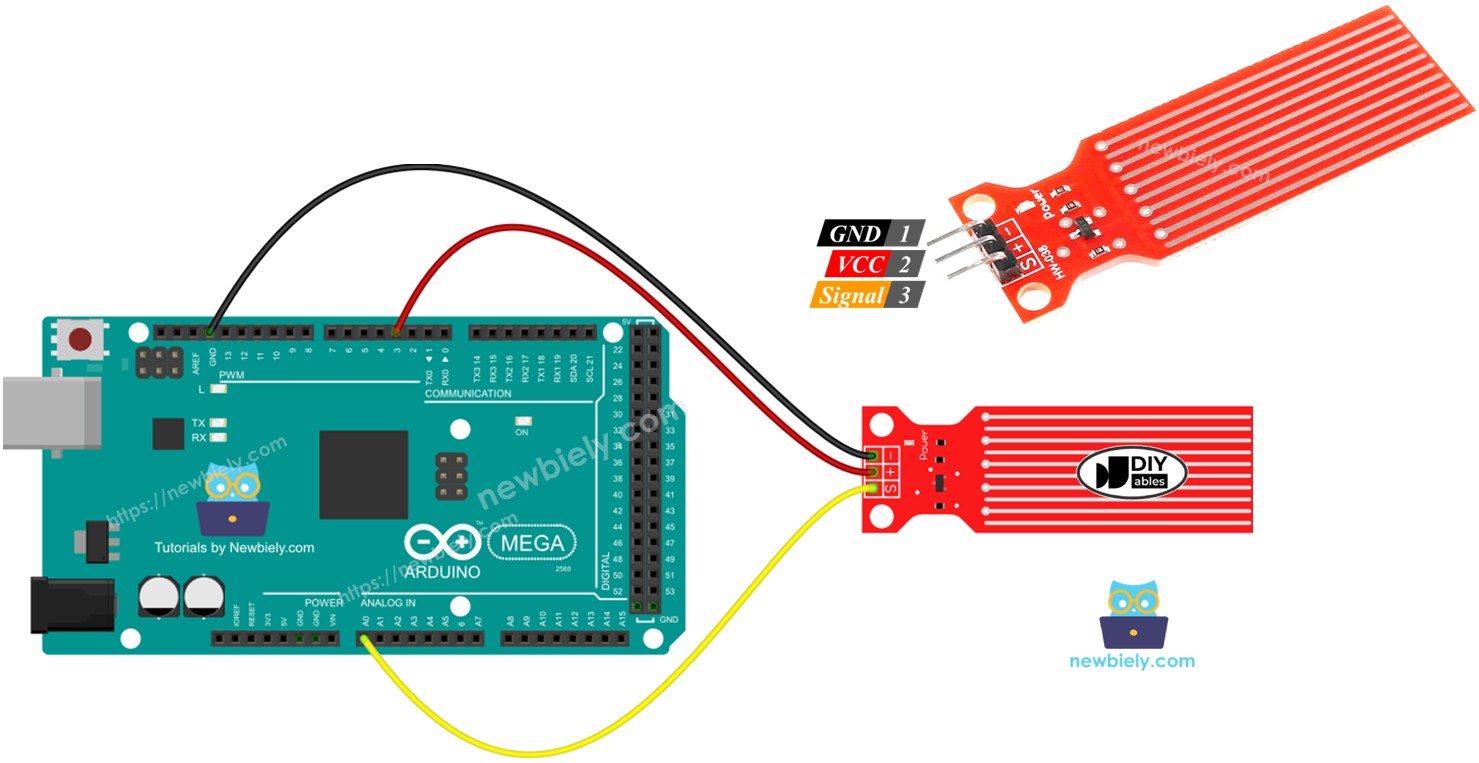
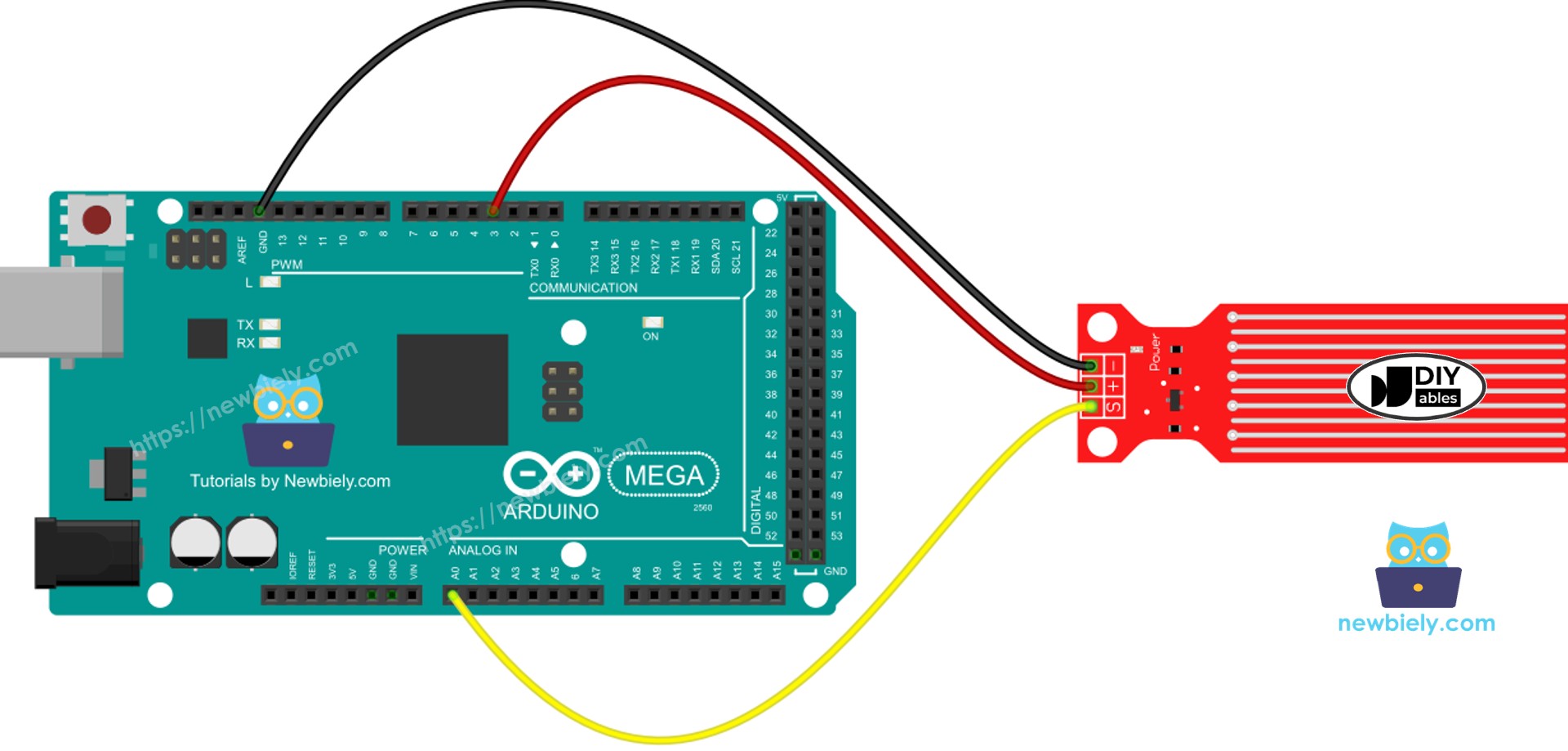
Wiring Diagram
Power the sensor by connecting its VCC to the Arduino Mega's 5V and its GND to the Arduino's GND.
But it's not a good idea to power the sensor all the time in a wet environment, because it can corrode quickly and shorten its life. To avoid this, we recommend powering the sensor only when you need to read its data. You can do this by connecting the sensor's VCC pin to a digital pin on an Arduino Mega. Set the pin to HIGH to read the sensor, and then set it to LOW when you're done.
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino Mega Code - Reading Value from Water Sensor
Detailed Instructions
Follow these steps one by one:
- Connect the water sensor to the Arduino Mega as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the Arduino Mega to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the Arduino Mega board and the correct COM port.
- Copy the given code and open it in the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button to send the code to the Arduino Mega.
- Slowly lower the sensor into the water (use a glass of water).
- Check the result in the Serial Monitor. It shows 0 when the sensor is not touching anything.
※ NOTE THAT:
Don't put the sensor completely underwater. Only the exposed parts on the circuit board may touch water. Please install it carefully.
How To Detect Water Leakage
To check if there is a water leak, rain, or the tank is overflowing, we simply compare the reading to a fixed limit. We set this limit during the setup in this guide.
Arduino Mega Code - Water Leak Detection
How To Measure The Water Level
