ESP32 MicroPython Electromagnetic Lock
In this guide, we will learn how to use the ESP32 and MicroPython to control an electromagnetic lock to lock and unlock your door. In detail, we will learn:
- How electromagnetic lock works
- How to connect electromagnetic lock to ESP32
- How to write MicroPython code for ESP32 to control electromagnetic lock
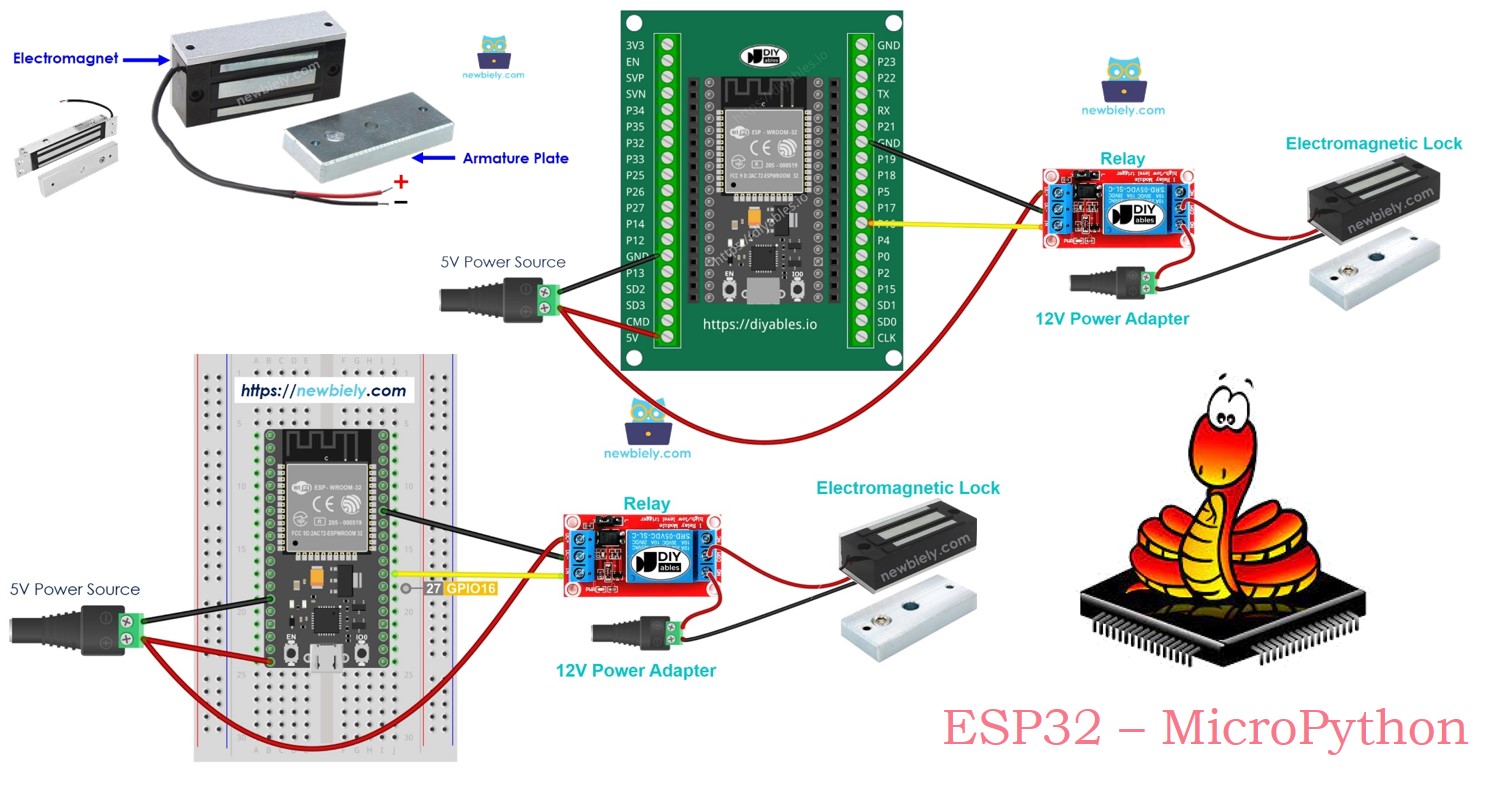
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Electromagnetic Lock
The electromagnetic lock, or maglock, is commonly used to secure doors. It often works with various devices like switches, fingerprint scanners, RFID/NFC readers, keypads, or software on computers and mobile devices to control access to doors and buildings.
