Arduino MicroPython Traffic Light
In this guide, we will show how to control a traffic light module with Arduino and MicroPython. We will learn about:
- How to connect a traffic light module to an Arduino
- How to program the Arduino using MicroPython to control the traffic light module
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Disclosure: Some of the links provided in this section are Amazon affiliate links. We may receive a commission for any purchases made through these links at no additional cost to you.
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Traffic Light Module
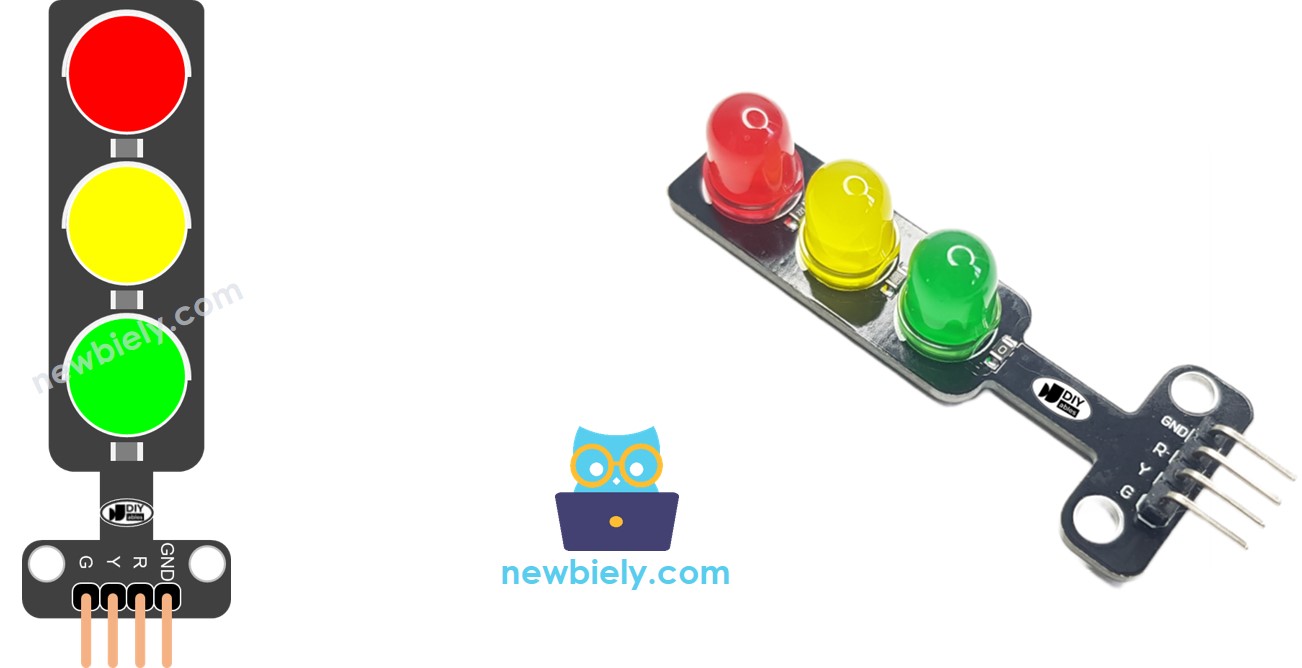
Pinout
The traffic light module has four pins.
- GND pin: Connect this ground pin to the Arduino's GND.
- R pin: This pin operates the red light. Attach it to a digital output on the Arduino.
- Y pin: This pin operates the yellow light. Attach it to a digital output on the Arduino.
- G pin: This pin operates the green light. Attach it to a digital output on the Arduino.

