Raspberry Pi Pico - OLED 128x32
This tutorial instructs you how to use a Raspberry Pi Pico with an OLED 128x32 I2C display. You will learn:
- How to connect a 128x32 OLED display to the Raspberry Pi Pico.
- How to display text and numbers on the 128x32 OLED screen using Raspberry Pi Pico.
- How to draw on the 128x32 OLED screen with Raspberry Pi Pico.
- How to show images on the 128x32 OLED screen using Raspberry Pi Pico.
- How to align text and numbers in the middle of the 128x32 OLED screen.
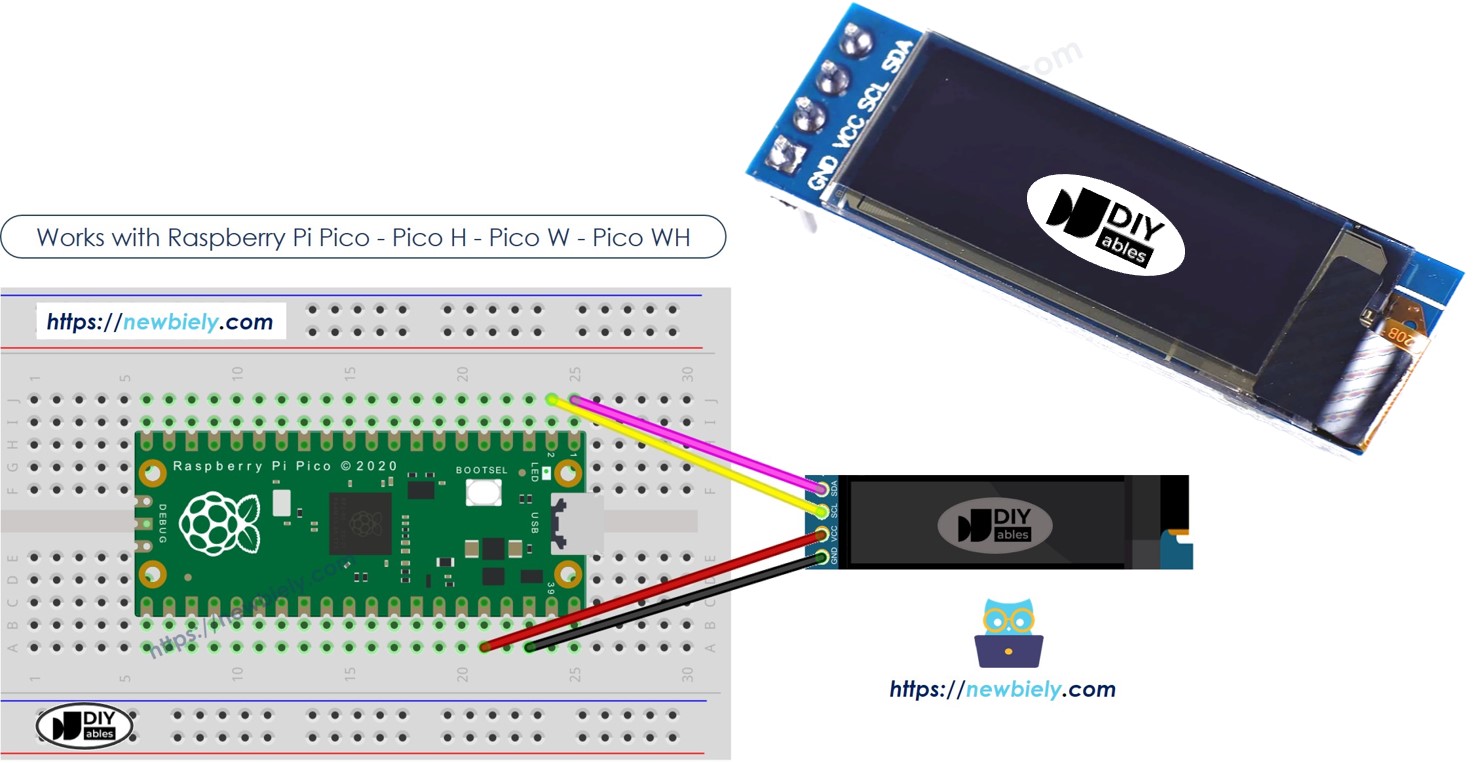
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of OLED Display
I2C OLED Display Pinout
- GND pin: Connect to Raspberry Pi Pico's ground.
