Raspberry Pi Pico - DHT11 - LCD
We will learn how to program the Raspberry Pi Pico to read temperature and humidity from the DHT11 module and display them on an LCD I2C screen.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of DHT11 and LCD
Discover how to use the DHT11 sensor and LCD. Explore their pin connections, roles, and how to program them with these guides:
Wiring Diagram
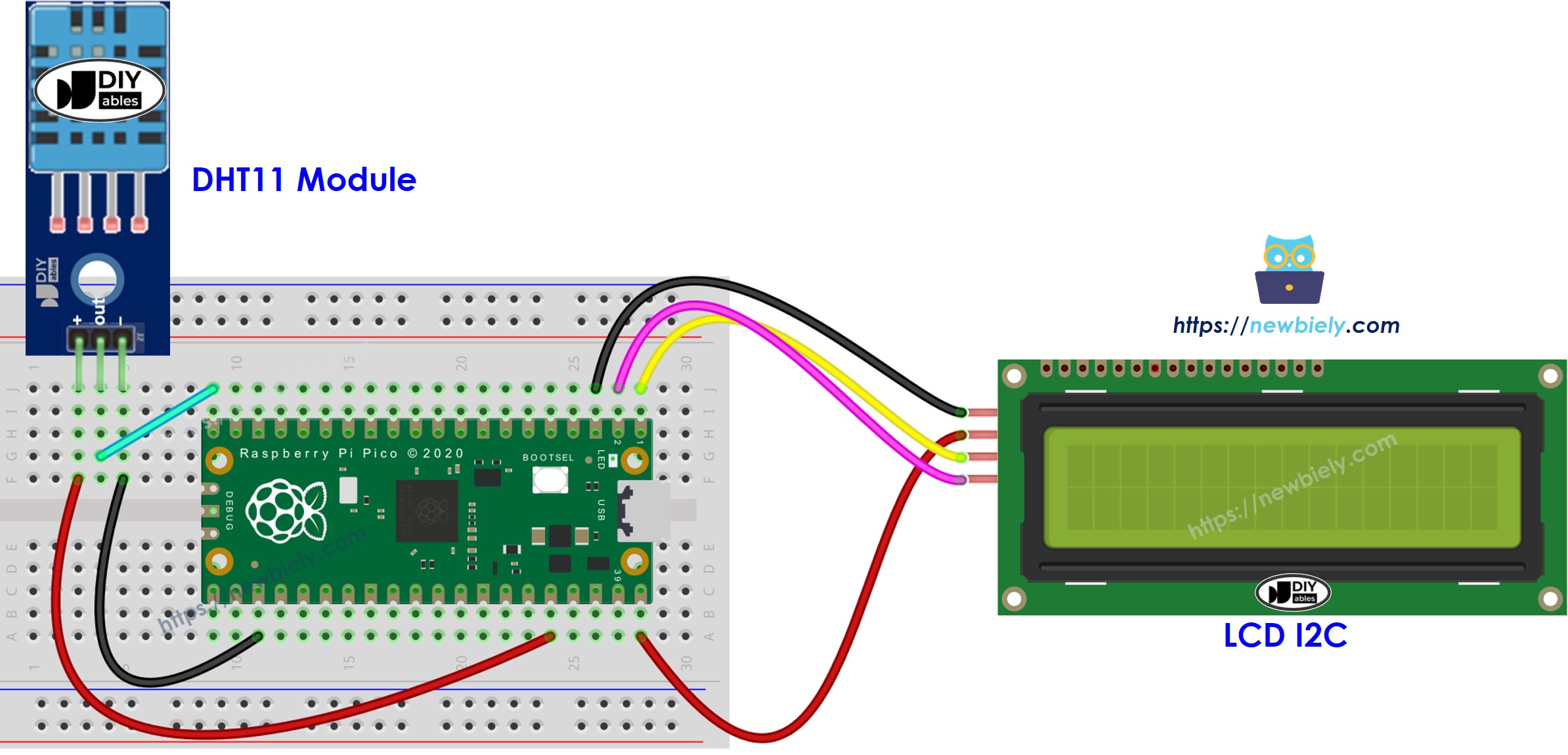
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Raspberry Pi Pico Code - DHT11 Sensor - LCD I2C
※ NOTE THAT:
The LCD I2C address can vary depending on the manufacturer. In our code, we used the address 0x27 as given by the manufacturer, DIYables.
