Raspberry Pi Pico - Blink multiple LED
This guide teaches you how to program a Raspberry Pi Pico to blink several LEDs at various speeds without using the time.sleep() function. It provides the code in two different methods:
- Raspberry Pi Pico makes multiple LEDs blink.
- Raspberry Pi Pico uses a array to blink multiple LEDs.
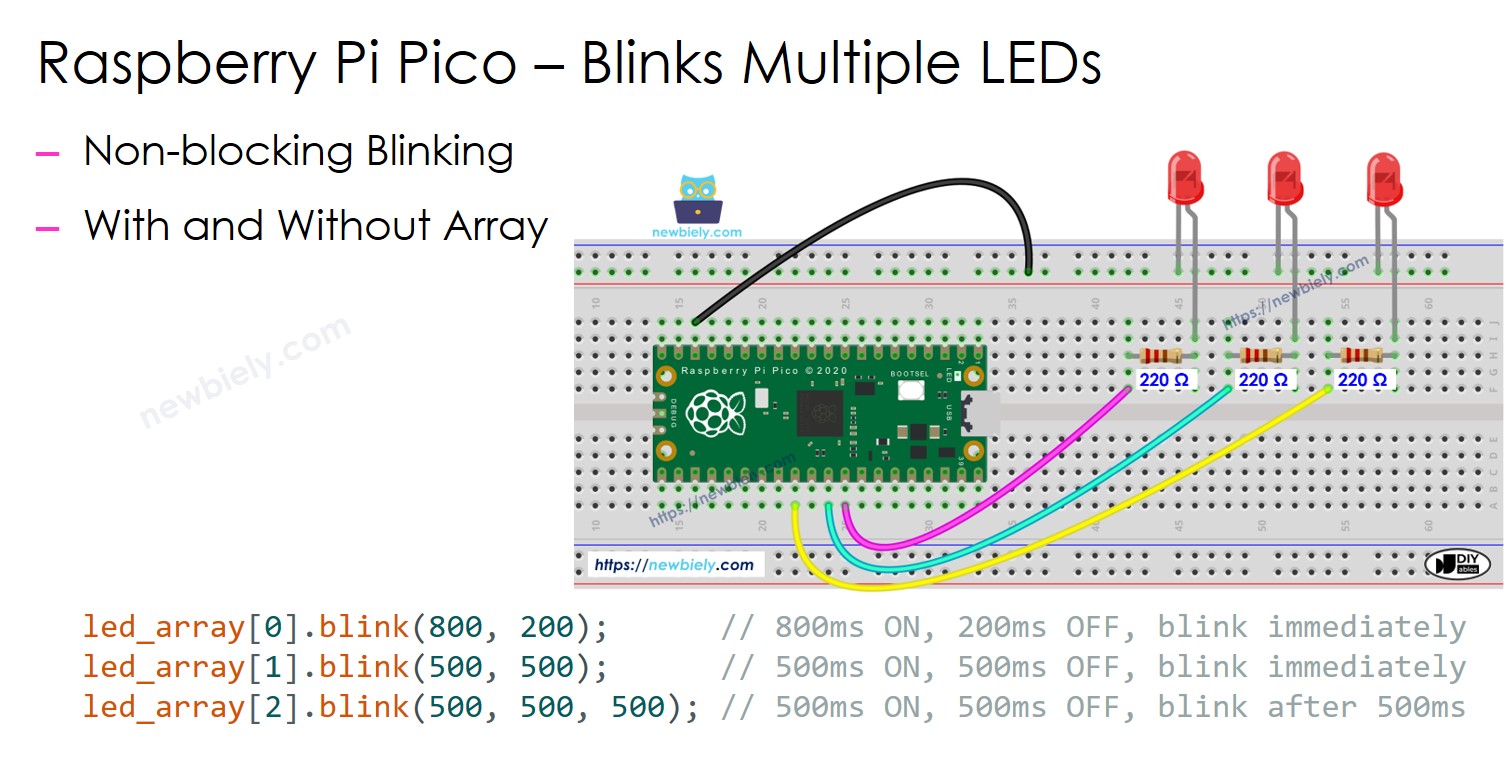
We will show how to do this with three LEDs. You can simply change it for two, four, or more LEDs.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Buy Note: Use the LED Module for easier wiring. It includes an integrated resistor.
