ESP32 MicroPython Fade LED
This tutorial instructs you how to fade LED using ESP32 and MicroPython. In detail, we will learn:
- How to connect LED to ESP32.
- How to write MicroPython code for ESP32 to control the brightness of LED.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Buy Note: Use the LED Module for easier wiring. It includes an integrated resistor.
Overview of LED
Pinout
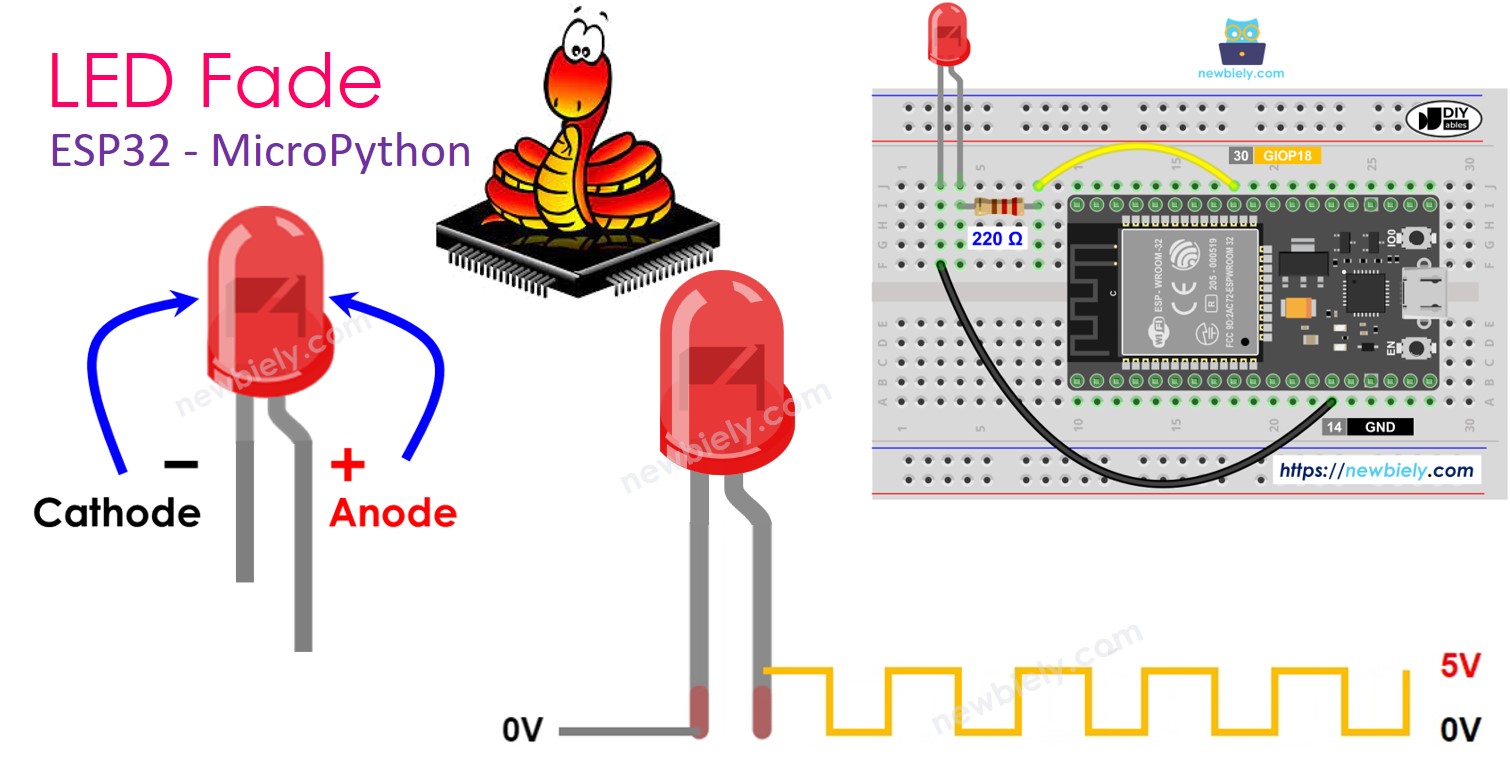
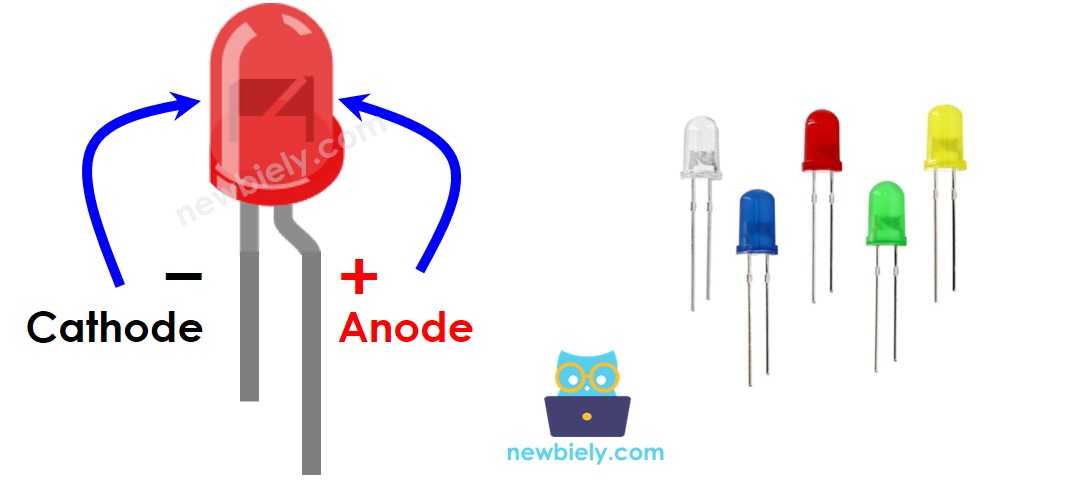
LED has two metal pins.
- Negative (-) pin: Connect it to ground (0V).
- Positive (+) pin: Use it to control the LED's state.
How It Works
After connecting the negative side, also called the cathode, to the ground (GND):
- If you connect the ground (GND) to the positive side of the LED, the LED will turn off.
- If you connect the power supply (VCC) to the positive side of the LED, the LED will light up.
- By using a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal on the positive side of the LED, you can change how bright it is. The PWM value can be between 0 and 255. The LED shines brighter with a higher PWM value and less brightly with a lower value.
- If the PWM value is 0, the LED switches off, like connecting it to GND.
If the PWM value is 255, the LED is completely on, just like it's connected directly to VCC.

※ NOTE THAT:
For most LEDs, you need to connect a resistor from the positive side (anode) to the power supply. The resistor's value depends on the LED's requirements.
ESP32 - fade LED
To adjust the brightness of an LED with the ESP32, use pins that produce a PWM signal. First, connect the LED's positive pin (+) to a pin on the ESP32. Then, link the LED's negative pin (-) to the ground (GND). After that, set up the chosen pin on the ESP32 to send out a PWM signal.
Wiring Diagram
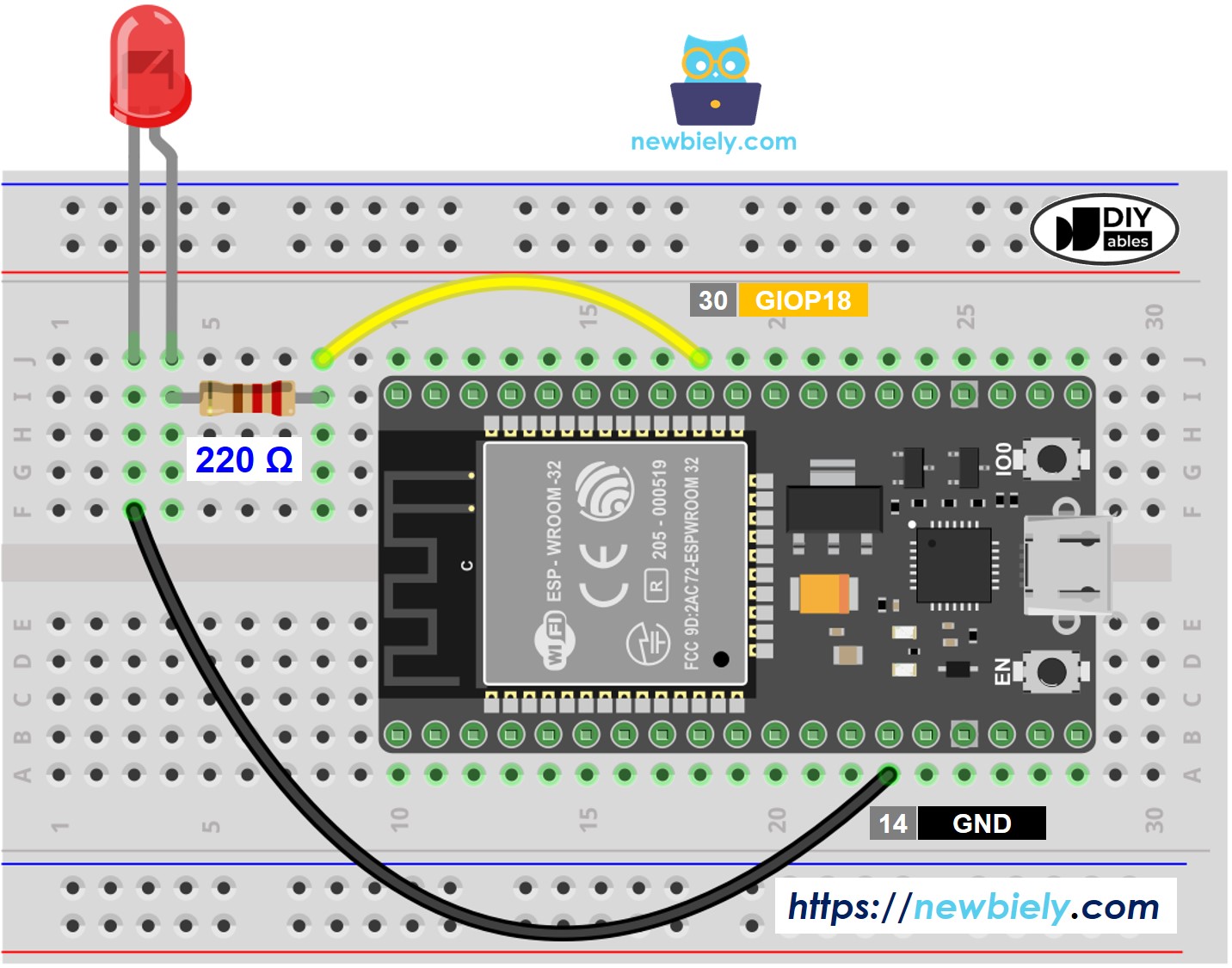
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
ESP32 MicroPython Code
Detailed Instructions
Here’s instructions on how to set up and run your MicroPython code on the ESP32 using Thonny IDE:
- Make sure Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Confirm that MicroPython firmware is loaded on your ESP32 board.
- If this is your first time using an ESP32 with MicroPython, check out the ESP32 MicroPython Getting Started guide for step-by-step instructions.
- Connect the ESP32 board to the LED according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the ESP32 board to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open Thonny IDE on your computer.
- In Thonny IDE, go to Tools Options.
- Under the Interpreter tab, choose MicroPython (ESP32) from the dropdown menu.
- Make sure the correct port is selected. Thonny IDE usually detects it automatically, but you might need to select it manually (like COM12 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
- Copy the provided MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny's editor.
- Save the code to your ESP32 by:
- Clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
- In the save dialog, choose MicroPython device.
- Name the file main.py.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the script.
- Observe the LED to see how it reacts.
Code Explanation
The explanation is in the comments at the top of the ESP32 MicroPython code.
※ NOTE THAT:
In the example, we used a function called sleep() to slowly adjust the light's brightness. However, this function makes the brightness change less smoothly and stops other parts of the program. Next, we will learn how to smoothly fade the light while allowing the rest of the program to continue using the LED library from DIYables.
How to fade in/out LED
With the LED library made by DIYables, making the LED fade in/out is very easy. You can adjust the brightness level and the fading speed.
Detailed Instructions
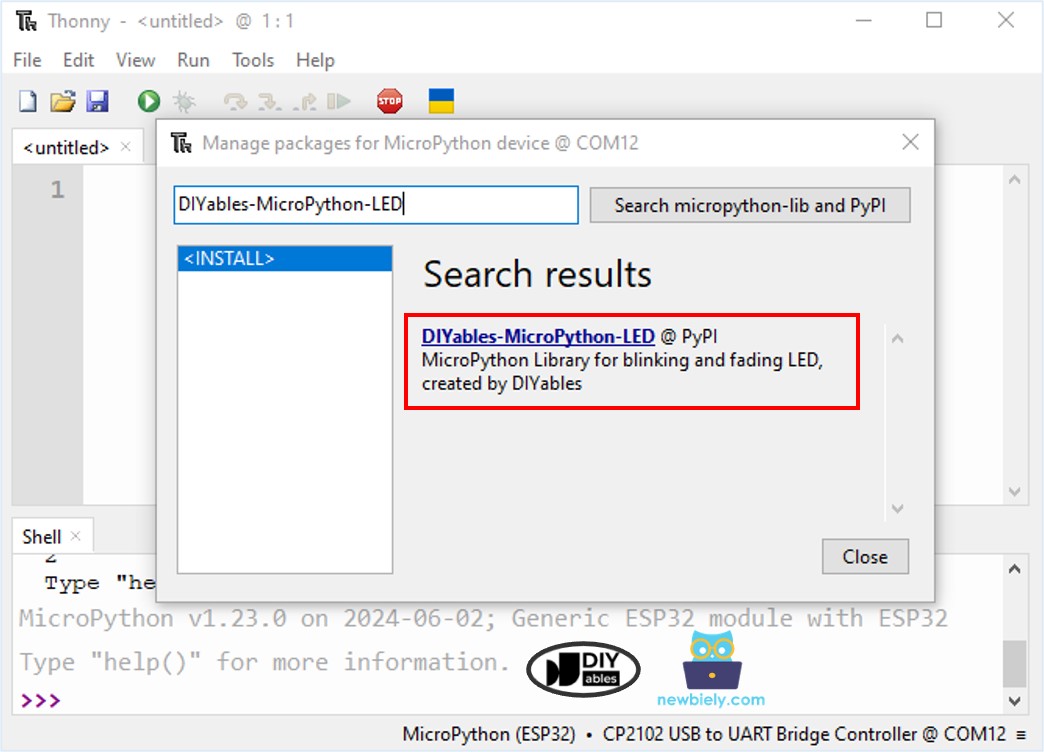
- In Thonny IDE, Go to Tools Manage packages.
- Search for “DIYables-MicroPython-LED” and find the LED library by DIYables.
- Click on DIYables-MicroPython-LED and then click the Install button to install the LED library on the ESP32 board.
- Copy the provided MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny's editor.
- Save the code to your ESP32 by:
- Clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
- In the save dialog, choose MicroPython device.
- Name the file main.py.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the script.
- Check out the LED's state.
