Arduino Mega - Motion Sensor
This guide shows you how to use the HC-SR501 motion sensor and an Arduino Mega to detect a person. Here’s what we’ll learn:
- What the HC-SR501 motion sensor does
- How to wire the HC-SR501 motion sensor to the Arduino Mega
- How to program the Arduino Mega to read data from the HC-SR501 motion sensor
- How to use the Arduino Mega and motion sensor to detect when someone enters
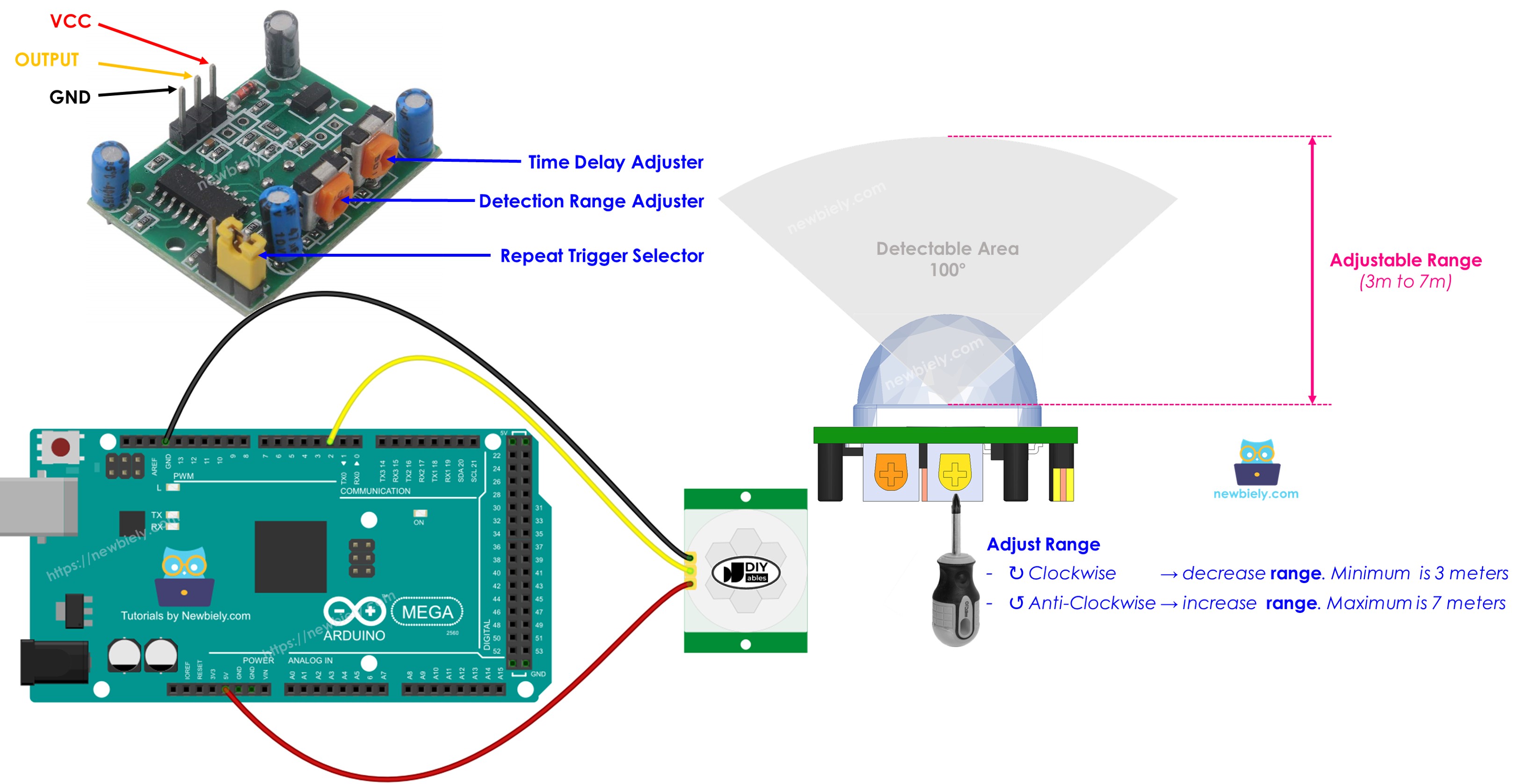
Hardware Preparation
| 1 | × | Arduino Mega | |
| 1 | × | USB 2.0 cable type A/B (for USB-A PC) | |
| 1 | × | USB 2.0 cable type C/B (for USB-C PC) | |
| 1 | × | HC-SR501 Motion Sensor | |
| 1 | × | Alternatively, AM312 Mini Motion Sensor | |
| 1 | × | Jumper Wires |
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of HC-SR501 Motion Sensor

HC-SR501 is a PIR sensor that detects people or animals moving. It is often used for many tasks, such as turning lights on and off, opening and closing doors, controlling escalators, and spotting intruders.