Pinout
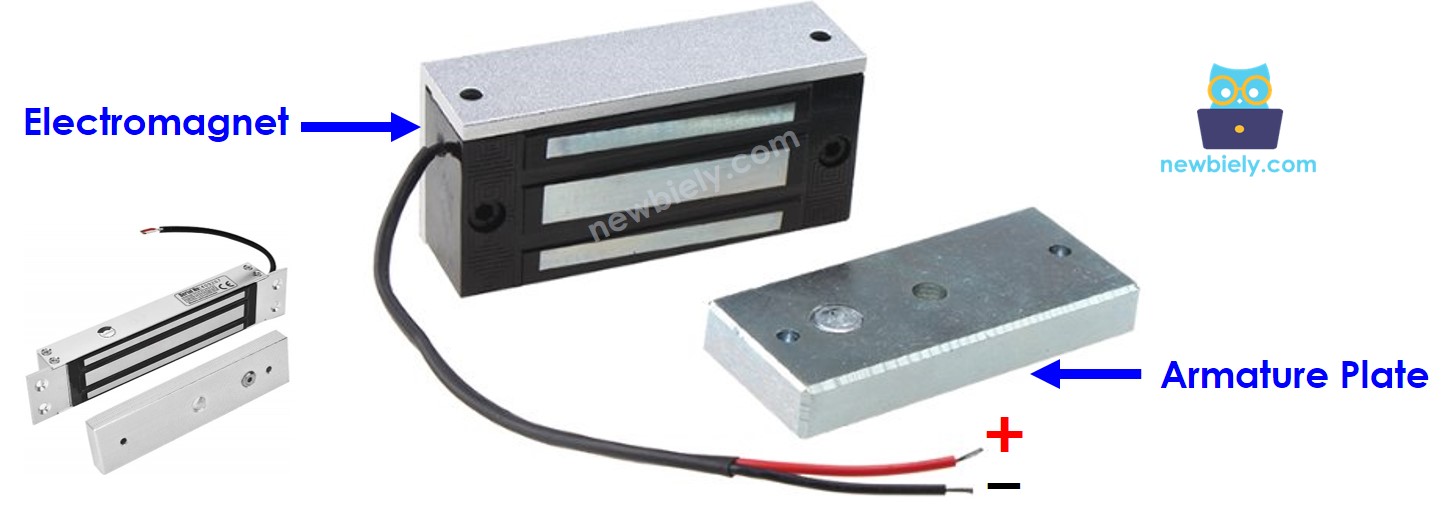
An electromagnetic lock is made up of two parts:
- An electromagnet with two pins
- An armature plate
How It Works
- When the electromagnet is powered on, an electric current flows through it, generating a magnetic field that pulls the armature plate toward it, locking the door.
- When the electromagnet is powered off, the magnetic field disappears, releasing the armature plate and unlocking the door.
※ NOTE THAT:
The electromagnetic lock typically needs a 12V, 24V, or 48V power supply, so it can't be connected directly to an ESP32 pin. Instead, it should be connected to the ESP32 through a relay.
If the electromagnetic lock is connected to a relay set to 'normally open':
- When the relay is open, the door remains unlocked.
- When the relay is closed, the door stays locked.
You can connect an ESP32 to a relay to control the electromagnetic lock. For more details on how to connect a relay to an ESP32, check out the ESP32 MicroPython Relay tutorial.
To install the lock, attach the armature plate to the door or window (the moving part) and mount the electromagnet to the door frame (the stationary part). Make sure these two parts come into contact when the door is closed.