How It Works
Wiring Diagram
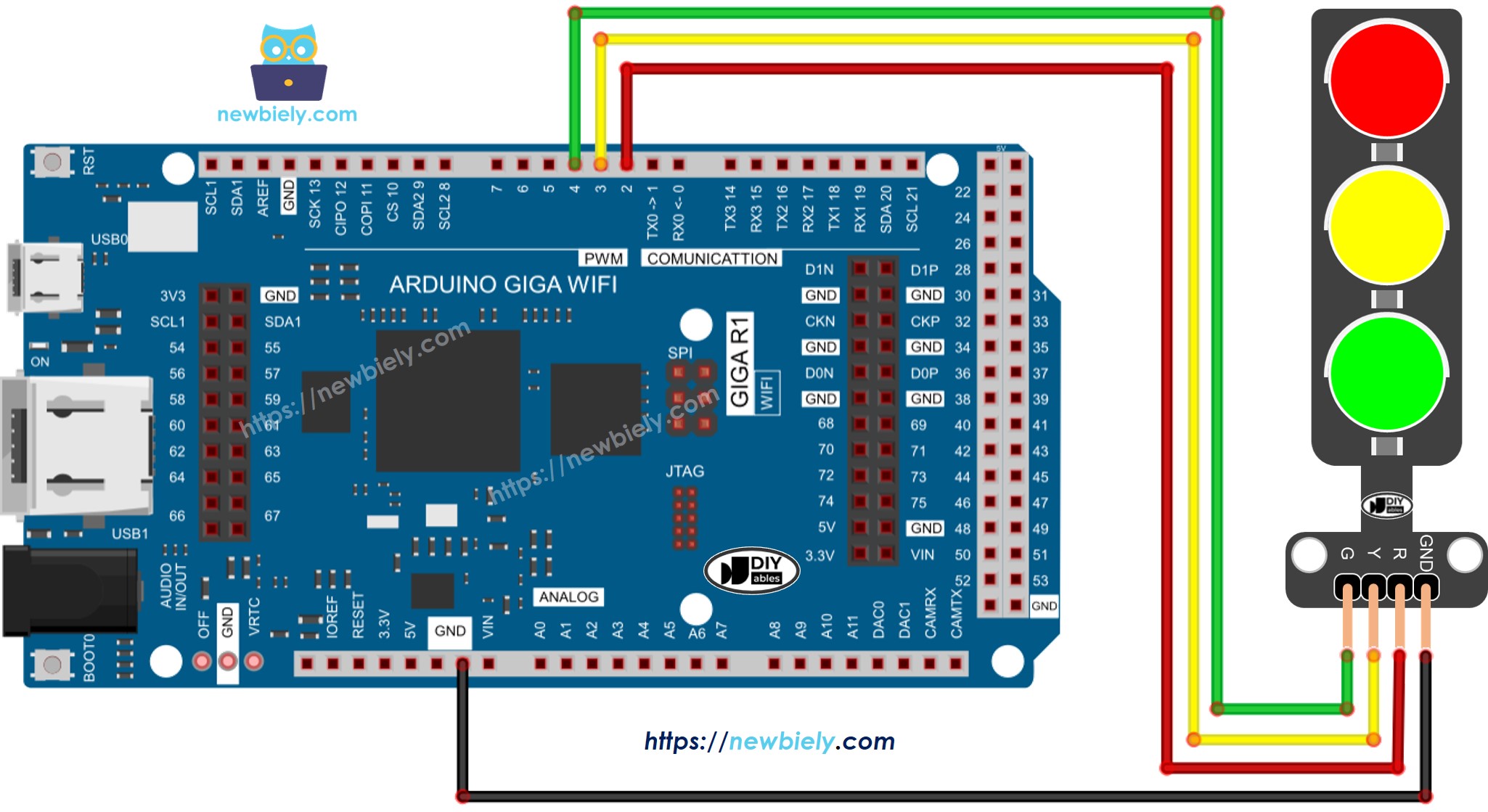
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino MicroPython Code
"""
This Arduino MicroPython script was developed by newbiely.com
This Arduino MicroPython script is made available for public use without any restriction
For comprehensive instructions and wiring diagrams, please visit:
https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-micropython/arduino-micropython-traffic-light
"""
import machine
import time
# Define pin numbers (you can change these to match your wiring)
PIN_RED = 'D2' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D2 connected to the traffic light module's red pin
PIN_YELLOW = 'D3' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D3 connected to the traffic light module's yellow pin
PIN_GREEN = 'D4' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D4 connected to the traffic light module's green pin
# Define times in seconds (MicroPython uses seconds for time.sleep)
RED_TIME = 4 # RED time in seconds
YELLOW_TIME = 4 # YELLOW time in seconds
GREEN_TIME = 4 # GREEN time in seconds
# Setup pins as output
red = machine.Pin(PIN_RED, machine.Pin.OUT)
yellow = machine.Pin(PIN_YELLOW, machine.Pin.OUT)
green = machine.Pin(PIN_GREEN, machine.Pin.OUT)
# Main loop
while True:
# Red light on
red.value(1) # turn on red
yellow.value(0) # turn off yellow
green.value(0) # turn off green
time.sleep(RED_TIME) # keep red light on for the defined period
# Yellow light on
red.value(0) # turn off red
yellow.value(1) # turn on yellow
green.value(0) # turn off green
time.sleep(YELLOW_TIME) # keep yellow light on for the defined period
# Green light on
red.value(0) # turn off red
yellow.value(0) # turn off yellow
green.value(1) # turn on green
time.sleep(GREEN_TIME) # keep green light on for the defined period
Detailed Instructions
Here’s instructions on how to run the above MicroPython code on Arduino with Thonny IDE:
- Make sure Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Make sure MicroPython firmware is installed on your Arduino board.
- If you are new to Arduino with MicroPython, see the Getting Started with Arduino and MicroPython.
- Connect the Arduino board to the traffic light module according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the Arduino board to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open Thonny IDE and go to Tools Options.
- Under the Interpreter tab, select MicroPython (generic) from the dropdown menu.
- Select the COM port corresponding to your Arduino board (e.g., COM33 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
