Arduino MicroPython Obstacle Avoidance Sensor
This guide will teach you how to use an infrared obstacle avoidance sensor with an Arduino and MicroPython to detect obstacles. You will learn:
- How the obstacle avoidance sensor works.
- How to connect the obstacle avoidance sensor to the Arduino.
- How to write MicroPython code for the Arduino to detect obstacles.
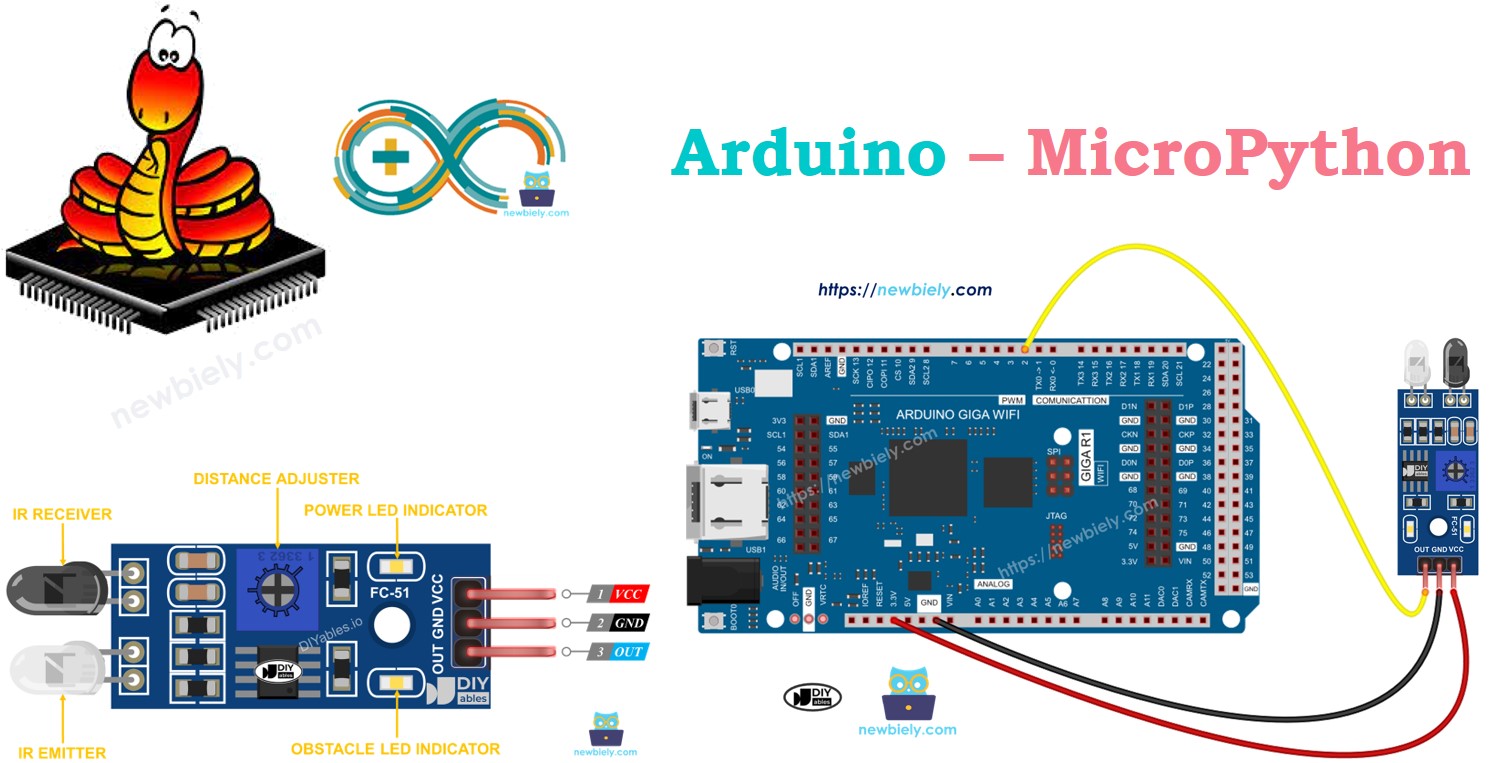
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
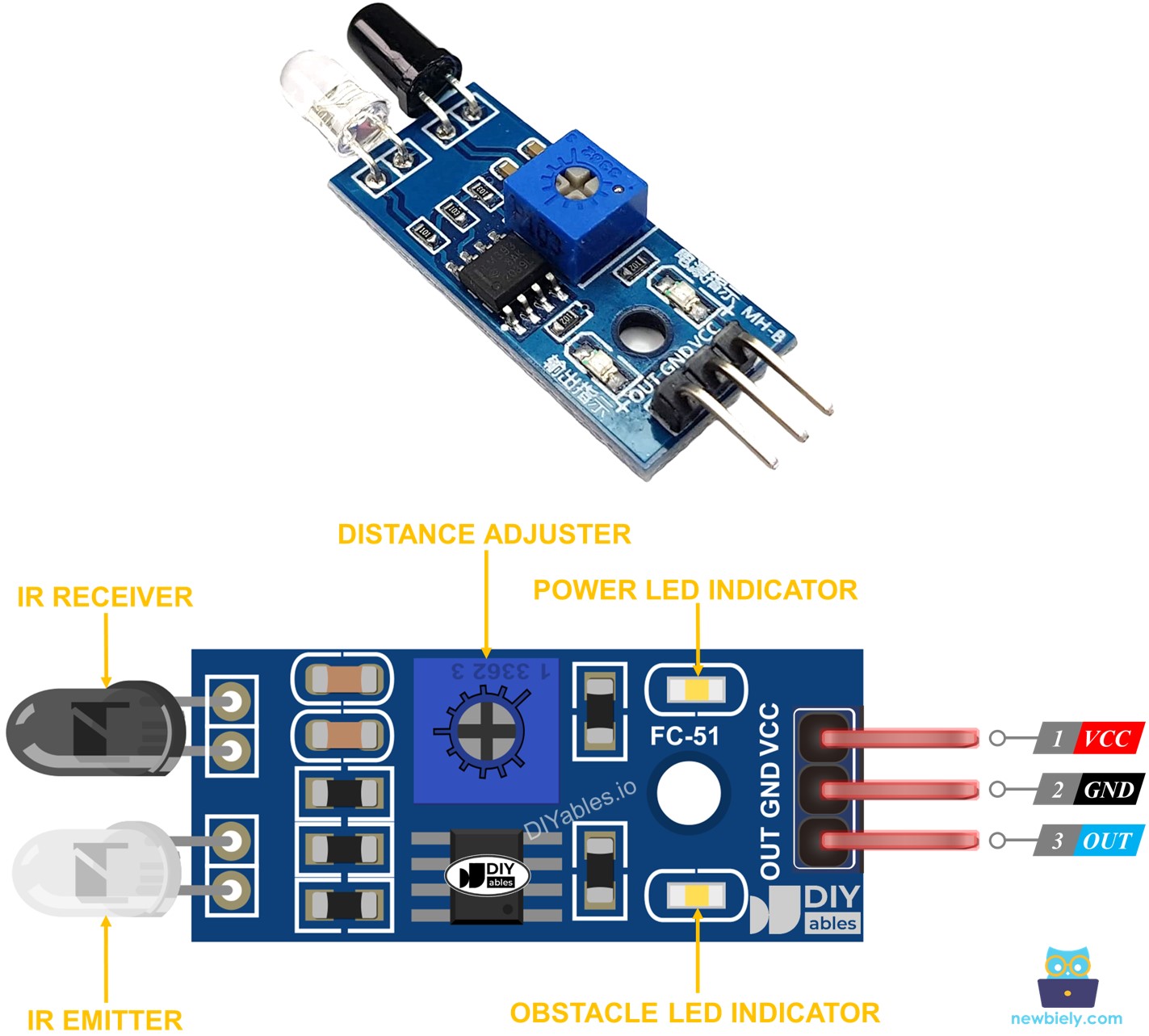
Overview of IR Obstacle Avoidance Sensor
The infrared (IR) obstacle sensor detects objects by emitting an infrared signal. It can sense obstacles within a range of 2 cm to 30 cm. The detection range can be adjusted with an onboard potentiometer.
Pinout
The IR obstacle avoidance sensor has three pins:
- GND pin: Connect to ground (0 volts).
- VCC pin: Connect to a voltage supply (5 volts or 3.3 volts).
- OUT pin: This output pin goes LOW when an obstacle is detected and HIGH when no obstacle is present. Connect it to an input pin on the Arduino.
How It Works
An infrared obstacle sensor module includes an IR transmitter and an IR receiver. The IR transmitter emits an infrared signal, and the IR receiver detects the reflected signal to determine if an object is present. The OUT pin indicates the presence of an obstacle:
- The OUT pin goes LOW if an obstacle is in front of the sensor.
- The OUT pin stays HIGH if no obstacle is in front of the sensor.
※ NOTE THAT:
The sensor may get deformed during shipping, causing it to malfunction. If the sensor is not working properly, adjust the IR transmitter and receiver so that they are aligned parallel to each other.