Overview of LED
Check out our detailed guide on LEDs. Learn about connecting the hardware, understanding how they function, setting them up with Raspberry Iron Pico, and how to program them. Learn more here:
Wiring Diagram
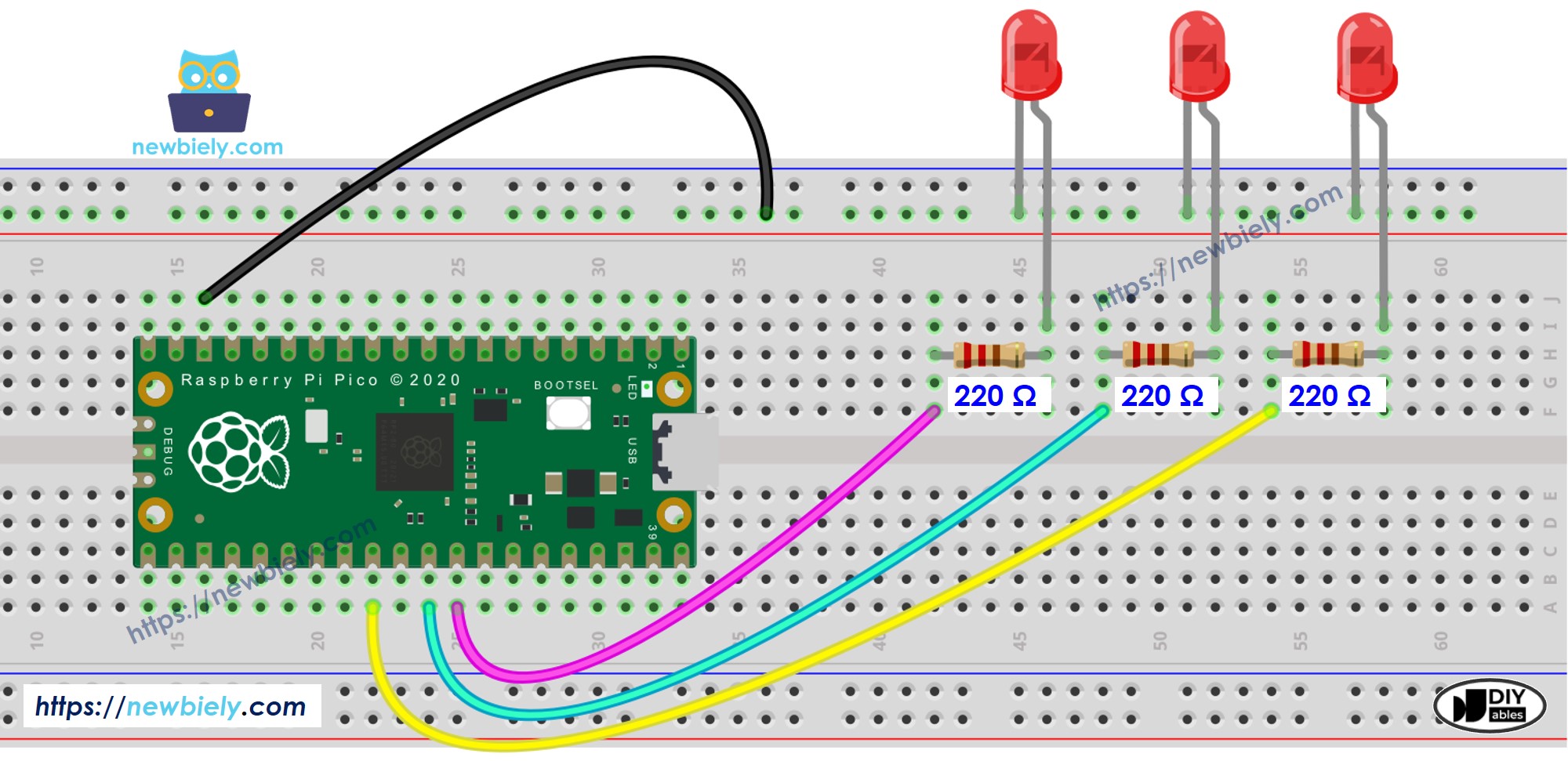
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Raspberry Pi Pico Code - Blink Multiple LEDs
To make multiple LEDs blink simultaneously, avoid using the time.sleep() function, as it halts other code execution and prevents LEDs from blinking at the same time. Instead, use the timestamp to manage the timing.
If you are new to programming and find it hard to handle the timing when blinking multiple LEDs, the DIYables_MicroPython_LED library simplifies it by managing the timing for you. This means you don't have to deal with timing issues on your own when using the library.
