Arduino Mega - Potentiometer
This guide shows you how to use an Arduino Mega with a potentiometer. Here is what we will learn:
- How a potentiometer works
- How to connect a potentiometer to the Arduino Mega
- How to program the Arduino Mega to read values from the potentiometer and turn them into useful numbers
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Potentiometer
A knob called a rotary potentiometer, or a rotary angle sensor, lets you change settings by turning it, such as stereo volume, lamp brightness, or oscilloscope zoom.
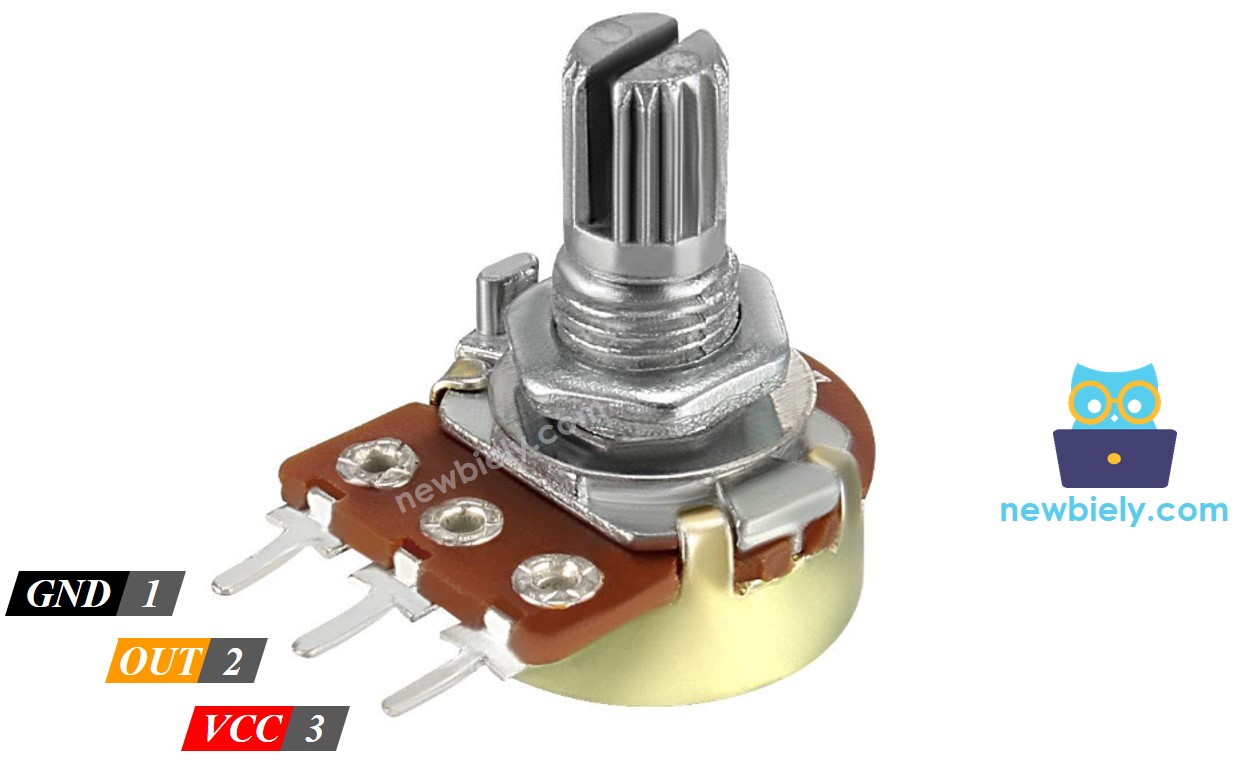
Pinout
A potentiometer usually has three pins.
- GND pin: connect to ground (0 volts)
- VCC pin: connect to 5V or 3.3V
- Output pin: sends voltage to the Arduino Mega's input pin

※ NOTE THAT:
You can swap the ground pin and the power pin.