- Copy the provided Arduino MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny's editor.
- Save the MicroPython code to your Arduino by:
- Clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
- In the save dialog, choose MicroPython device and name the file main.py.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the code.
- Check out the traffic light status.
Traffic lights work differently depending on how they are designed in each place. Here is an easy explanation of how traffic lights control traffic. The code above lets you control each light one by one. Now, we will improve the code to make it work better.
Arduino MicroPython Code Optimization
- Let's improve the code by creating a function to manage the light.
"""
This Arduino MicroPython script was developed by newbiely.com
This Arduino MicroPython script is made available for public use without any restriction
For comprehensive instructions and wiring diagrams, please visit:
https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-micropython/arduino-micropython-traffic-light
"""
import machine
import time
# Define pin numbers (you can change these to match your wiring)
PIN_RED = 'D2' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D2 connected to the traffic light module's red pin
PIN_YELLOW = 'D3' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D3 connected to the traffic light module's yellow pin
PIN_GREEN = 'D4' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D4 connected to the traffic light module's green pin
# Define times in seconds (MicroPython uses seconds for time.sleep)
RED_TIME = 2 # RED time in seconds
YELLOW_TIME = 1 # YELLOW time in seconds
GREEN_TIME = 2 # GREEN time in seconds
# Define indexes
RED = 0
YELLOW = 1
GREEN = 2
# Setup pins as output and store them in a list
pins = [
machine.Pin(PIN_RED, machine.Pin.OUT),
machine.Pin(PIN_YELLOW, machine.Pin.OUT),
machine.Pin(PIN_GREEN, machine.Pin.OUT)
]
# Define the times array
times = [RED_TIME, YELLOW_TIME, GREEN_TIME]
def trafic_light_on(light):
for i in range(RED, GREEN + 1):
if i == light:
pins[i].value(1) # turn on
else:
pins[i].value(0) # turn off
# Main loop
while True:
# Red light on
trafic_light_on(RED)
time.sleep(times[RED]) # keep red light on during a period of time
# Yellow light on
trafic_light_on(YELLOW)
time.sleep(times[YELLOW]) # keep yellow light on during a period of time
# Green light on
trafic_light_on(GREEN)
time.sleep(times[GREEN]) # keep green light on during a period of time
- We can improve the code by using a for loop.