- VCC pin: Connect to the 5 volts pin on Raspberry Pi Pico for power.
- SCL pin: This is the clock pin for I2C communication.
- SDA pin: This is the data pin for I2C communication.
※ NOTE THAT:
The pin setup on an OLED module may vary depending on the maker and type of the module. Always look and follow the markings on the OLED module. Pay attention!
This guide is for an OLED screen using the SSD1306 I2C driver. We tried it with an OLED screen from DIYables and it worked very well with no issues.
Wiring Diagram
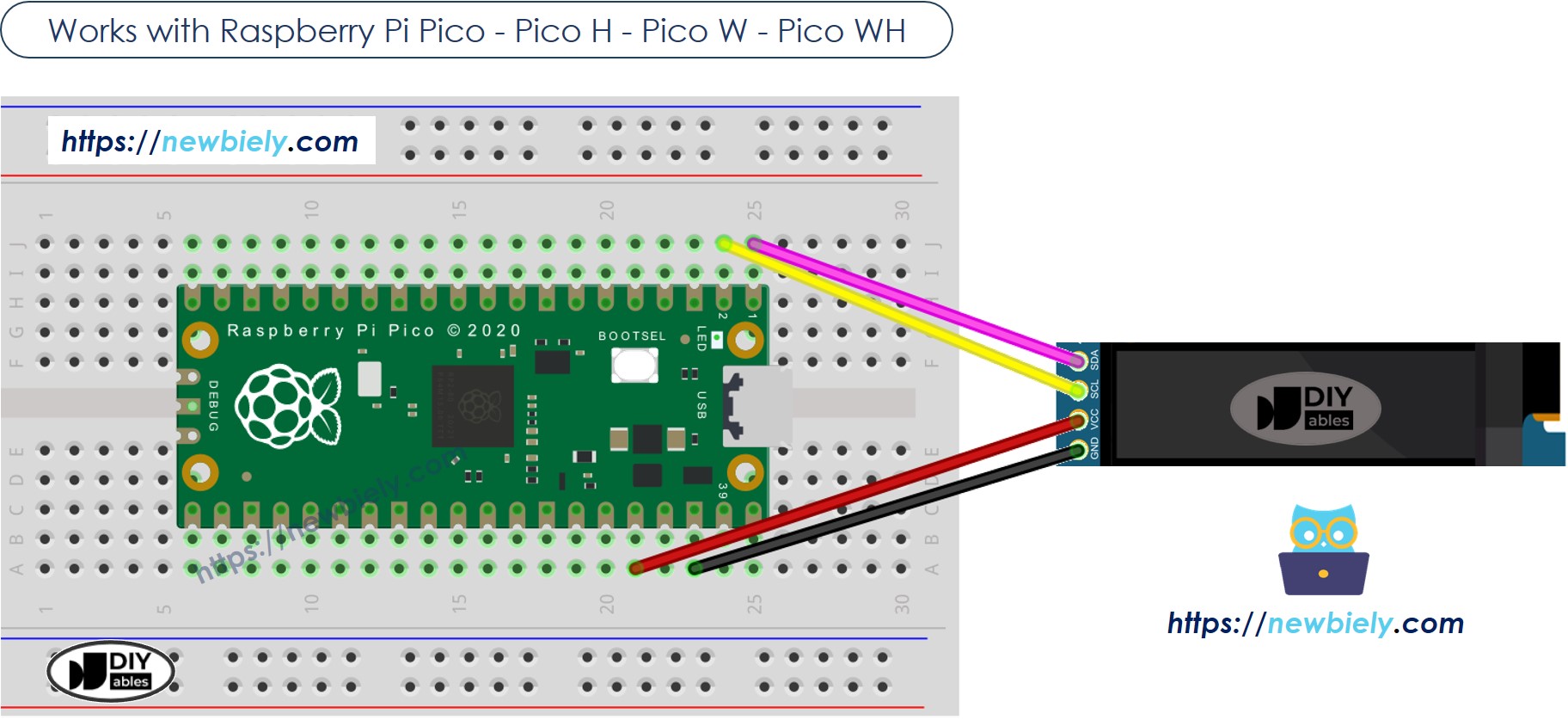
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
The below is the wiring table between 128x32 OLED Module and Raspberry Pi Pico
| 128x32 OLED Module | Raspberry Pi Pico |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SDA | GP0 |
| SCL | GP1 |
Raspberry Pi Pico Code - Display Text, Integer and Float Number on OLED
Detailed Instructions
Please follow these instructions step by step:
- Ensure that Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Ensure that MicroPython firmware is installed on your Raspberry Pi Pico.