How It Works
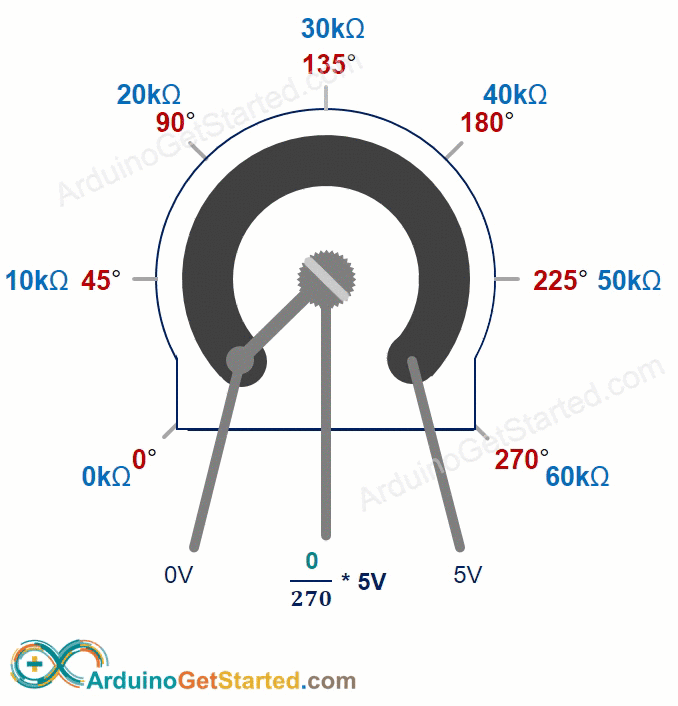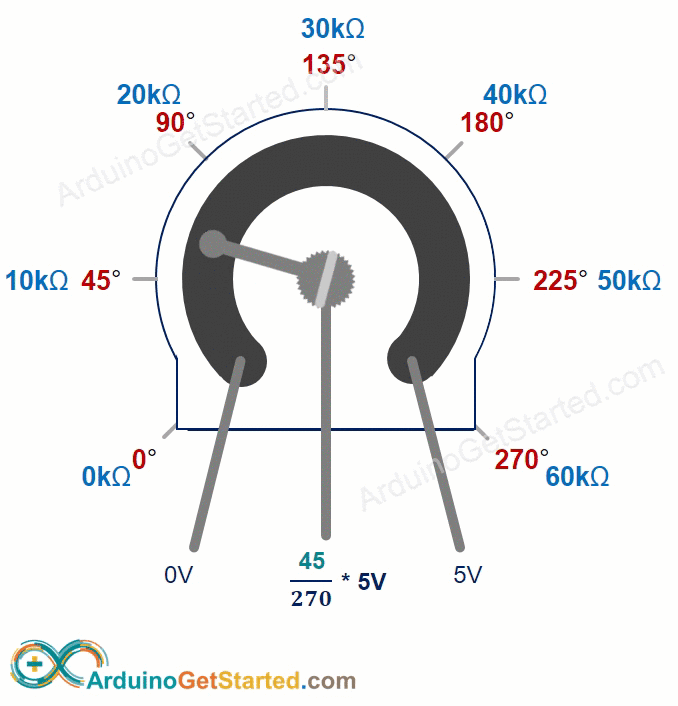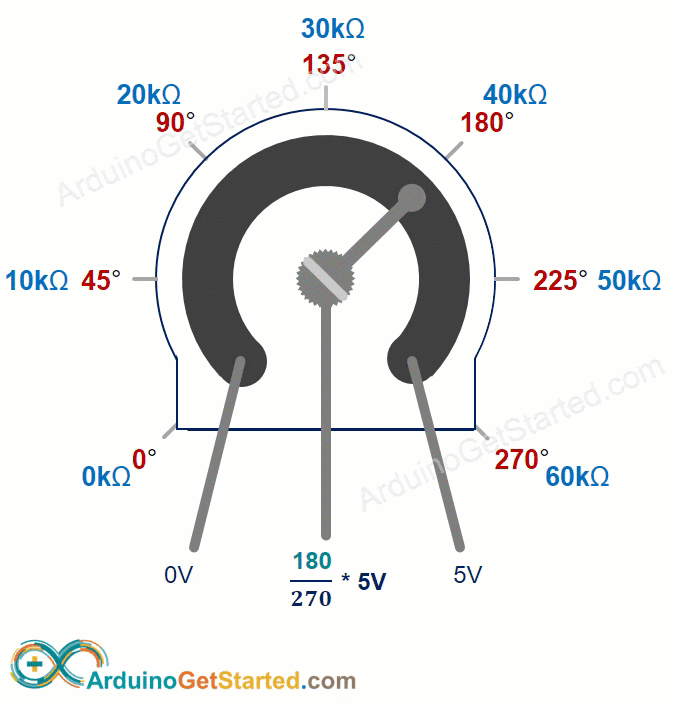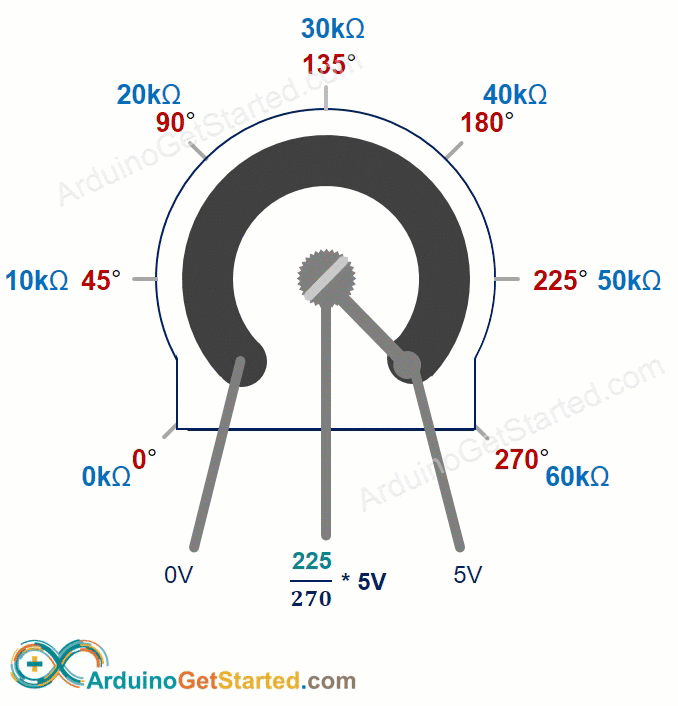
The potentiometer knob can turn from 0° (closest to GND) to the maximum angle (closest to the VCC pin), called ANGLE_MAX.
The output pin voltage can vary from ground to the supply voltage. The output voltage changes directly as you turn the shaft.
- If the angle is 0 degrees, the output voltage is 0 volts.
- If the angle equals ANGLE_MAX, the output voltage is VCC.
- If the angle is between 0 and ANGLE_MAX, output_voltage = angle times VCC divided by ANGLE_MAX.
※ NOTE THAT:
ANGLE_MAX value varies by manufacturer. Usually we don’t worry about ANGLE_MAX unless we need to calculate the rotation angle (see the use cases section).
Arduino Mega - Rotary Potentiometer
The A0 to A5 pins on the Arduino Mega can be used as analog inputs. They read a voltage from 0 volts up to the supply voltage (VCC) and turn it into numbers from 0 to 1023. These numbers are called ADC values (analog-to-digital converter values).
If you connect the potentiometer's output pin to an analog input pin on the Arduino Mega, you can program the Arduino to read the analog value and turn it into a useful number.
The number the Arduino Mega gets isn’t an angle or a voltage. It’s a whole number from 0 to 1023.
We read the value from the analog input pin and change it to another value. Now, let's see how we use it.
Use Cases
- Convert the ADC value to an angle.
- Convert the ADC value to a voltage.
- Convert the ADC value to a control value (for example, volume, brightness, or motor speed). This is the most common use.