Wiring Diagram
- How to connect ESP32 and electromagnetic lock using breadboard (powered via USB cable)
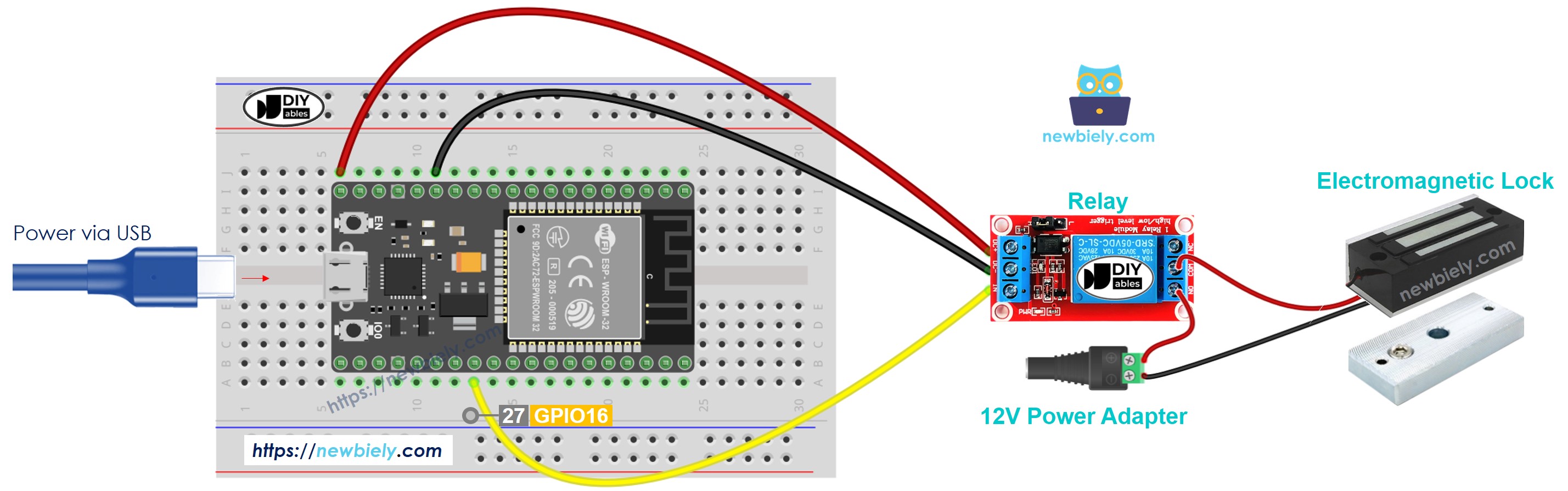
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
- How to connect ESP32 and electromagnetic lock using breadboard (powered via Vin pin)
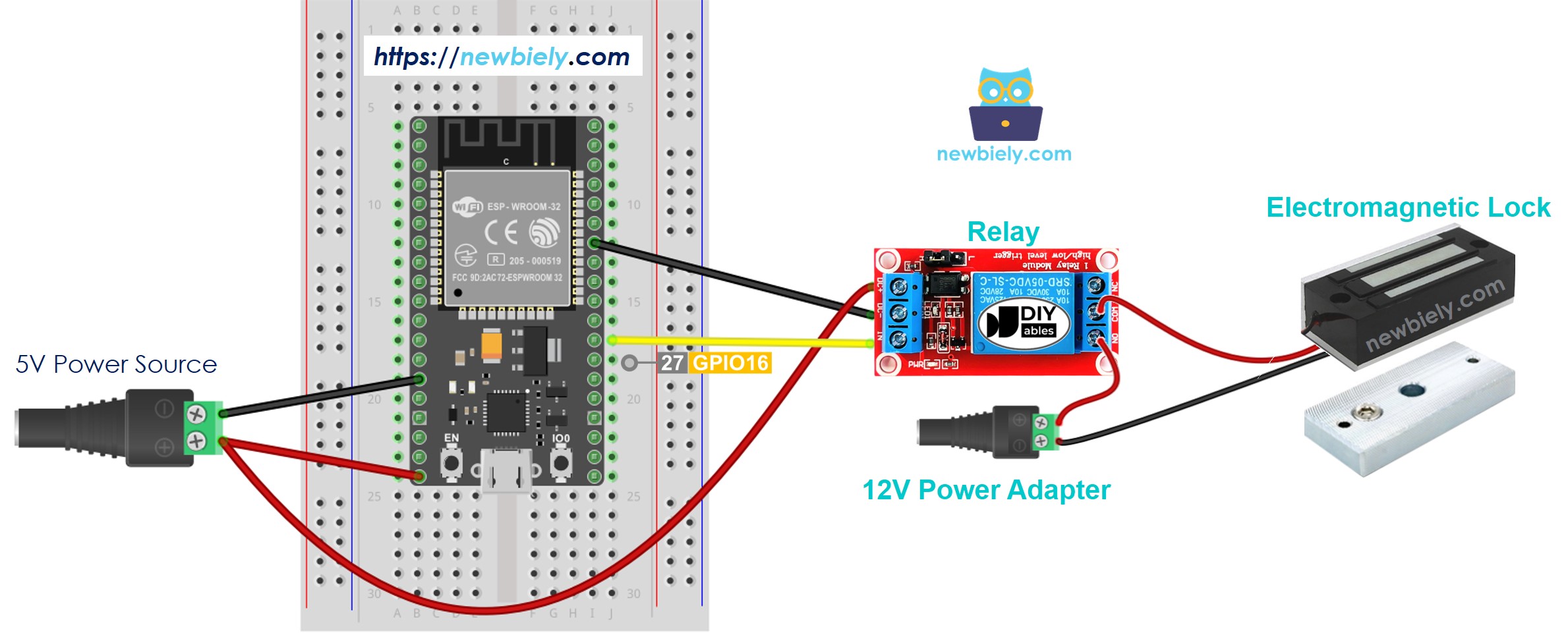
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
- How to connect ESP32 and electromagnetic lock using screw terminal block breakout board (powered via USB cable)
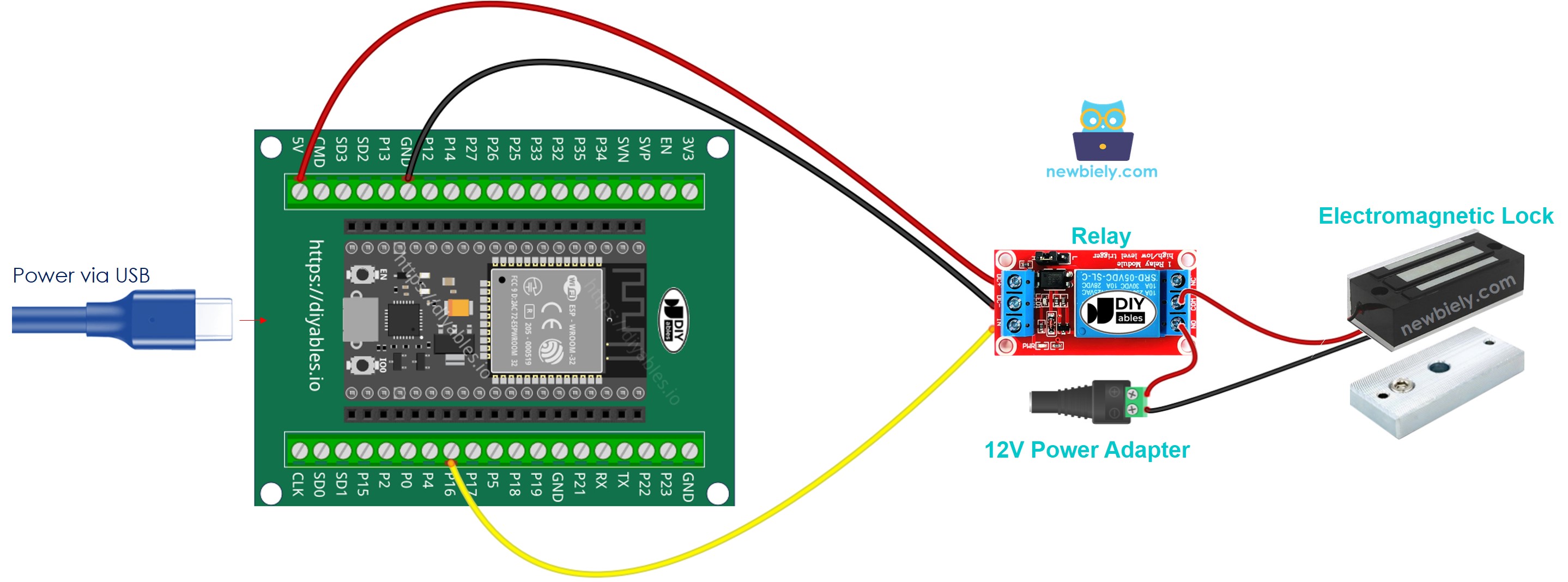
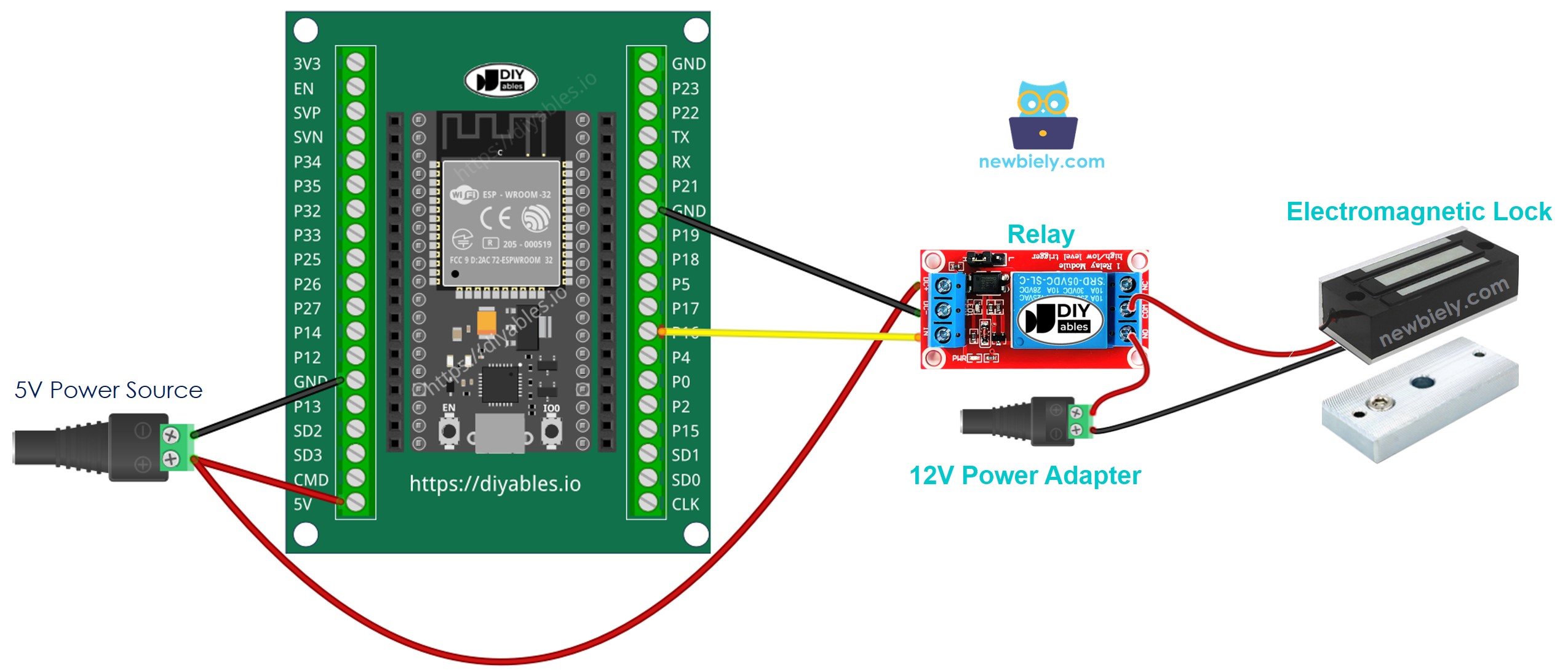
- How to connect ESP32 and electromagnetic lock using screw terminal block breakout board (powered via Vin pin)
ESP32 MicroPython Code
This code makes the door lock and unlock every 5 seconds.
Detailed Instructions
Here’s instructions on how to set up and run your MicroPython code on the ESP32 using Thonny IDE:
- Make sure Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Confirm that MicroPython firmware is loaded on your ESP32 board.
- If this is your first time using an ESP32 with MicroPython, check out the ESP32 MicroPython Getting Started guide for step-by-step instructions.
- Connect the ESP32 board to the electromagnetic lock according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the ESP32 board to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open Thonny IDE on your computer.
- In Thonny IDE, go to Tools Options.
- Under the Interpreter tab, choose MicroPython (ESP32) from the dropdown menu.
- Make sure the correct port is selected. Thonny IDE usually detects it automatically, but you might need to select it manually (like COM12 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
- Copy the provided MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny's editor.
- Save the code to your ESP32 by:
- Clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
- In the save dialog, choose MicroPython device.
- Name the file main.py.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the script.
- Place the armature plate close to the electromagnet.
- Check out how the armature plate is attracted to the electromagnet.
