Arduino MicroPython Control Heating Element
This tutorial teaches you how to control a heating element with an Arduino using MicroPython. Specifically, we will learn:
- How a heating element functions
- How to connect a heating element to the Arduino
- How to write MicroPython code for the Arduino to control the heating element
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Heating Element
Pinout

A heating element typically has two pins:
- Connect the positive (+) pin (red) to the 12V DC power supply.
- Connect the negative (-) pin (black) to the ground (GND) of the DC power supply.
How to Control Heating Element
When a 12V heating element is connected to a 12V power source, it produces heat. To control the heating element with an Arduino, we use a relay. The Arduino sends signals to the relay, which then controls the heating element. If you need more information on how a relay works, its pin configuration, or how to set it up, check out the Arduino MicroPython Relay tutorial.
Wiring Diagram
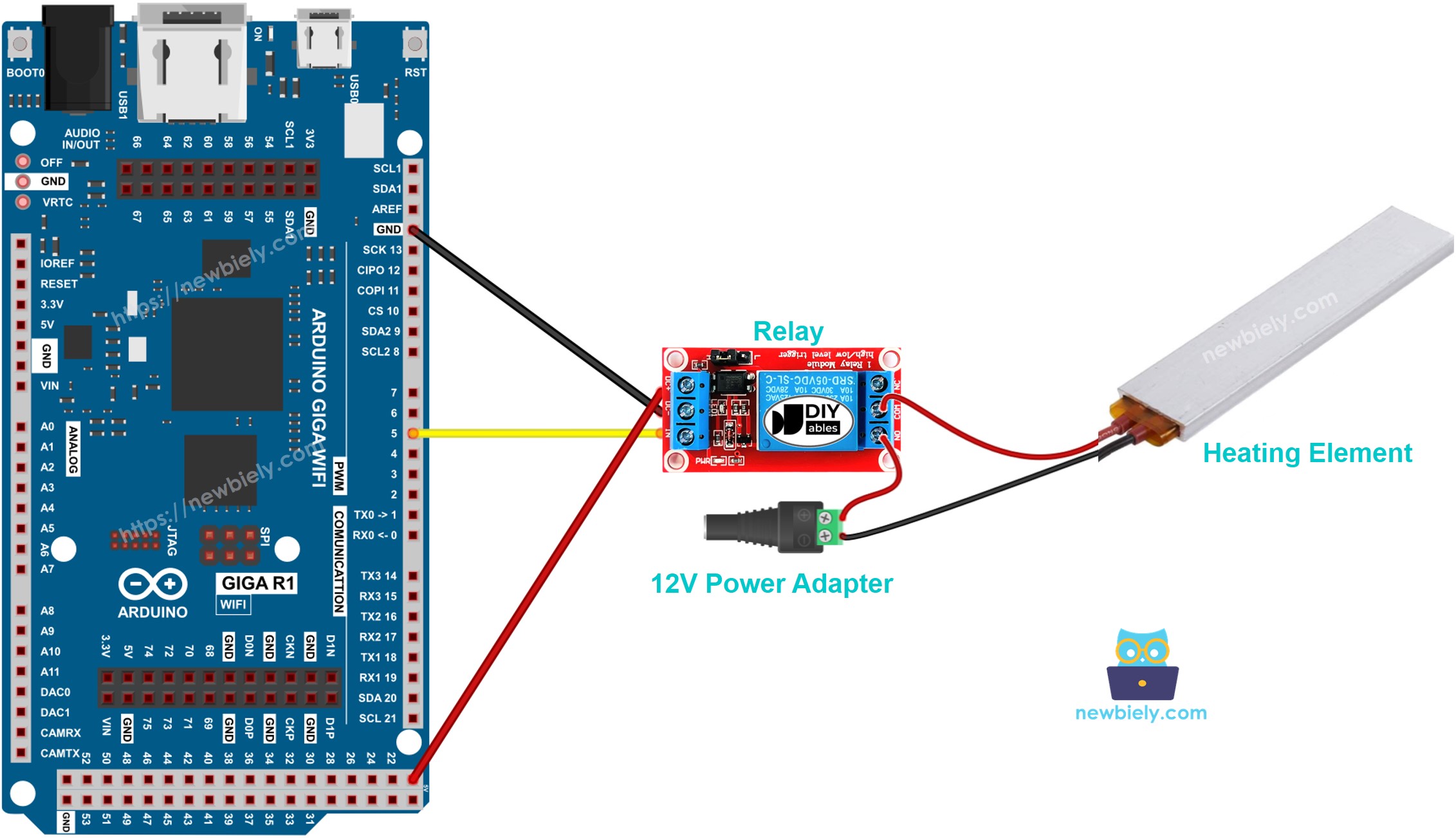
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino MicroPython Code
This code switches the heating element ON for five seconds and then turns it OFF for five also, doing this continuously.
Detailed Instructions
Here’s instructions on how to run the above MicroPython code on Arduino with Thonny IDE:
- Make sure Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Make sure MicroPython firmware is installed on your Arduino board.
- If you are new to Arduino with MicroPython, see the Getting Started with Arduino and MicroPython.
- Connect the Arduino board to the heating element according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the Arduino board to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open Thonny IDE and go to Tools Options.
- Under the Interpreter tab, select MicroPython (generic) from the dropdown menu.
- Select the COM port corresponding to your Arduino board (e.g., COM33 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
- Copy the provided Arduino MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny's editor.
- Save the MicroPython code to your Arduino by:
- Clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
- In the save dialog, choose MicroPython device and name the file main.py.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the code.
- Check the temperature of the heating element.
WARNING
Be careful, as handling this incorrectly can cause burns or even start a fire at home. Your safety is very important. If you are unsure, don’t attempt to do it yourself—seek help from someone experienced. We are not responsible for your safety.
Code Explanation
The explanation can be found in the comments section above this Arduino MicroPython code.