Wiring Diagram
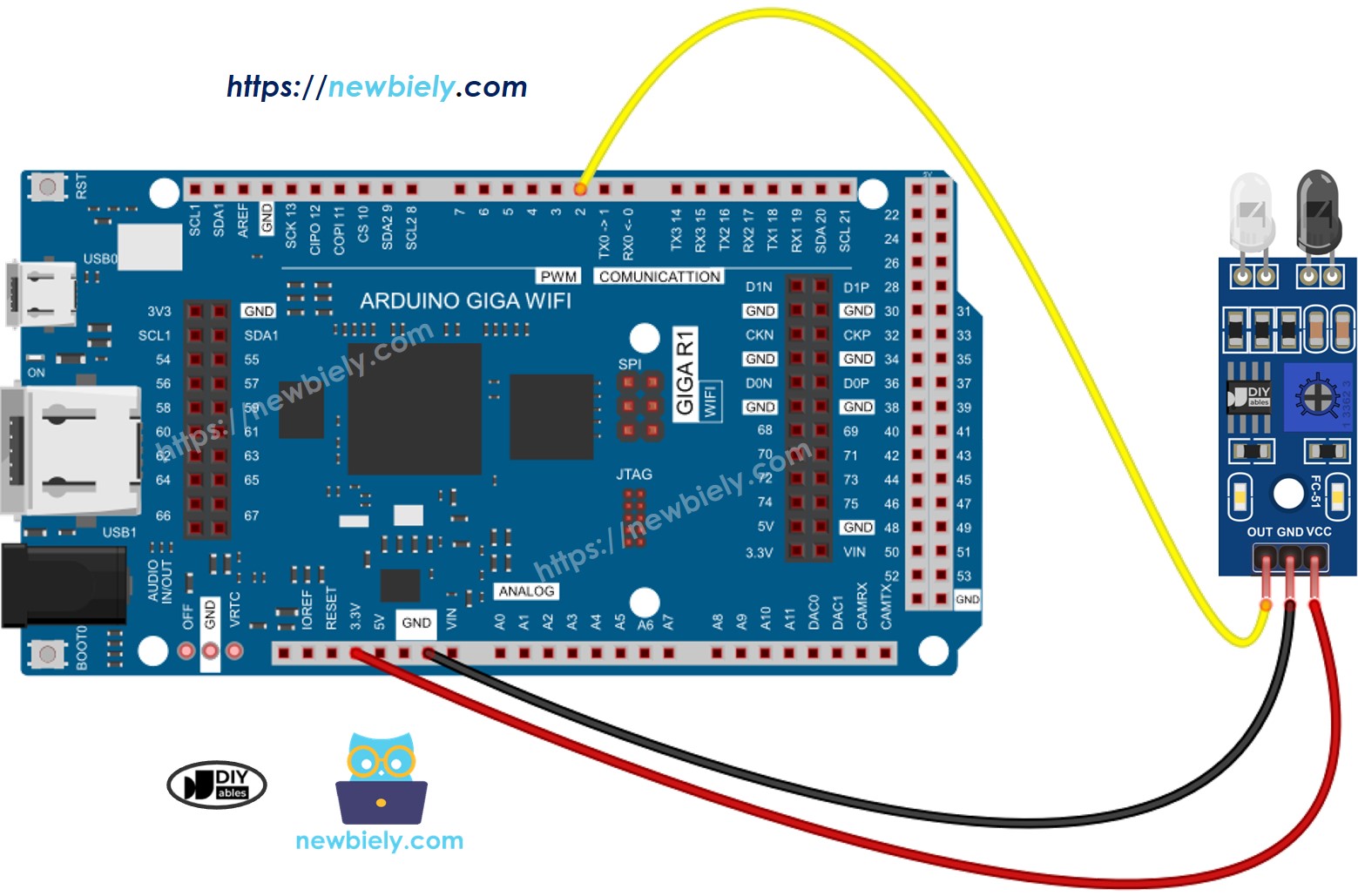
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino MicroPython Code
There are two approaches to programming an obstacle avoidance application:
- Perform or skip an action based on whether the obstacle is present or absent.
- Perform or skip an action when the obstacle is detected or cleared.
Arduino MicroPython code for checking if the obstacle is present
Detailed Instructions
Here’s instructions on how to run the above MicroPython code on Arduino with Thonny IDE:
- Make sure Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Make sure MicroPython firmware is installed on your Arduino board.
- If you are new to Arduino with MicroPython, see the Getting Started with Arduino and MicroPython.
- Wire the obstacle avoidance sensor to the Arduino according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the Arduino board to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open Thonny IDE and go to Tools Options.
- Under the Interpreter tab, select MicroPython (generic) from the dropdown menu.
- Select the COM port corresponding to your Arduino board (e.g., COM33 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
- Copy the provided Arduino MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny's editor.
- Save the MicroPython code to your Arduino by:
- Clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
- In the save dialog, choose MicroPython device and name the file main.py.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the code.
- Put an obstacle in front of the sensor for a while, then remove it.
- Check out the message in the Shell at the bottom of Thonny.
Arduino MicroPython code for detecting obstacle
Detailed Instructions
- Copy the provided Arduino MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny's editor.
- Save the code to your Arduino.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the code.
- Put something in front of the sensor briefly, then remove it.
- Check out the message in the Shell at the bottom of Thonny.