- If this is your first time using a Raspberry Pico, refer to the Raspberry Pi Pico - Getting Started tutorial for detailed instructions.
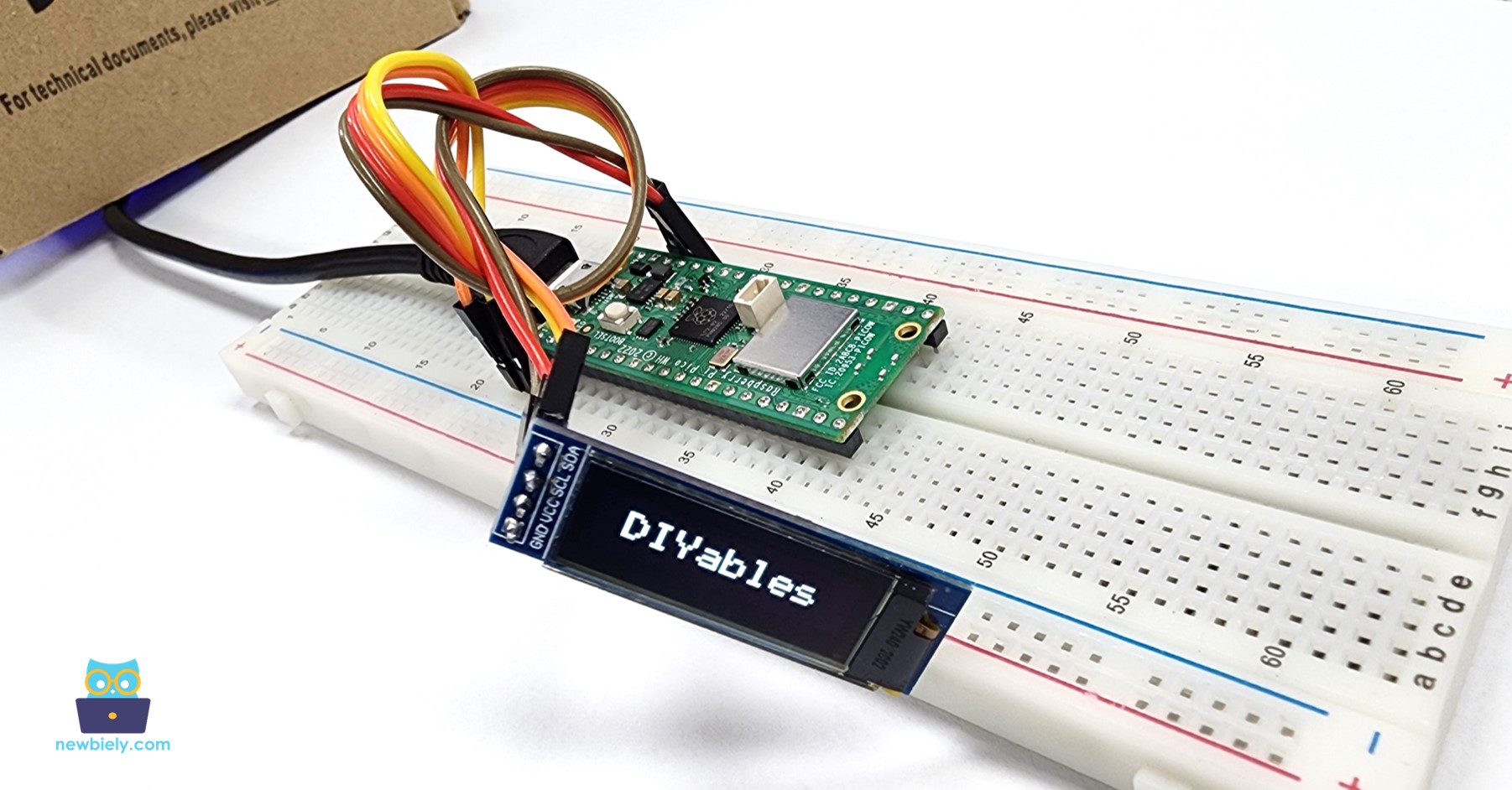
- Connect the OLED display to the Raspberry Pi Pico according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the Raspberry Pi Pico to your computer using a USB cable.