Have you ever seen doors that open and close on their own, lights that turn on and off on their own, or escalators that start on their own? Have you ever wondered, “How does this work?” If yes, this guide will explain how it works and also show you how to make it yourself. Let’s start!
Pinout
The HC-SR501 motion sensor has three pins.
- GND pin: connect to ground (0 V)
- VCC pin: connect to 5V
- OUTPUT pin: goes LOW when there is no motion, HIGH when there is motion. Connect this pin to the input pin of an Arduino Uno R4.
The HC-SR501 has one jumper and two adjustment knobs to change the sensor settings. Start with the default setting. For more information, see the “Advanced Uses” section. Advanced Uses
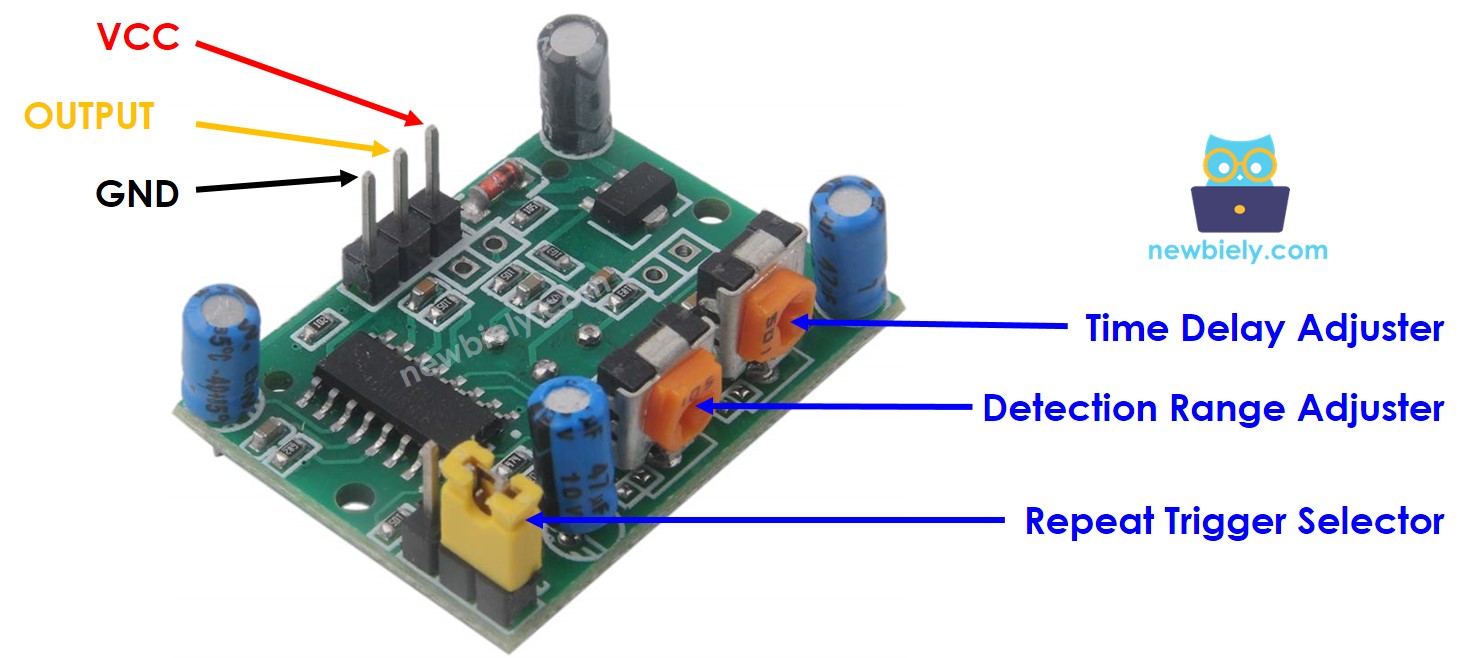
How It Works
The HC-SR501 sensor detects movement by watching changes in infrared light from the moving object. For the HC-SR501 to detect an object, two things must be true:
- It shakes or moves.