Detailed Instructions
Please follow these instructions step by step:
- Ensure that Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Ensure that MicroPython firmware is installed on your Raspberry Pi Pico.
- If this is your first time using a Raspberry Pico, refer to the Raspberry Pi Pico - Getting Started tutorial for detailed instructions.
- Connect the Raspberry Pi Pico to the DHT11 module and the LCD I2C according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the Raspberry Pi Pico to your computer using a USB cable.
- Launch the Thonny IDE on your computer.
- On Thonny IDE, select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) Interpreter by navigating to Tools Options.
- In the Interpreter tab, select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) from the drop-down menu.
- Ensure the correct port is selected. Thonny IDE should automatically detect the port, but you may need to select it manually (e.g., COM3 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
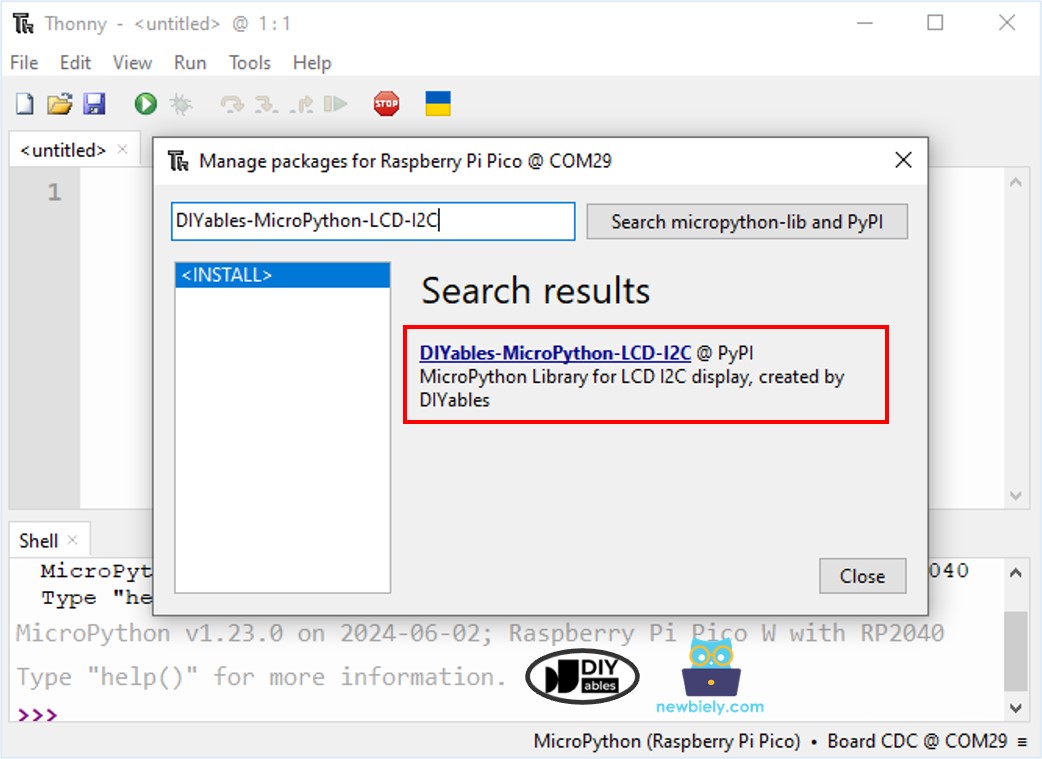
- Navigate to the Tools Manage packages on the Thonny IDE.
- Search “DIYables-MicroPython-LCD-I2C”, then find the LCD I2C library created by DIYables.
- Click on DIYables-MicroPython-LCD-I2C, then click Install button to install LCD I2C library.
- Copy the above code and paste it to the Thonny IDE's editor.
- Save the script to your Raspberry Pi Pico by:
- Click the Save button, or use Ctrl+S keys.
- In the save dialog, you will see two sections: This computer and Raspberry Pi Pico. Select Raspberry Pi Pico
- Save the file as main.py
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to run the script. The script will execute.
- Check out the message in the Shell at the bottom of Thonny.
- Adjust the temperature near the sensor to make it warmer or cooler.
- Look at the results displayed on the LCD screen. It should look like below:
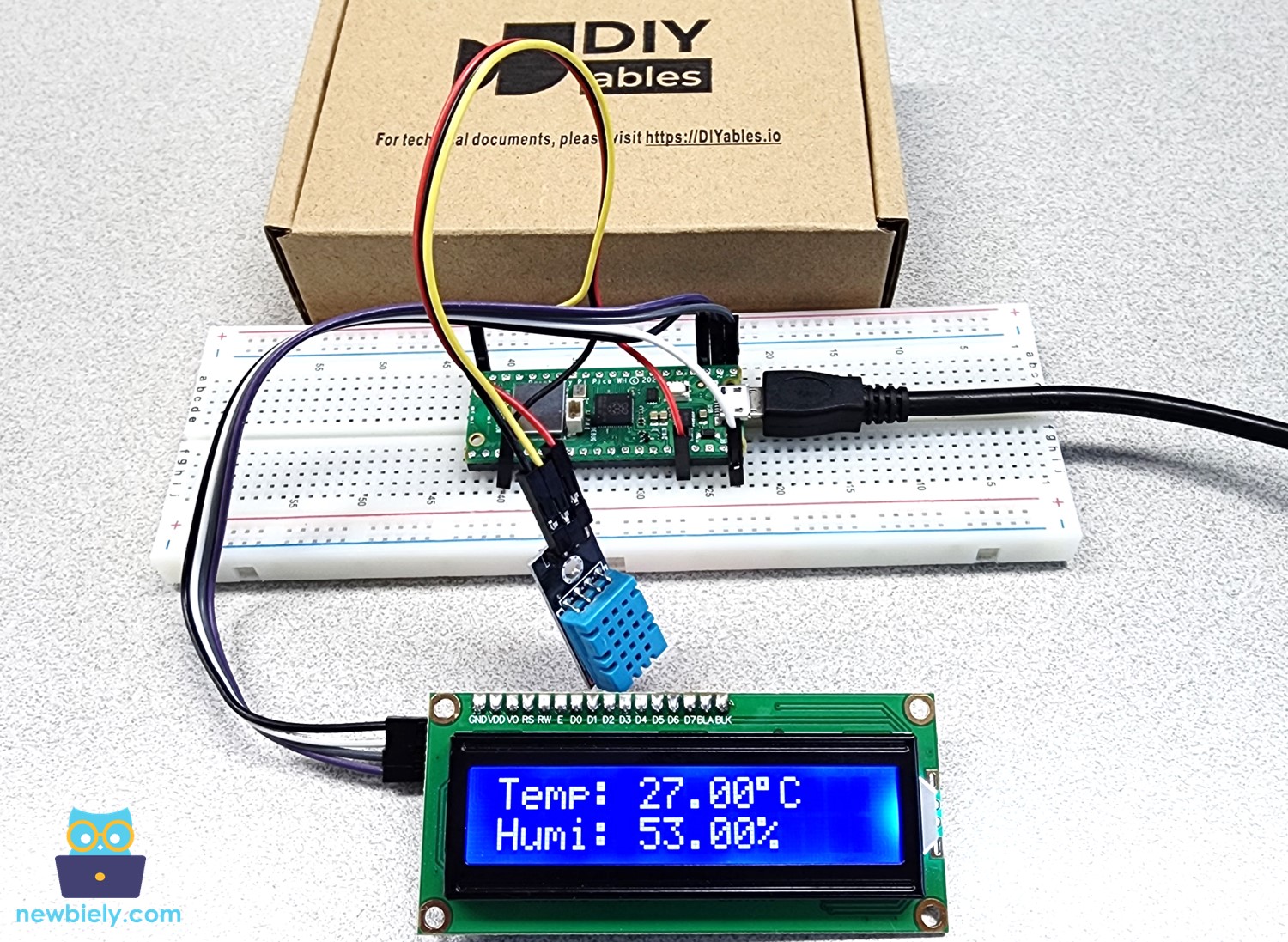
If the LCD screen is blank, visit the Troubleshooting on LCD I2C page for help.
If you name your script main.py and save it to the root directory of the Raspberry Pi Pico, it will automatically run each time the Pico is powered on or reset. This is useful for standalone applications that need to start running immediately upon power-up. If you name your script another name other than main.py, you will need to manually run it from Thonnys's Shell.