- Launch the Thonny IDE on your computer.
- On Thonny IDE, select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) Interpreter by navigating to Tools Options.
- In the Interpreter tab, select MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) from the drop-down menu.
- Ensure the correct port is selected. Thonny IDE should automatically detect the port, but you may need to select it manually (e.g., COM3 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
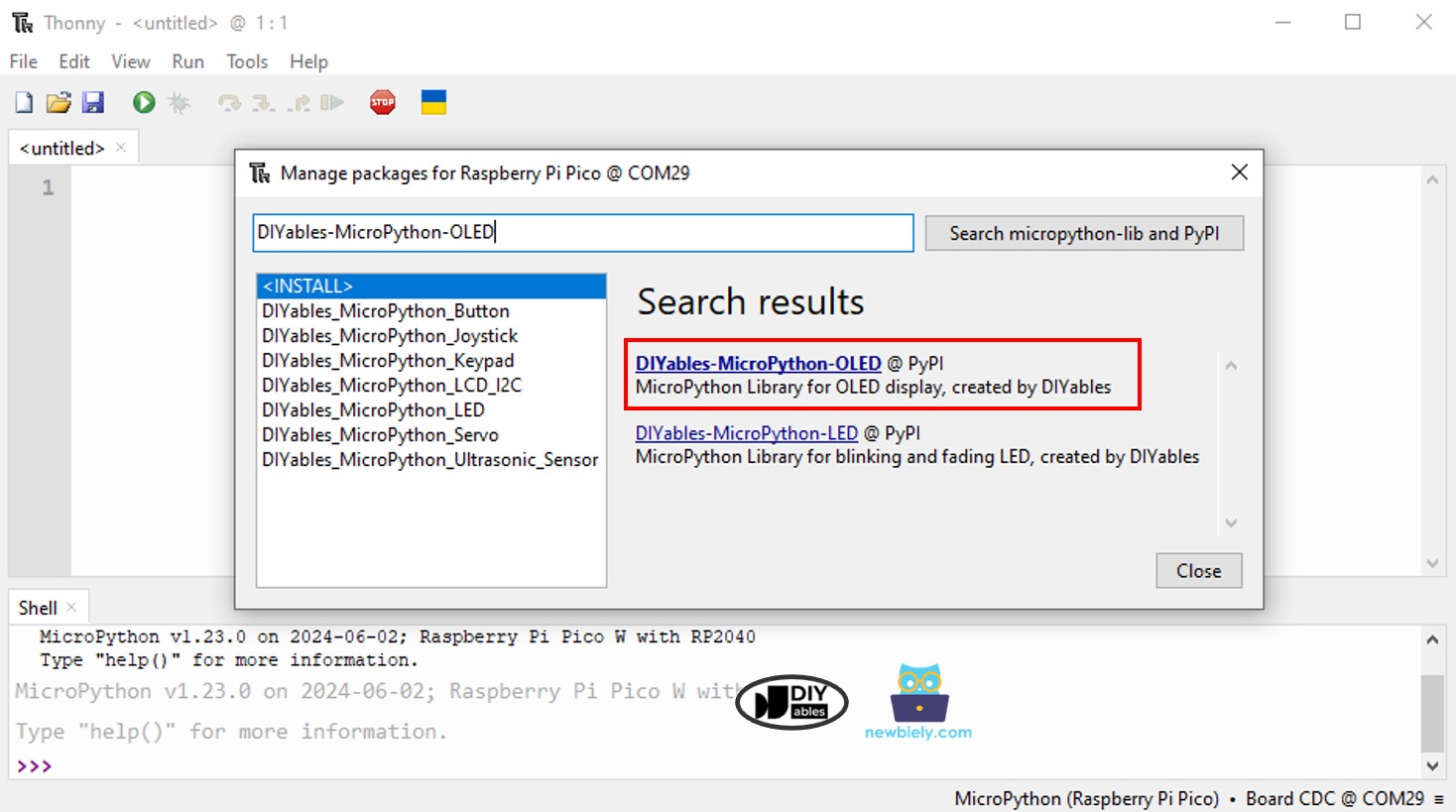
- Navigate to the Tools Manage packages on the Thonny IDE.