- It gives off infrared energy.
So:
- If something moves but does not give off infrared light (for example, a robot or a toy car), the sensor won't detect it.
- If something gives off infrared light but stays still (for example, a person standing still), the sensor won't detect it.
People and animals give off heat naturally. Because of this, the sensor can detect when people and animals move.
The status of the output pin:
- If nothing moves inside the sensor’s range, the OUTPUT pin is LOW.
- If a person or animal enters the sensor’s range, the OUTPUT pin changes from LOW to HIGH, showing motion is detected.
- If a person or animal leaves the sensor’s range, the OUTPUT pin changes from HIGH to LOW, showing motion has ended.
The video shows the main idea of how the motion sensor works. In real life, how it works can be a little different depending on its settings, as explained in the Advanced Uses section.
Arduino Mega - HC-SR501 Motion Sensor
When you set a pin on the Arduino Mega as a digital input, it can tell if what's connected to it is low or high.
Connect a pin on the Arduino Mega to the HC-SR501 sensor's OUTPUT pin. Then use simple Arduino code to read that pin's value to detect motion.
Wiring Diagram
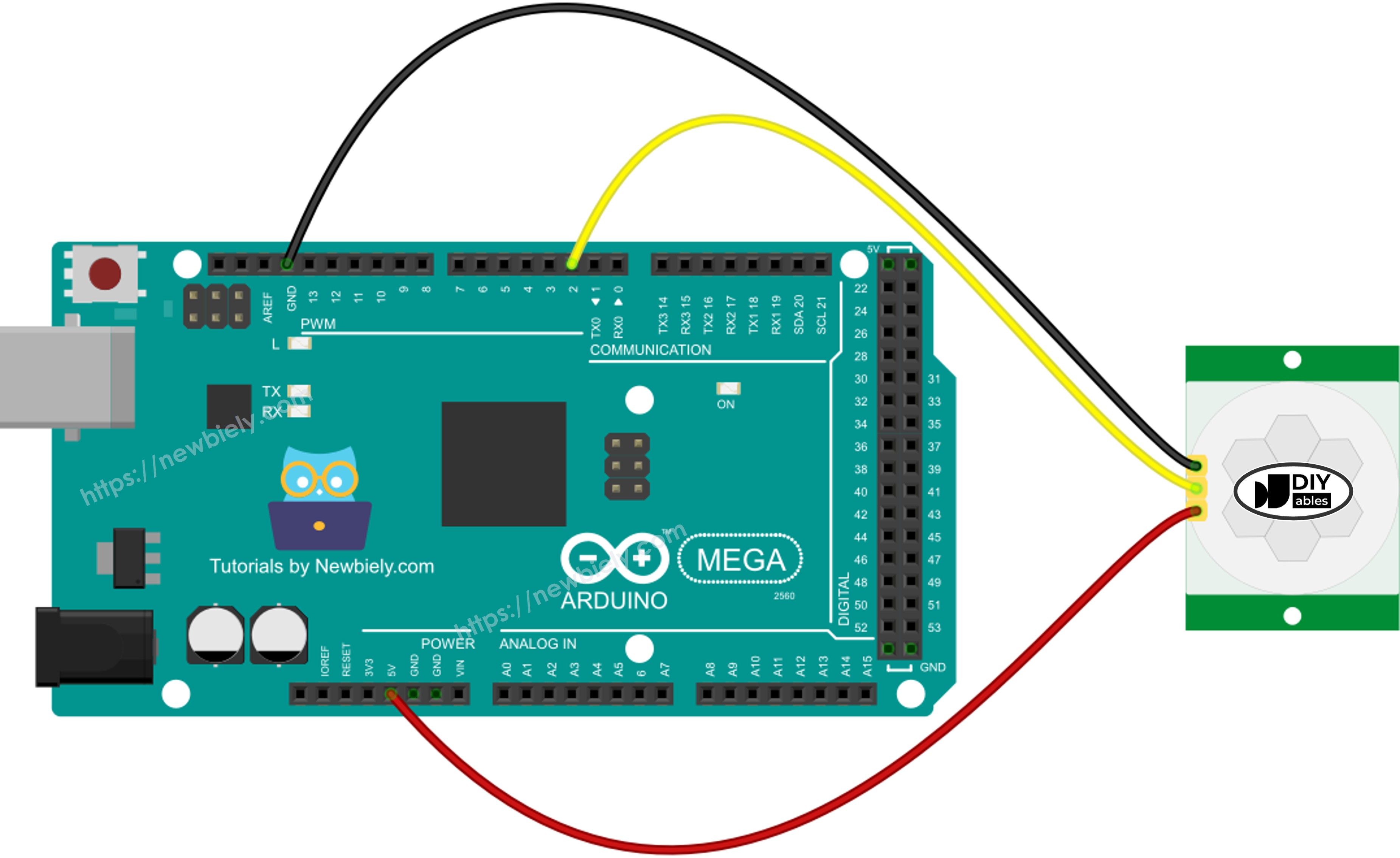
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
