Arduino MicroPython Light Sensor
This guide will show you how to use an LDR light sensor (also known as a photoresistor, light-dependent resistor, or photocell) with an Arduino and MicroPython. We’ll cover the following:
- How LDR light sensors function
- How to connect an LDR sensor to an Arduino
- How to write MicroPython code for the Arduino to read data from the LDR sensor
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
The LDR light sensor is very affordable, but it requires a resistor for wiring, which can make the setup more complex. To simplify the wiring, you can use an LDR light sensor module as an alternative.
Overview of Light Sensor
This guide explains how to use a photoresistor, also known as a Light-Dependent Resistor (LDR), to measure the brightness of surrounding light.
Pinout
A photoresistor has two pins. Since it is a resistor, you do not need to distinguish these pins. They are identical.
How It Works
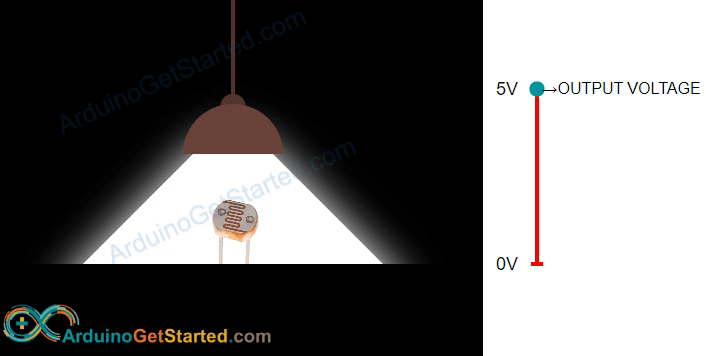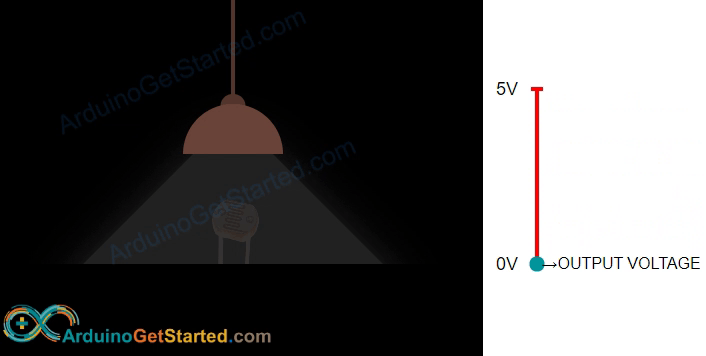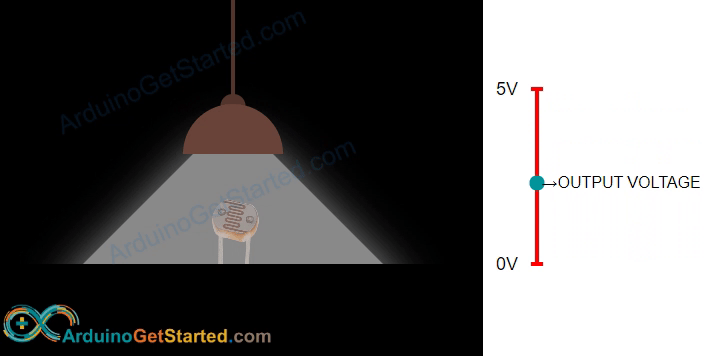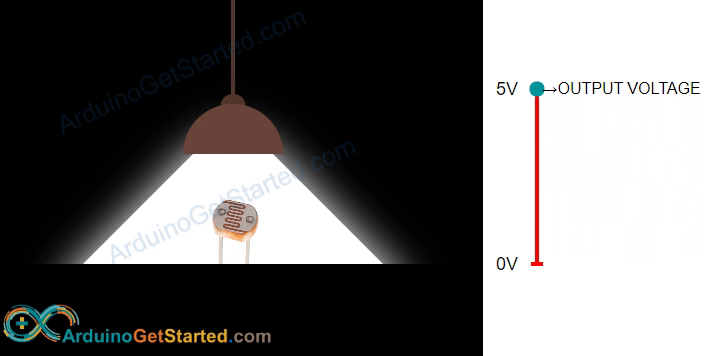
A photoresistor is a unique resistor that changes its resistance in response to light. Its resistance decreases in bright light and increases in darkness or no light. By measuring the photoresistor's resistance, we can determine the brightness or darkness of the surrounding light, making it useful for measuring light levels in different environments.
WARNING
The light sensor value provides a general indication of light brightness, but it's not a precise measurement. Use it when exact measurements are not required.