- Search “DIYables-MicroPython-OLED”, then find the OLED library created by DIYables.
- Click on DIYables-MicroPython-OLED, then click Install button to install OLED library.
- Copy the above code and paste it to the Thonny IDE's editor.
- Save the script to your Raspberry Pi Pico by:
- Click the Save button, or use Ctrl+S keys.
- In the save dialog, you will see two sections: This computer and Raspberry Pi Pico. Select Raspberry Pi Pico
- Save the file as main.py
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to run the script. The script will execute.
- Check out on the OLED display. It looks like the below:
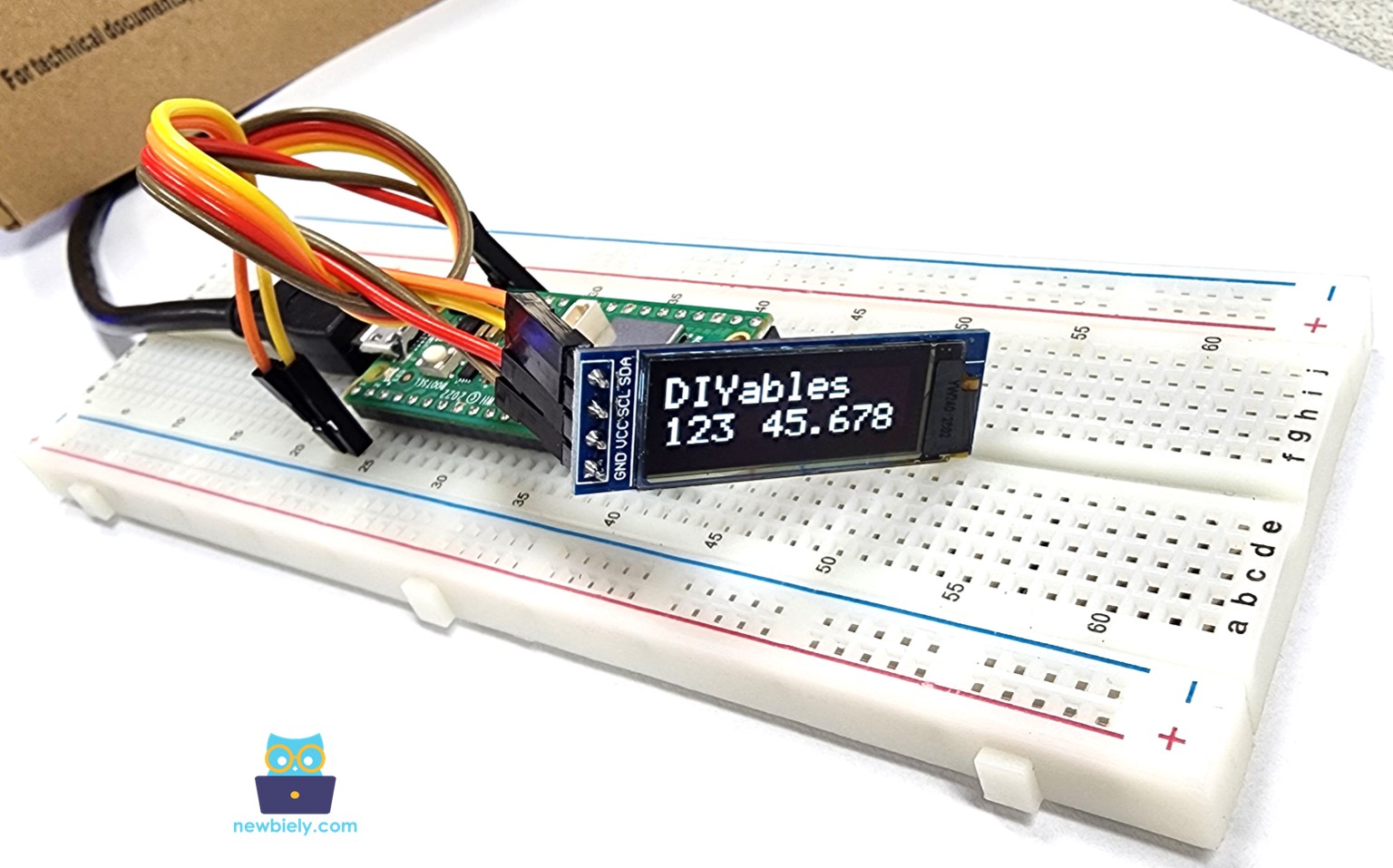
Raspberry Pi Pico Code - Drawing on OLED
When you run the code above, a rectangle, circle, and triangle will appear on the OLED screen, as demonstrated below.