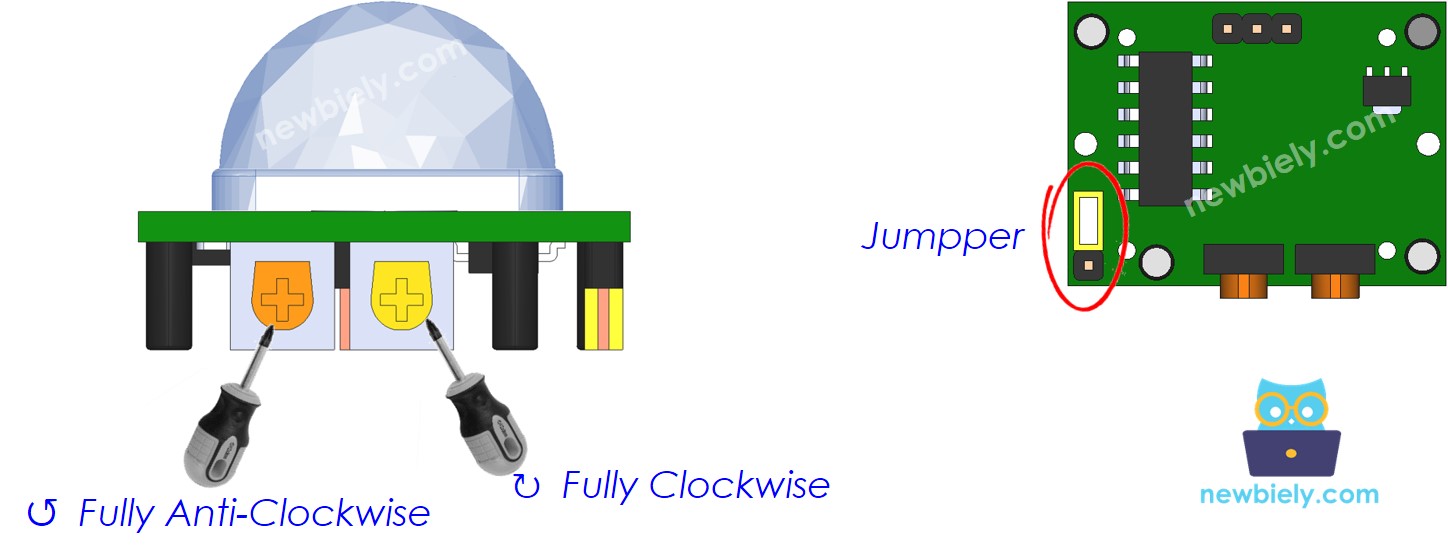
Initial Setting
| Time Delay Adjuster | Screw it in anti-clockwise direction fully. |
| Detection Range Adjuster | Screw it in clockwise direction fully. |
| Repeat Trigger Selector | Put jumper as shown on the image. |
How To Program For Motion Sensor
- Set an Arduino Mega pin as a digital input using the pinMode() function.
- Use the digitalRead() function to see if the sensor's OUTPUT pin is high or low.
- Detect when motion starts (the pin goes from low to high).
- Detect when there is no motion anymore (the pin goes from HIGH to LOW).
Arduino Mega Code
Detailed Instructions
Follow these steps one by one:
- Connect the parts as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the Arduino Mega board to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct board: Arduino Mega, and select the COM port.
- Copy the code above and open it in the Arduino IDE.
- Press the Upload button to send the code to the Arduino Mega.
- Open the Serial Monitor.
- Move your hand in front of the sensor.
- Check the output in the Serial Monitor.
Video Tutorial
Advanced Uses
We can adjust the sensor settings with one jumper and two knobs, as described above.
Detection Range Adjuster
This knob lets you change how far it can detect things (about 3 to 7 meters).