To divide the highest water level into several stages and check which stage you are on, use the method shown in the code below. Remember, the highest water level matches the sensor’s height. This code divides the highest height into 4 stages.
※ NOTE THAT:
- The minimum sensor value (SENSOR_MIN) and the maximum sensor value (SENSOR_MAX) are set during calibration.
- The mapping method shown above may not be exact, but it works well in many cases. To be more accurate, measure the threshold values for each level as explained in the calibration section.
Water Level Sensor Calibration
How the sensor shows results depends on the water level and how well the water conducts electricity. Pure water does not conduct electricity. But water with minerals or other substances does conduct electricity. The more conductive the water, the more sensitive the sensor is. Also, the reading changes when you use different voltages on the sensor’s VCC pin.
To get accurate readings from the water sensor, set it up for the exact kind of water you will measure.
Before you set a limit for an action, first get the real reading from the sensor by testing it.
How to do the test
- Look at the picture to read the sensor value.
- Put the sensor in the water up to the level you want.
- Note the number shown in the Serial Monitor.
- Use this number as the limit to trigger an action.
This test may need a few tries to get it right.
The test can also help us find out:
- The smallest sensor reading when the sensor is out of water.
- The largest sensor reading when it is fully in water.
- A limit to detect water leaks.
- The limits for each level on your scale.