"""
This Arduino MicroPython script was developed by newbiely.com
This Arduino MicroPython script is made available for public use without any restriction
For comprehensive instructions and wiring diagrams, please visit:
https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-micropython/arduino-micropython-traffic-light
"""
import machine
import time
# Define pin numbers (you can change these to match your wiring)
PIN_RED = 'D2' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D2 connected to the traffic light module's red pin
PIN_YELLOW = 'D3' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D3 connected to the traffic light module's yellow pin
PIN_GREEN = 'D4' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D4 connected to the traffic light module's green pin
# Define times in milliseconds (MicroPython can handle time in milliseconds with time.sleep_ms)
RED_TIME = 2000 # RED time in milliseconds
YELLOW_TIME = 1000 # YELLOW time in milliseconds
GREEN_TIME = 2000 # GREEN time in milliseconds
# Define indexes
RED = 0
YELLOW = 1
GREEN = 2
# Setup pins as output and store them in a list
pins = [
machine.Pin(PIN_RED, machine.Pin.OUT),
machine.Pin(PIN_YELLOW, machine.Pin.OUT),
machine.Pin(PIN_GREEN, machine.Pin.OUT)
]
# Define the times array
times = [RED_TIME, YELLOW_TIME, GREEN_TIME]
def trafic_light_on(light):
for i in range(RED, GREEN + 1):
if i == light:
pins[i].value(1) # turn on
else:
pins[i].value(0) # turn off
# Main loop
while True:
for light in range(RED, GREEN + 1):
trafic_light_on(light)
time.sleep_ms(times[light]) # keep light on during a period of time
- Let's improve the code by using the millis() function instead of time.sleep().
"""
This Arduino MicroPython script was developed by newbiely.com
This Arduino MicroPython script is made available for public use without any restriction
For comprehensive instructions and wiring diagrams, please visit:
https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-micropython/arduino-micropython-traffic-light
"""
import machine
import time
# Define pin numbers (you can change these to match your wiring)
PIN_RED = 'D2' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D2 connected to the traffic light module's red pin
PIN_YELLOW = 'D3' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D3 connected to the traffic light module's yellow pin
PIN_GREEN = 'D4' # The Arduino Giga R1 WiFi's pin D4 connected to the traffic light module's green pin
# Define times in milliseconds (MicroPython can handle time in milliseconds with time.sleep_ms)
RED_TIME = 2000 # RED time in milliseconds
YELLOW_TIME = 1000 # YELLOW time in milliseconds
GREEN_TIME = 2000 # GREEN time in milliseconds
# Define indexes
RED = 0
YELLOW = 1
GREEN = 2
# Setup pins as output and store them in a list
pins = [
machine.Pin(PIN_RED, machine.Pin.OUT),
machine.Pin(PIN_YELLOW, machine.Pin.OUT),
machine.Pin(PIN_GREEN, machine.Pin.OUT)
]
# Define the times array
times = [RED_TIME, YELLOW_TIME, GREEN_TIME]
# Initialize variables
last_time = time.ticks_ms()
light = RED # start with RED light
def trafic_light_on(light):
for i in range(RED, GREEN + 1):
if i == light:
pins[i].value(1) # turn on
else:
pins[i].value(0) # turn off
# Initialize the first light
trafic_light_on(light)
# Main loop
while True:
current_time = time.ticks_ms()
if time.ticks_diff(current_time, last_time) > times[light]:
light += 1
if light >= 3:
light = RED # reset to RED for a new cycle
trafic_light_on(light)
last_time = current_time
# TO DO: your other code