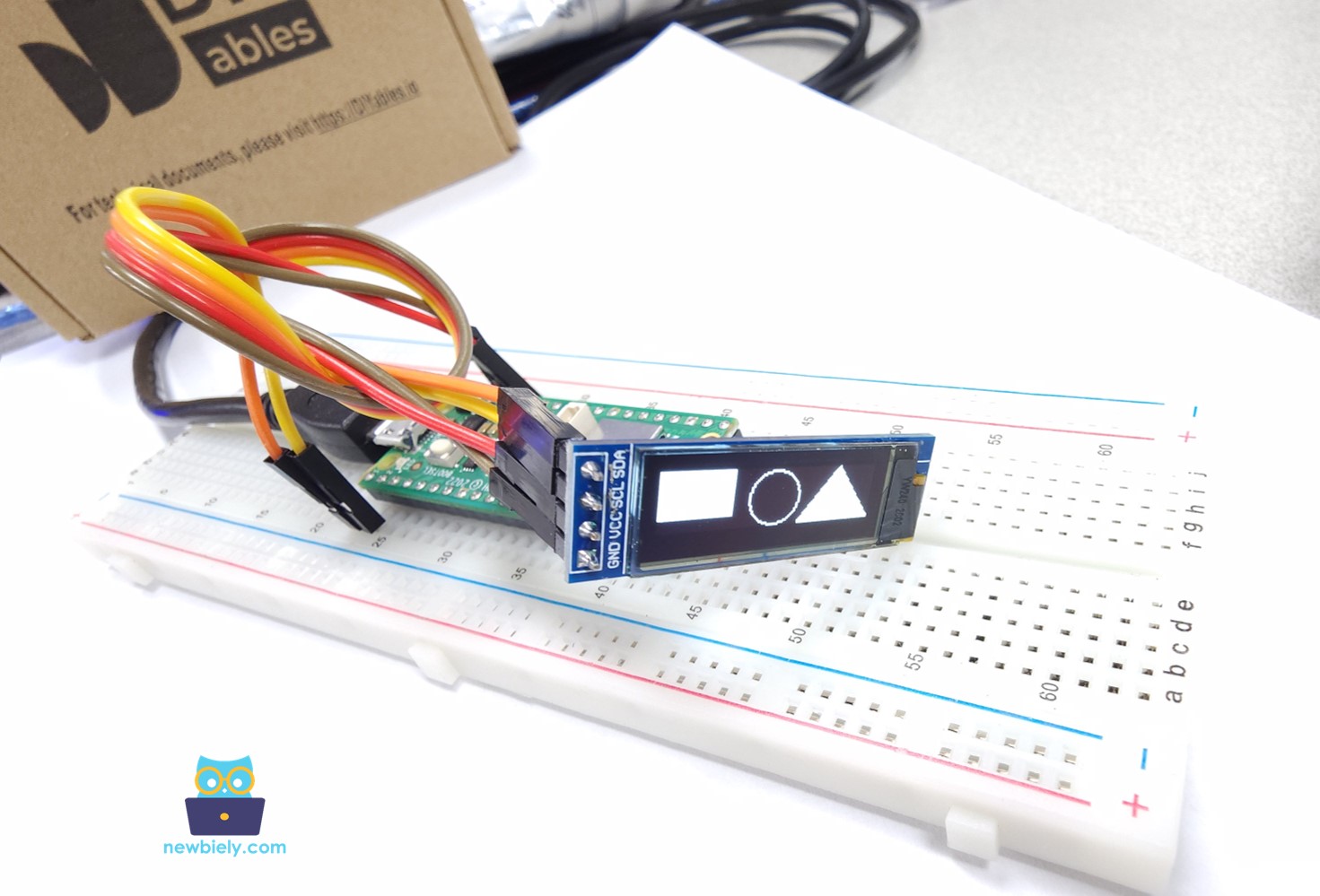
Raspberry Pi Pico Code – Display Image on OLED