Detailed Instructions
Please follow these instructions step by step:
- Ensure that Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Ensure that MicroPython firmware is installed on your Raspberry Pi Pico.
- If this is your first time using a Raspberry Pico, refer to the Raspberry Pi Pico - Getting Started tutorial for detailed instructions.
- Connect the Raspberry Pi Pico to the LEDs according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the Raspberry Pi Pico to your computer using a USB cable.
- Launch the Thonny IDE on your computer.
- On Thonny IDE, select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) Interpreter by navigating to Tools Options.
- In the Interpreter tab, select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) from the drop-down menu.
- Ensure the correct port is selected. Thonny IDE should automatically detect the port, but you may need to select it manually (e.g., COM3 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
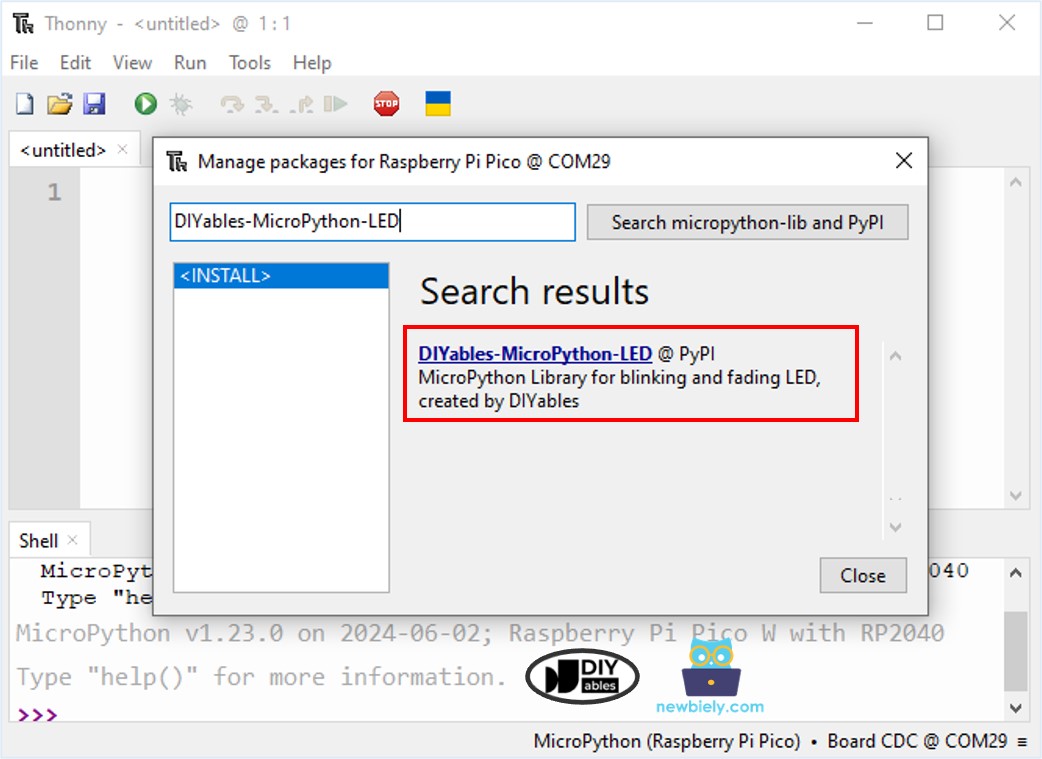
- On Thonny IDE, Navigate to the Tools Manage packages on the Thonny IDE.
- Search “DIYables-MicroPython-LED”, then find the LED library created by DIYables.
- Click on DIYables-MicroPython-LED, then click Install button to install LED library.
- Copy the above code and paste it to the Thonny IDE's editor.
- Save the script to your Raspberry Pi Pico by:
- Click the Save button, or use Ctrl+S keys.
- In the save dialog, you will see two sections: This computer and Raspberry Pi Pico. Select Raspberry Pi Pico
- Save the file as main.py
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to run the script. The script will execute.
- Check out the message in the Shell at the bottom of Thonny.
- Check if the LED is turned on or off.
Raspberry Pi Pico Code - Blink Multiple LEDs by using array
We can improve the above code by using an array of LEDs. The code below uses this array to handle LED objects.
With the DIYables_MicroPython_LED library, you can easily make multiple LEDs blink like this:
- Make multiple LEDs blink at different frequencies.
- Make multiple LEDs begin blinking at different time.
- Set each LED to blink for a specific length of time.
- Set each LED to blink a specific number of times.