Wiring Diagram
How to connect Arduino and light sensor
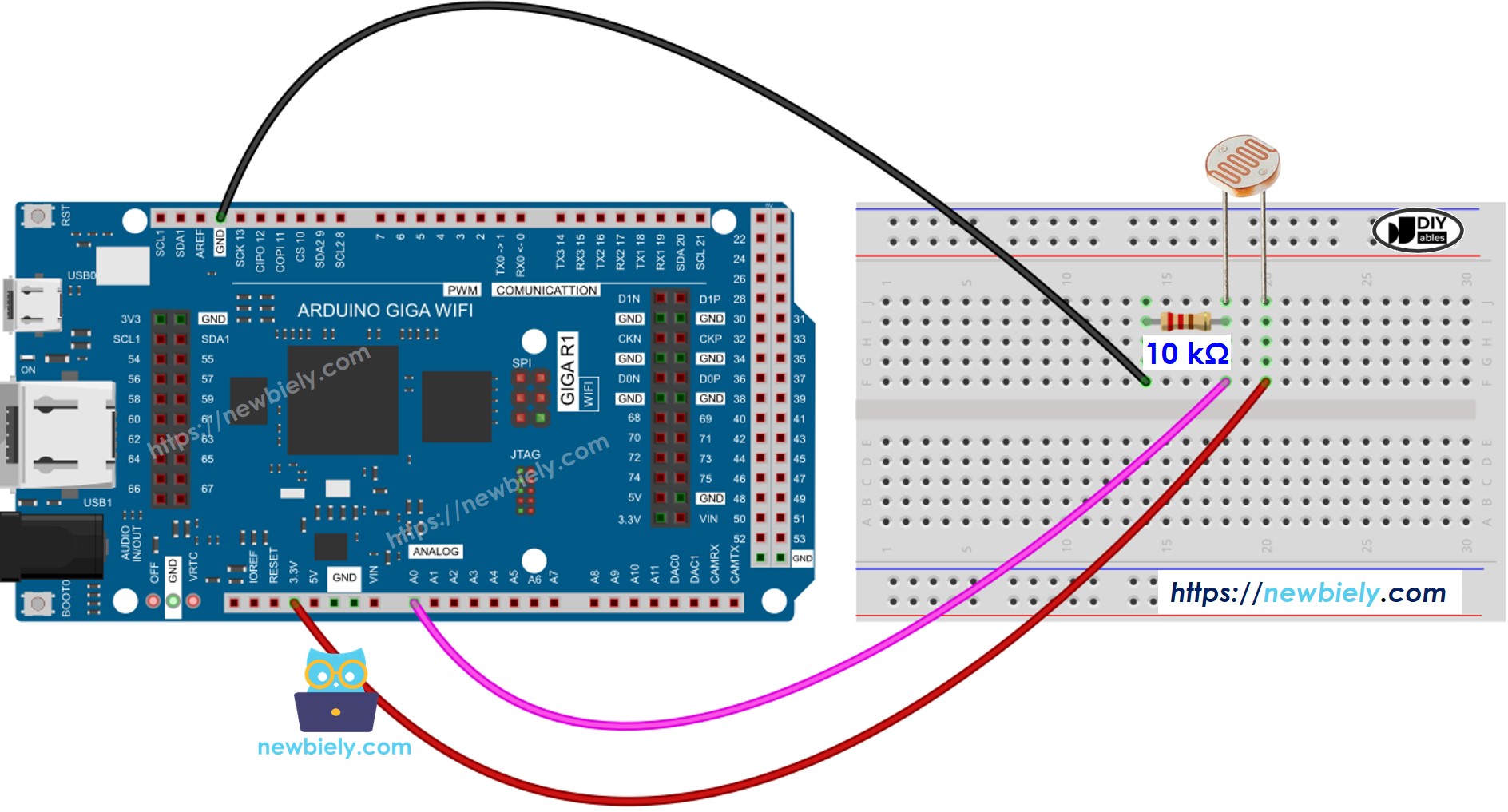
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino MicroPython Code
This code checks the light amount using a photocell and describes how bright it is.
Detailed Instructions
Here’s instructions on how to run the above MicroPython code on Arduino with Thonny IDE:
- Make sure Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Make sure MicroPython firmware is installed on your Arduino board.
- If you are new to Arduino with MicroPython, see the Getting Started with Arduino and MicroPython.
- Connect the LDR light sensor to the Arduino according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the Arduino board to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open Thonny IDE and go to Tools Options.
- Under the Interpreter tab, select MicroPython (generic) from the dropdown menu.
- Select the COM port corresponding to your Arduino board (e.g., COM33 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
- Copy the provided MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny\'s editor.
- Save the MicroPython code to your Arduino by:
- Clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
- In the save dialog, choose MicroPython device and name the file main.py.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the code.
- Direct light onto the sensor.
- Check out the message in the Shell at the bottom of Thonny.