- When turned all the way to the right, it can detect up to about 3 meters.
- When turned all the way to the left, it can detect up to about 7 meters.
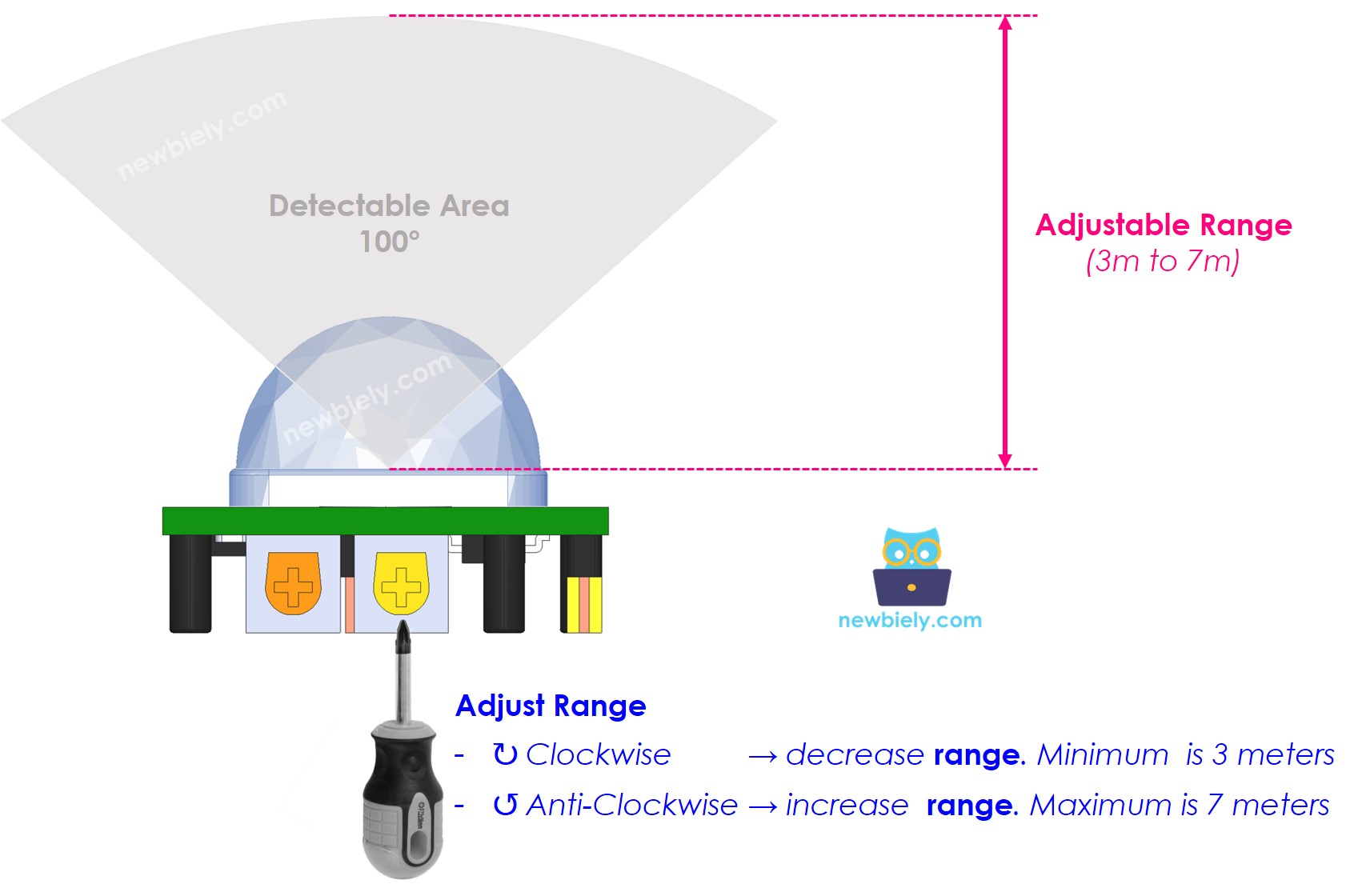
We can adjust the pot to set the range between 3 and 7 meters.