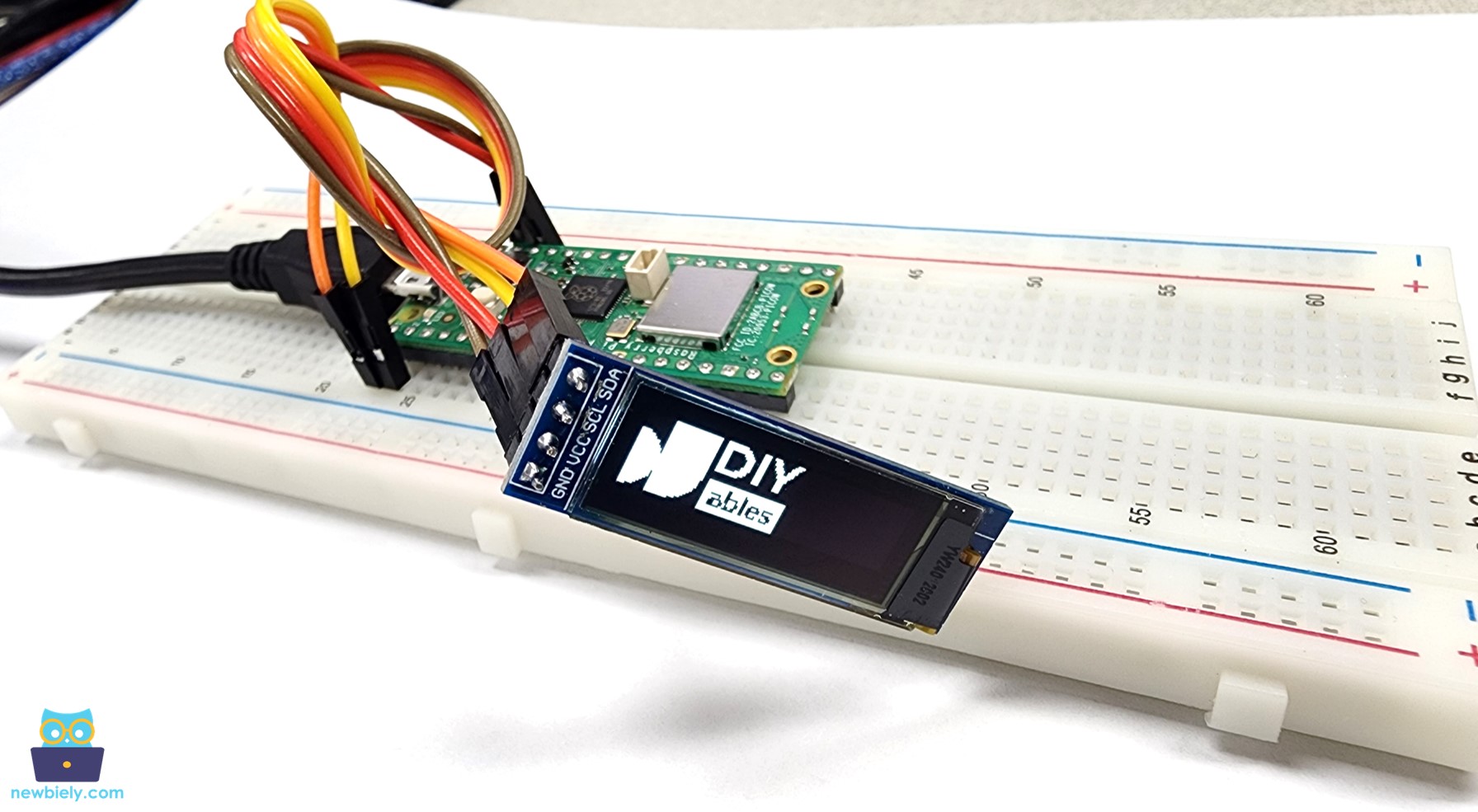
The below code draws an image to LCD display. The image is DIYables icon.