Rescale Range
| FROM | TO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angle | rotated by user | 0° | → | ANGLE_MAX |
| Voltage | from potentiometer's pin | 0V | → | VCC |
| ADC value | read by Arduino Mega | 0 | → | 1023 |
| Other value | converted by Arduino Mega | VALUE_MIN | → | VALUE_MAX |
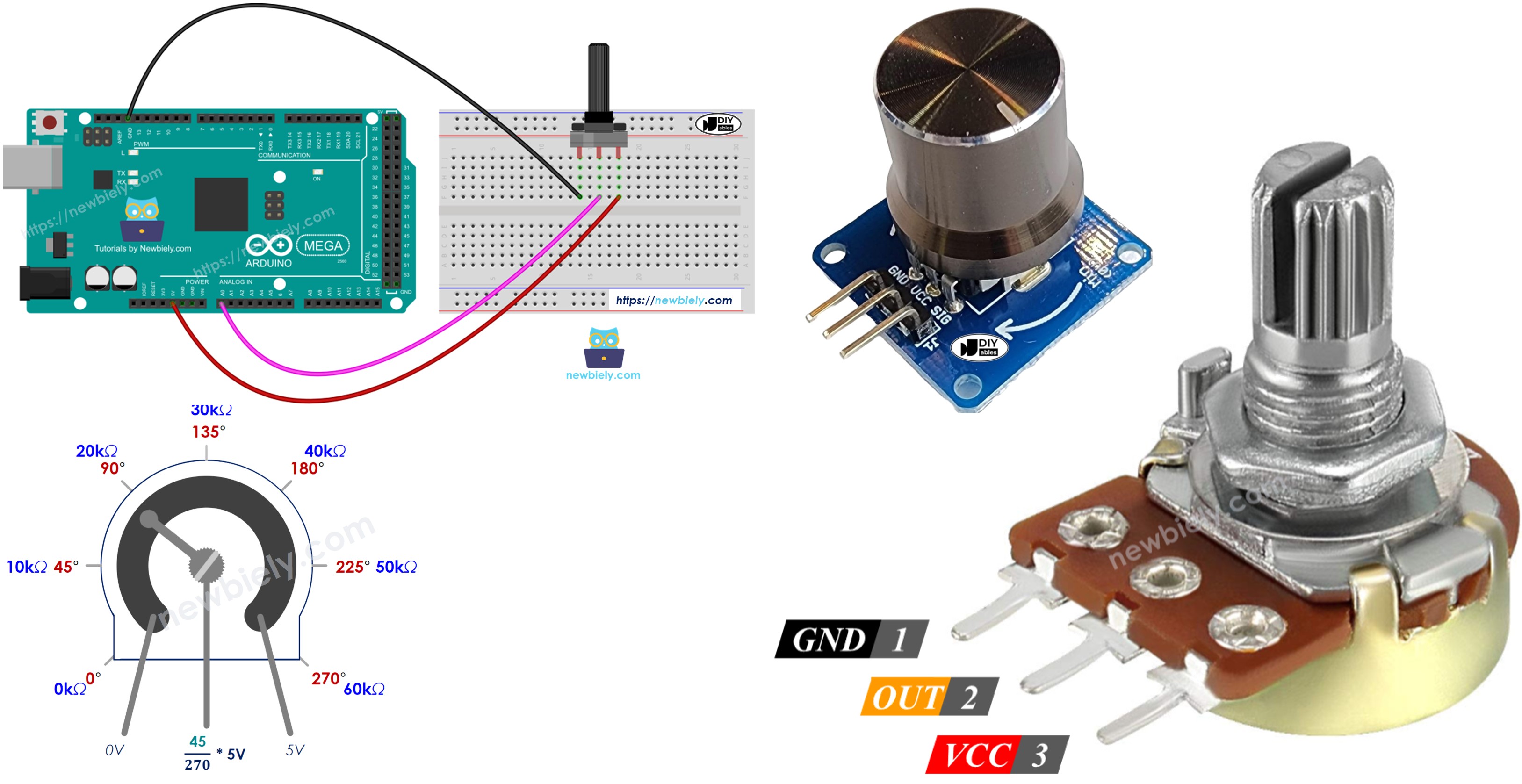
Wiring Diagram
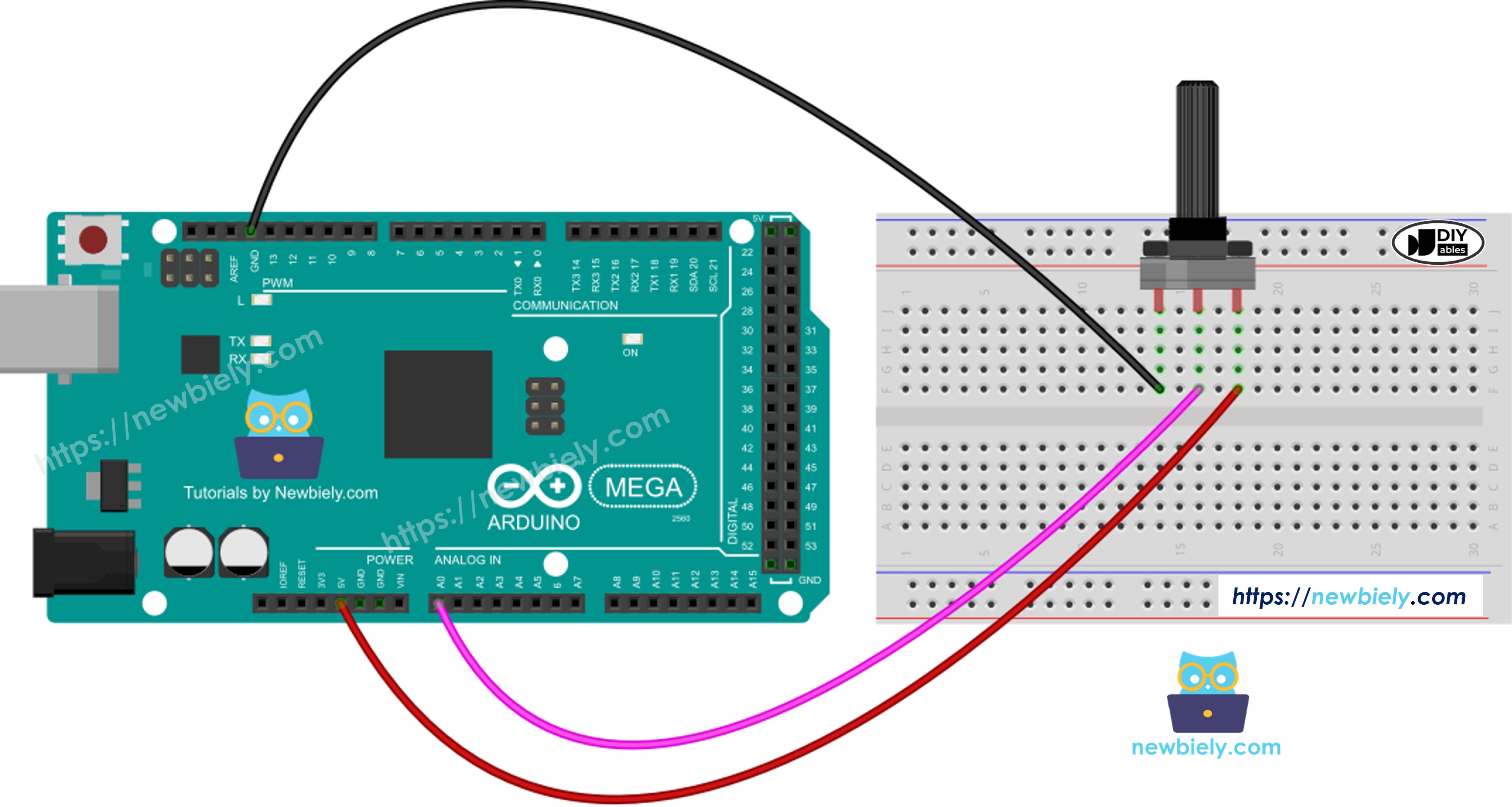
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
If using the potentiometer module:
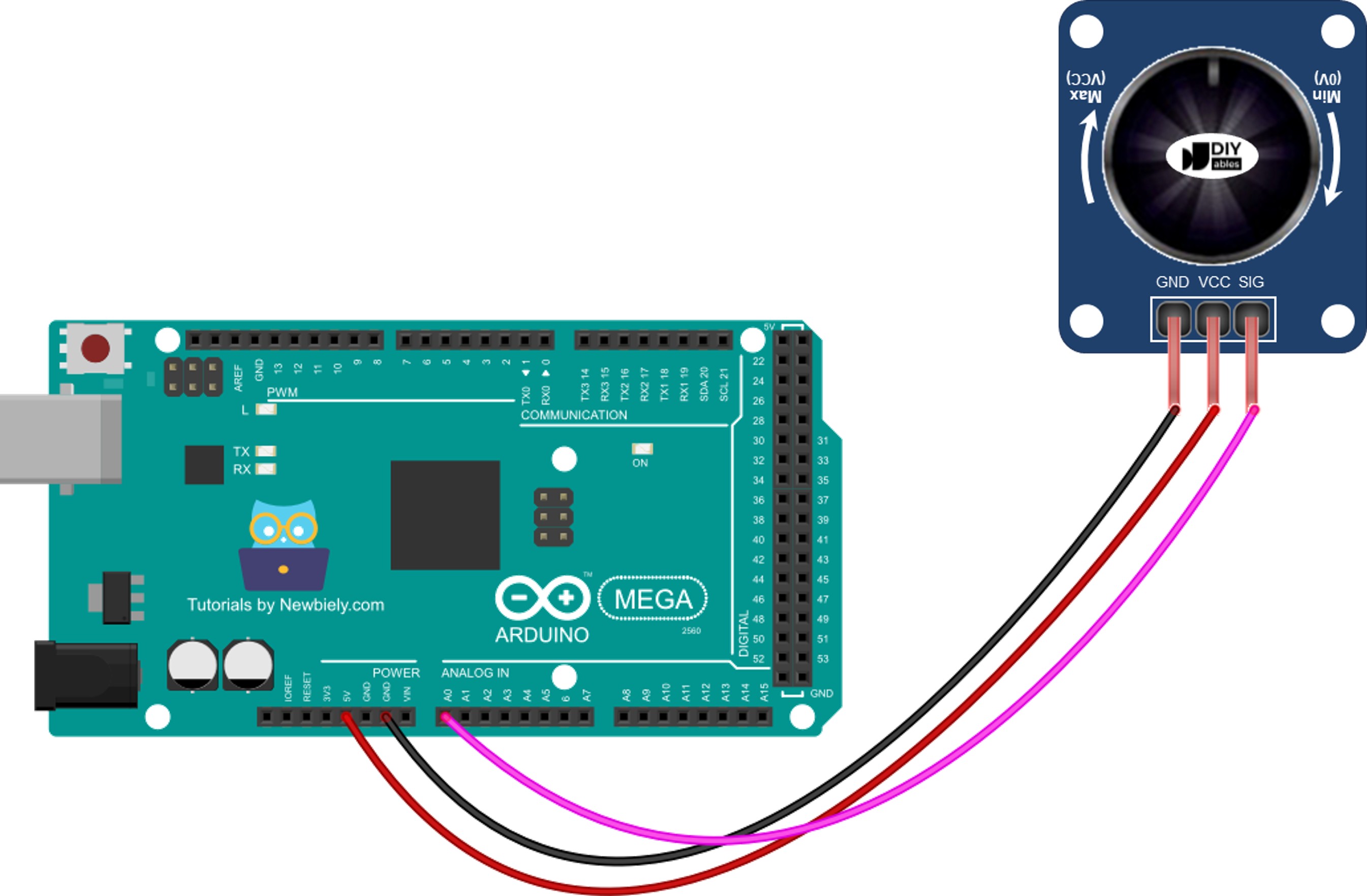
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
How To Program For Potentiometer
- Use the analogRead() function to read the value from the pin connected to the potentiometer’s output.
- Turn the ADC reading into the potentiometer angle using the map() function.
- Turn the ADC value into a voltage:
- Turn the ADC value into a simple level you can use (for example, to control the stereo volume, brightness, or the speed of a DC motor).
- Example: adjusting how bright an LED is. You control brightness with a PWM value from 0 (off) to 255 (fully on). So we can match the ADC value to the LED brightness (from off to the brightest) like this:
※ NOTE THAT:
map() converts an analog value to an int or long. If you need a float value, use floatMap() instead.
The floatMap function:
Arduino Mega Code
Detailed Instructions
Do these steps one by one.
- Connect the potentiometer to the Arduino Mega as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the Arduino Mega to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Select the correct Arduino Mega board (for example, Arduino Mega) and the port.
- Copy the code above and open it in the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to upload the code to the Arduino Mega.
- Open the Serial Monitor
- Turn the pot
- Look at the Serial Monitor to see the result