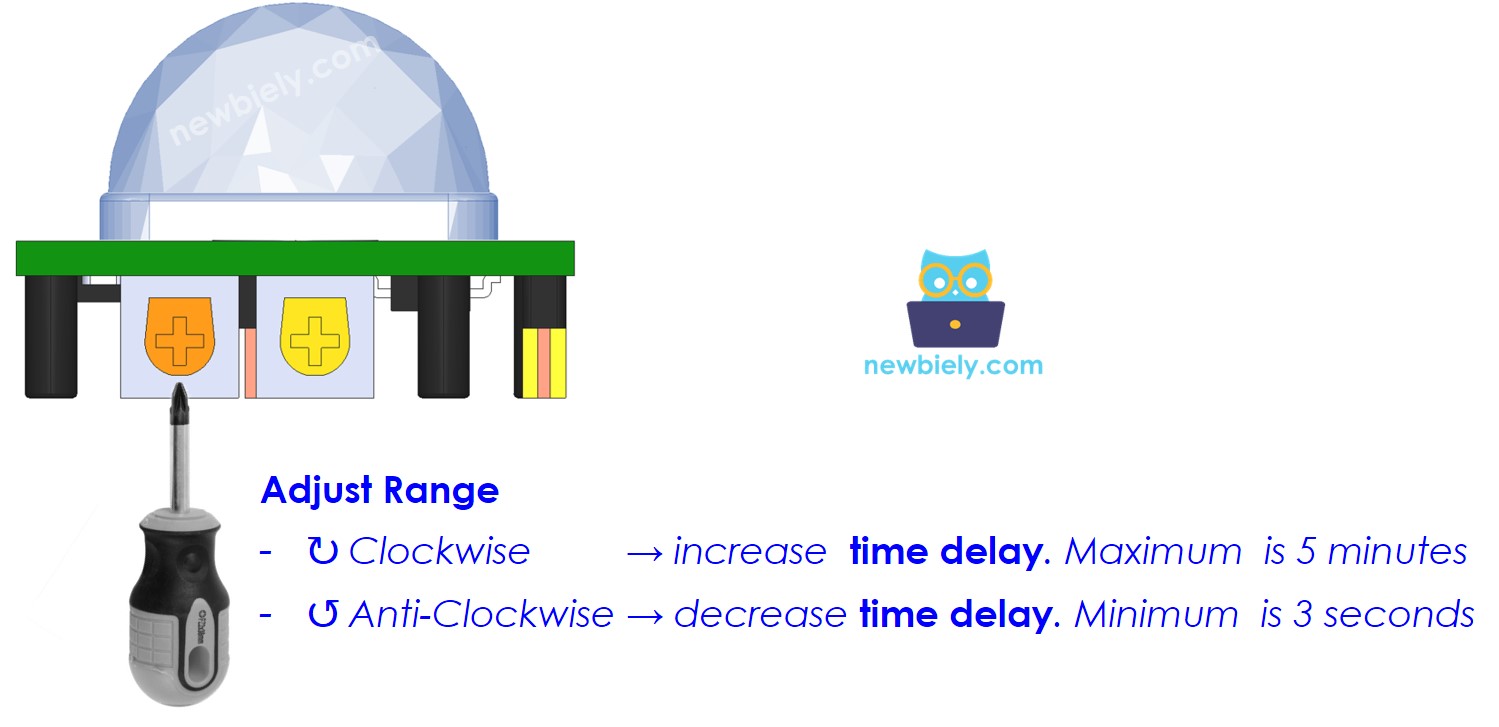
Time Delay Adjuster
This knob sets the delay time.
- Turn it all the way to the right, and the delay will be about 5 minutes.
- Turn it all the way to the left, and the delay will be about 3 seconds.
Next, we'll explain what a time delay is and how it works with the Repeat Trigger.
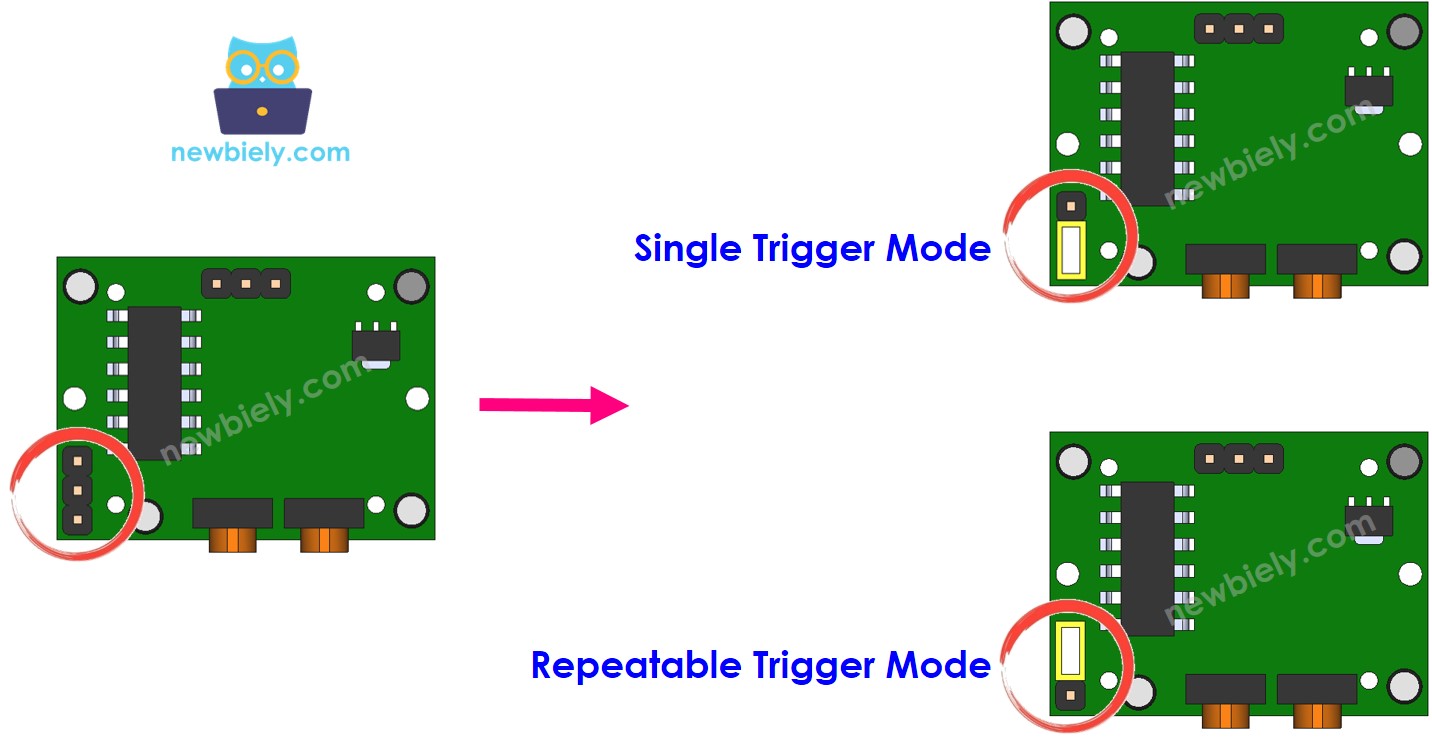
Repeat Trigger Selector
This switch lets you choose how the trigger works: one-time trigger or repeating trigger.
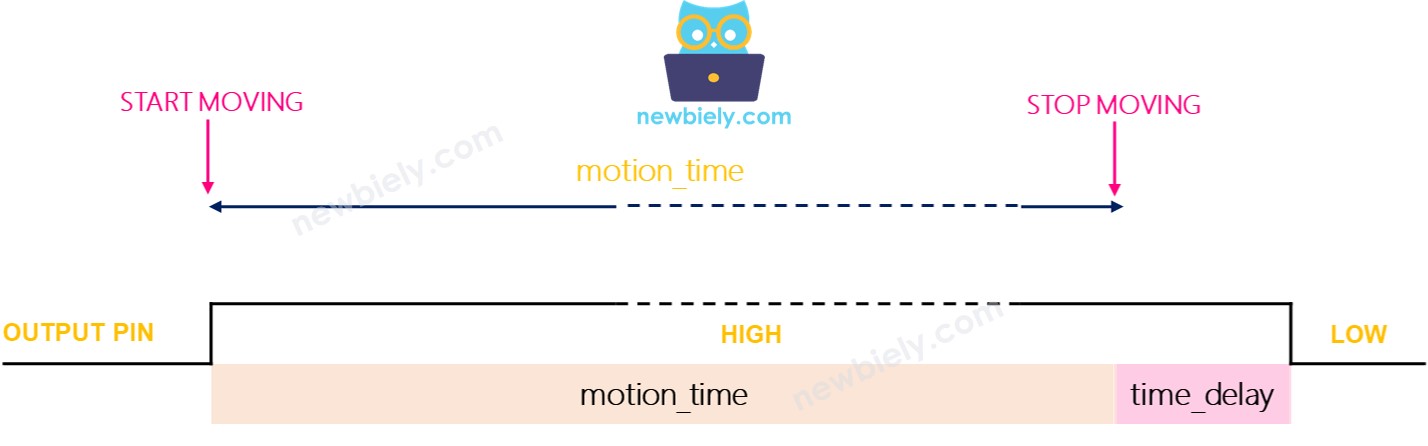
We call the time delay setting time_delay (you change it with the Time Delay Adjuster). Imagine you keep moving inside the sensor’s detection area for a long time. That is motion_time, which is much longer than time_delay.
- In one-shot mode, the OUTPUT pin goes on and off several times. It stays on for a time equal to time_delay and stays off for a fixed 3 seconds.
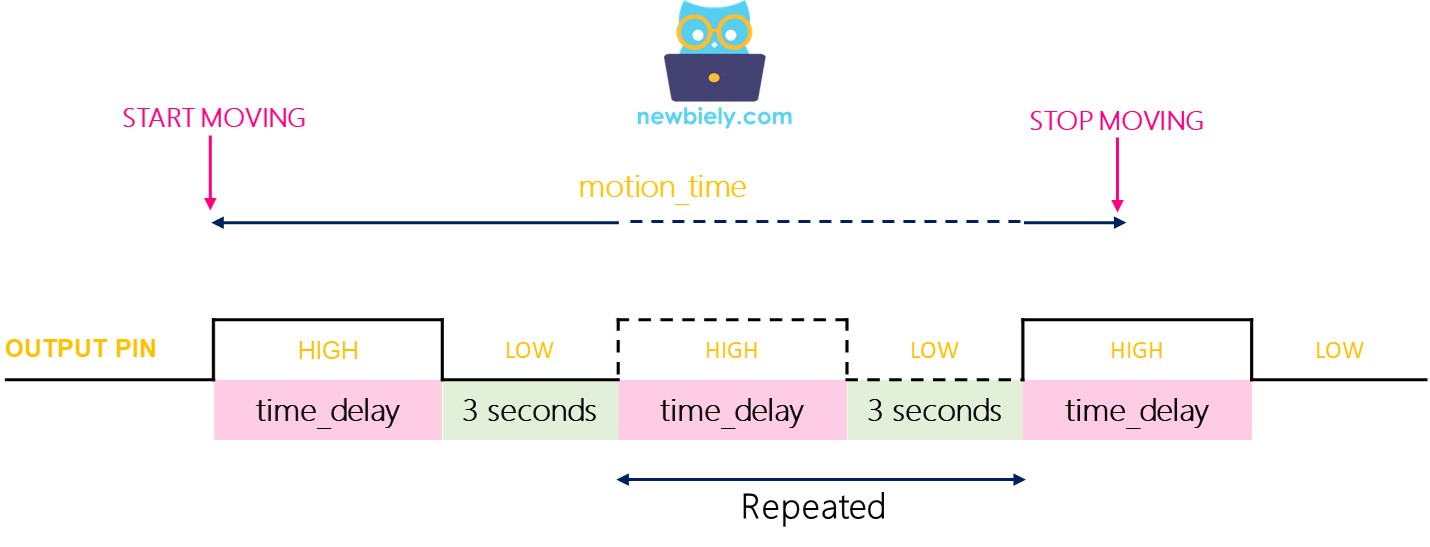
- The OUTPUT pin stays HIGH for the movement time plus the delay.
Testing
Let's test the trigger modes. Turn the delay knob all the way to the left to set the delay to 3 seconds.
- Single Trigger Mode:
- Set the jumper to single trigger mode.
- Move your hand in front of the sensor for 10 seconds.
- Take your hand away from the sensor.
- Wait 3 seconds, then check the serial monitor to see the output.
- Repeatable Trigger Mode:
- Put the jumper to start Repeatable Trigger mode.
- Hold your hand in front of the sensor for about 10 seconds.
- Remove your hand from the sensor.
- After about 3 seconds, check the serial monitor to see the output.
In one-shot mode, the sensor turns on two or three times. In repeatable trigger mode, it turns on only once.
※ NOTE THAT:
During the LOW period (3 seconds), the sensor cannot detect any motion. This means the sensor is not active during this time, but it usually does not cause problems.
We recommend using the repeatable trigger mode.
In real use:
- Devices or machines often turn on when someone is nearby.
- They do not turn off right away when the person leaves; they turn off after a short delay.