When you run the code above, the image will appear on the OLED screen, as shown below.
To display a different image on the OLED screen, follow these steps:
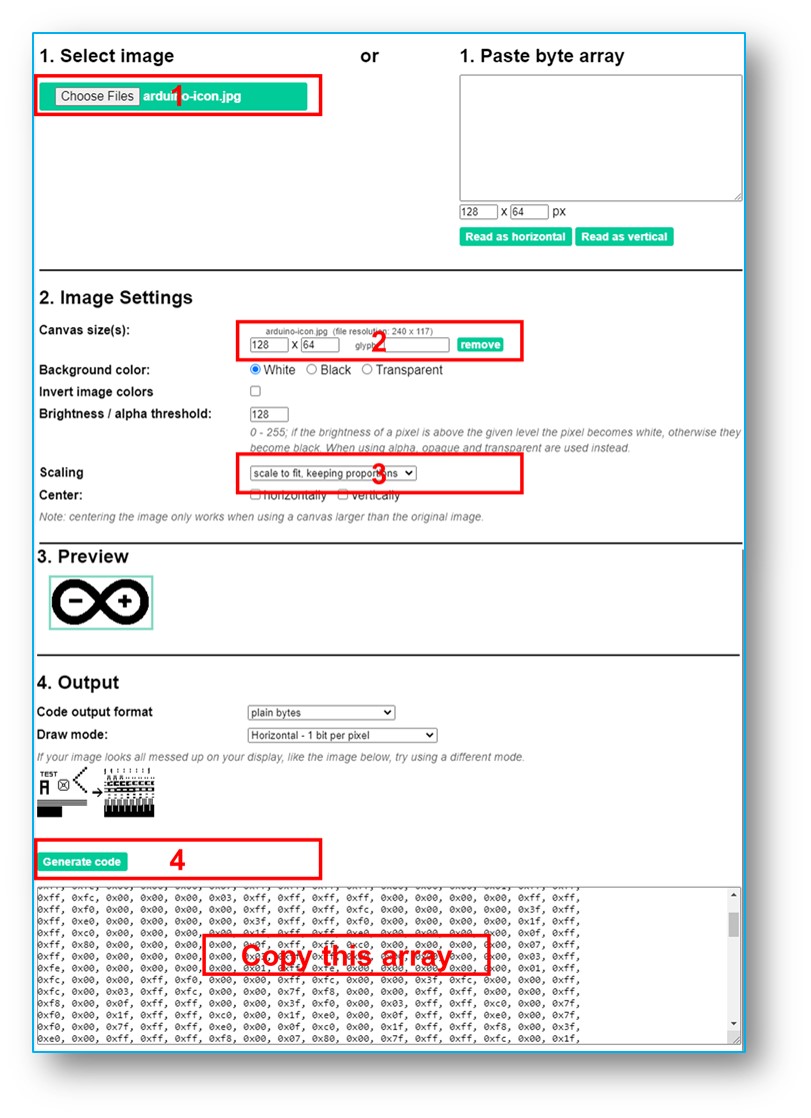
- Convert the image (in any format) to a bitmap array. You can use this online tool for conversion. Refer to the image below for guidance on how to convert an image to a bitmap array. In this example, I converted the Raspberry Pi Pico icon into a bitmap array.
- Replace the existing bitmap array in your Raspberry Pi Pico code with the newly converted array.
- Adjust the image width and height in your Raspberry Pi Pico code to match the dimensions of the new image.
Note: Ensure the image size is equal to or smaller than the OLED screen size.
How to automatically vertical and horizontal center align text/number on OLED
The MicroPython code below automatically centers the text both vertically and horizontally on the OLED screen.
After running the code, the text will be centered both vertically and horizontally on the OLED screen.
OLED Troubleshooting
If nothing is displayed on the 128x32 OLED screen, please try the following steps:
- Verify that all wiring connections are correct.
- Ensure that your I2C OLED is using an SSD1306 driver.
- Determine the I2C address of your OLED by running the I2C Address Scanner code on a Raspberry Pi Pico.
Output in the Shell at the bottom of Thonny:
