ESP32 MicroPython Joystick Servo Motor
This guide will demonstrate how to control two servo motors or a pan-tilt kit using an ESP32 and a joystick with MicroPython.
A joystick contains two control components, called potentiometers, arranged in a cross pattern, referred to as the X-axis and Y-axis. These potentiometers generate signals, the X-value and Y-value, which come from the VRX and VRY pins of the joystick. These signals are used to control two servo motors: the X-value controls servo motor #1, while the Y-value controls servo motor #2. When used with a pan-tilt kit, the two servo motors work together to move in three dimensions.
The application can be used in two ways:
- Use case 1: Moving the joystick controls the servo motors:
- The servo motors’ angles correspond to the joystick's left-right (X) and up-down (Y) movements.
- Releasing the joystick returns both it and the servo motors to their initial positions.
- Use case 2: Use the joystick to direct the servo motors:
- Moving the joystick left rotates servo motor #1 clockwise.
- Moving the joystick right rotates servo motor #1 counterclockwise.
- Moving the joystick upward rotates servo motor #2 clockwise.
- Moving the joystick downward rotates servo motor #2 counterclockwise.
- Releasing the joystick maintains the current positions of the servo motors.
- Pressing the joystick's button resets the servo motors to the center position.
- ESP32 MicroPython Getting Started tutorial
- How to connect ESP32 with joystick and servo motor using breadboard
- How to connect ESP32 with joystick and servo motor using screw terminal block breakout board
- Make sure Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Confirm that MicroPython firmware is loaded on your ESP32 board.
- If this is your first time using an ESP32 with MicroPython, check out the ESP32 MicroPython Getting Started guide for step-by-step instructions.
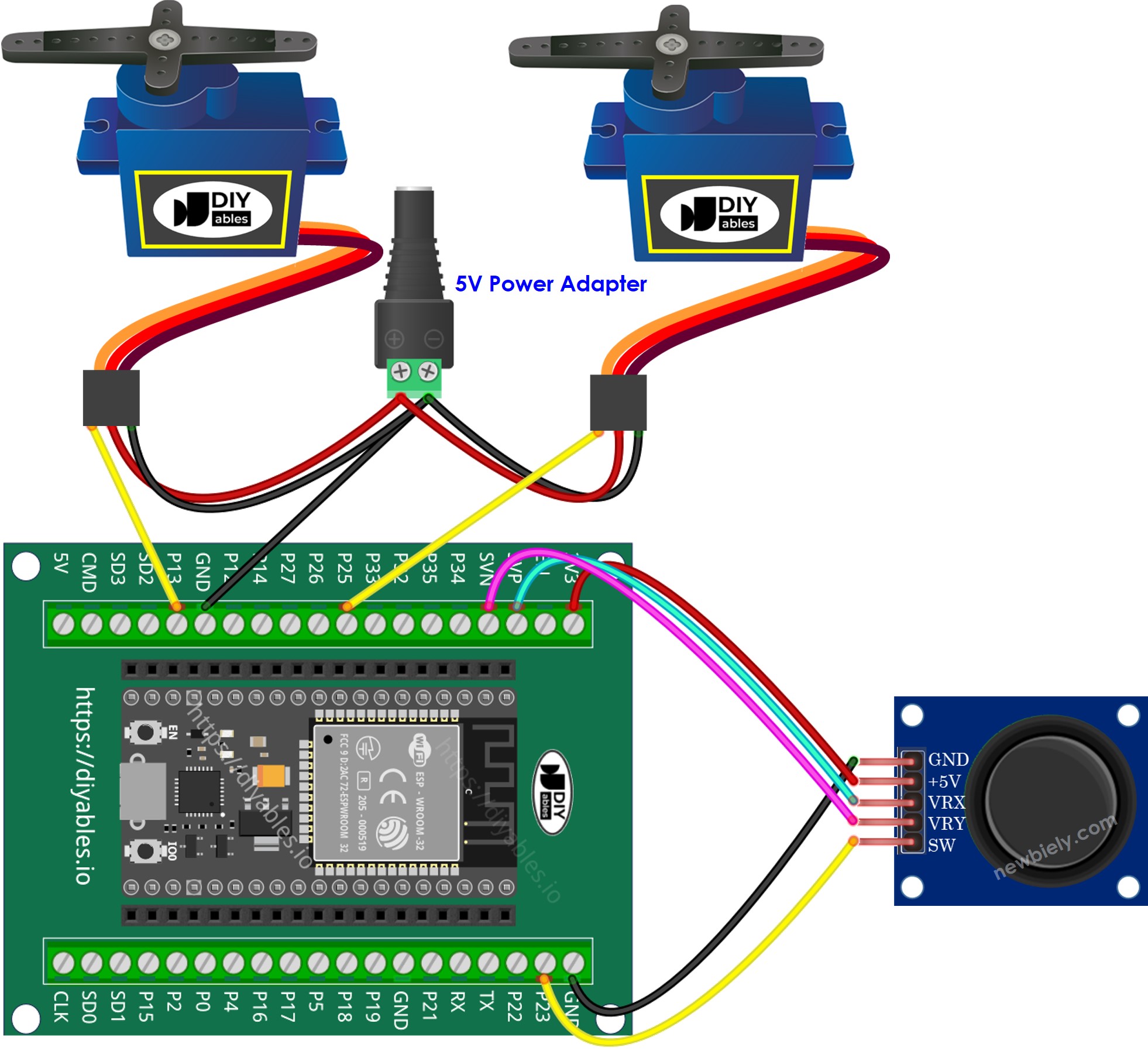
- Connect the ESP32 board to the joystick and servo motor according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the ESP32 board to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open Thonny IDE on your computer.
- In Thonny IDE, go to Tools Options.
- Under the Interpreter tab, choose MicroPython (ESP32) from the dropdown menu.
- Make sure the correct port is selected. Thonny IDE usually detects it automatically, but you might need to select it manually (like COM12 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
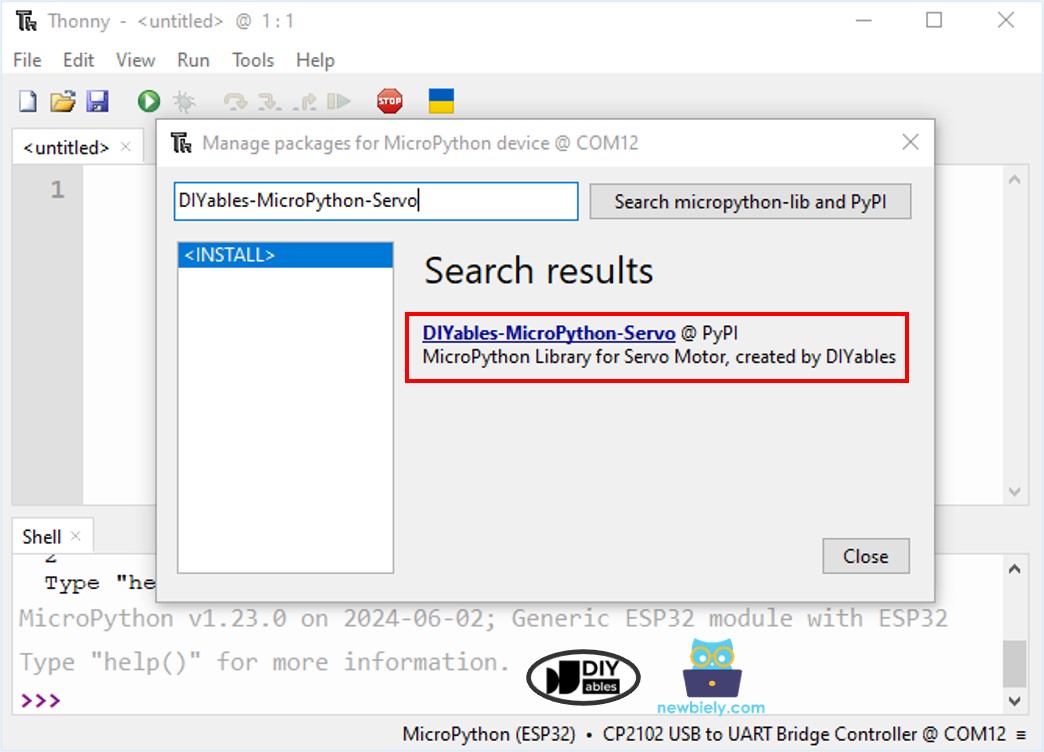
- Navigate to the Tools Manage packages on the Thonny IDE.
- Search “DIYables-MicroPython-Servo”, then find the Servo Motor library created by DIYables.
- Click on DIYables-MicroPython-Servo, then click Install button to install Servo Motor library.
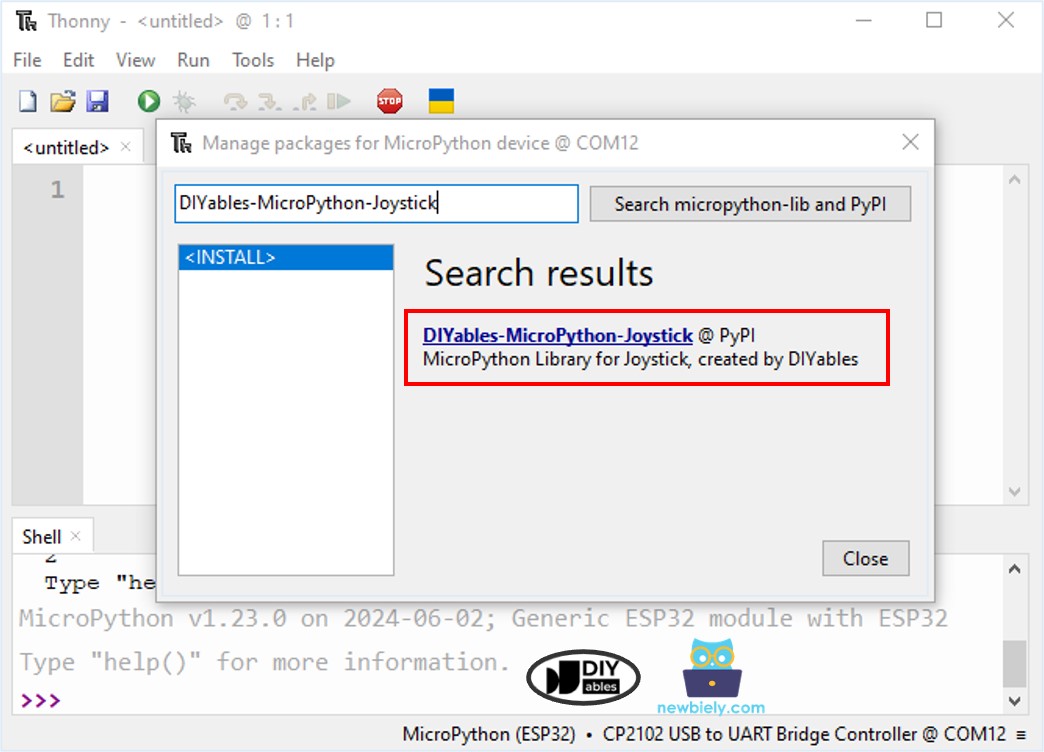
- Search “DIYables-MicroPython-Joystick”, then find the Joystick library created by DIYables.
- Click on DIYables-MicroPython-Joystick, then click Install button to install Joystick library.
- Copy the provided MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny's editor.
- Save the code to your ESP32 by:
- Clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
- In the save dialog, choose MicroPython device.
- Name the file main.py.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the script.
- Push the joystick in any direction.
- Watch the servo motor spin.
- Check out the message in the Shell at the bottom of Thonny.
- The ESP32 ADC is not perfectly accurate and may require calibration for precise results. Each ESP32 board may vary slightly, so calibration is necessary for each individual board.
- Calibration can be challenging, especially for beginners, and might not always yield the exact results you desire.
- Copy the above code and paste it into the editor of Thonny IDE.
- Save the script to your ESP32 board.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the script.
- Move the joystick in any direction.
- Observe the servo motor rotating.
- Check out the message in the Shell at the bottom of Thonny.
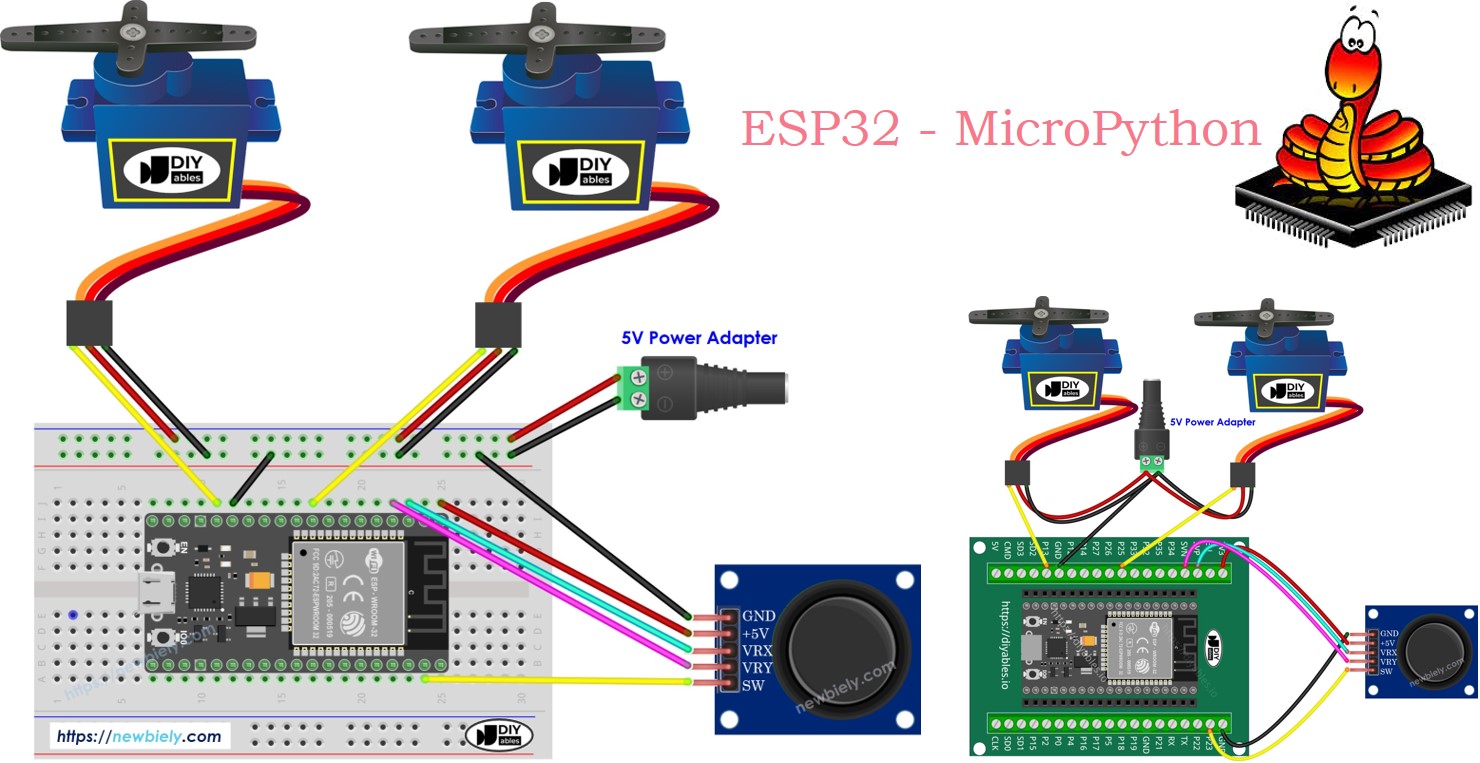
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Joystick and Servo Motor
If you're new to Joystick, Servo Motor, or MicroPython programming for the ESP32, I recommend checking out these tutorials:
These tutorials will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of Joystick and Servo Motor pinouts, how to connect these components to the ESP32, and how to effectively control their behavior using MicroPython code.
Wiring Diagram
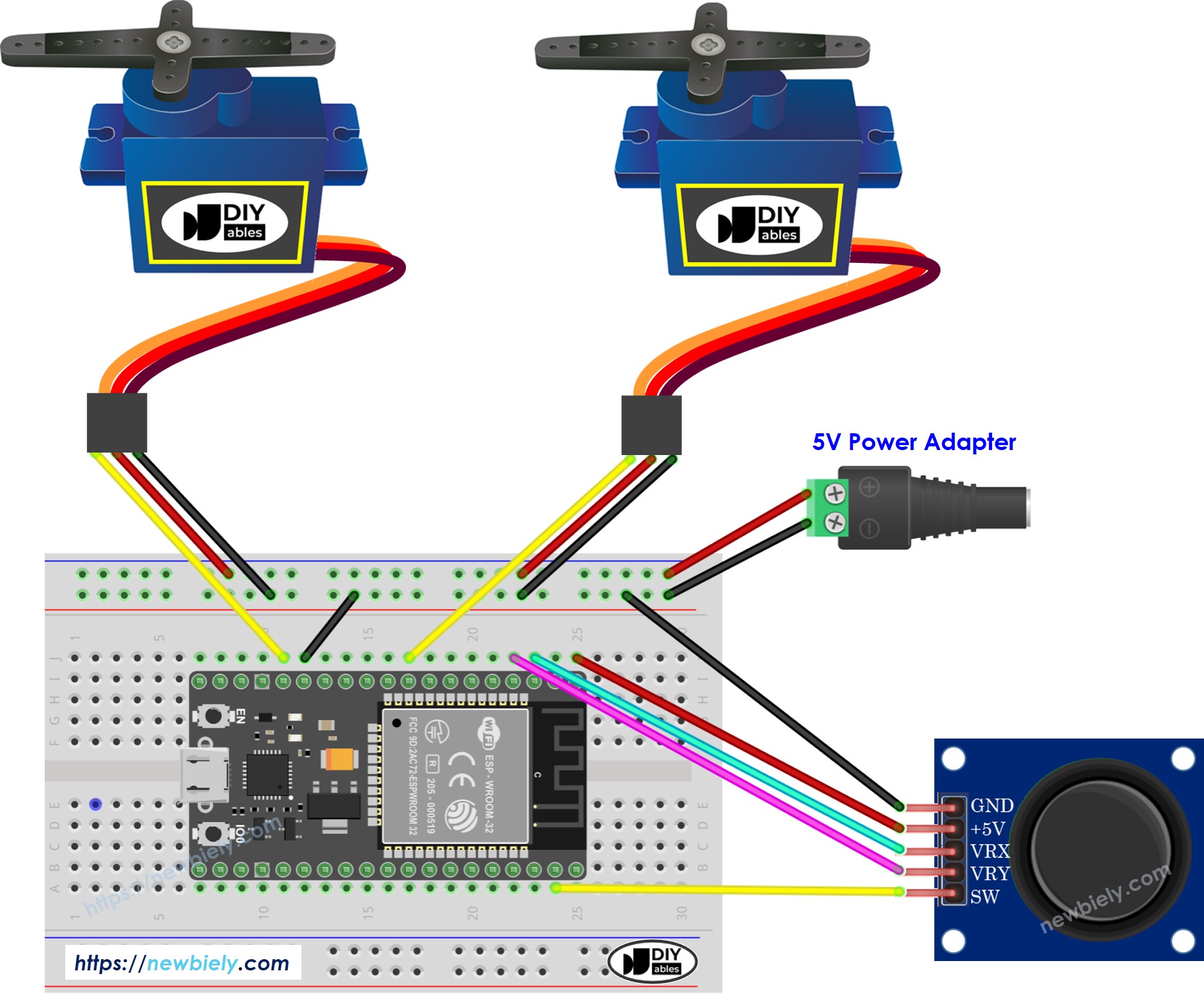
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
ESP32 MicroPython Code
ESP32 MicroPython Code - The servo motors rotate according to the movement of the joystick's thump
Detailed Instructions
Here’s instructions on how to set up and run your MicroPython code on the ESP32 using Thonny IDE:
※ NOTE THAT:
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the adc.read() function to read values from an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) connected to a joystick. The ESP32's ADC is suitable for projects that do not require high precision. However, if your project needs accurate measurements, keep the following in mind:
For projects requiring high precision, consider using an external ADC (e.g., ADS1115) with the ESP32 or opt for an Arduino, which has a more reliable ADC. If you still wish to calibrate the ESP32 ADC, refer to the ESP32 ADC Calibration Driver.
ESP32 MicroPython Code - Use the joystick to command servo motors
Detailed Instructions
Code Explanation
Look at the explanations in the comments in the source code.
