ESP32 MicroPython Force Sensor
This tutorial shows you how to use a force sensor with an ESP32 and MicroPython to detect the force or weight applied to it. We will learn:
- How a force sensor works
- How to connect the force sensor to ESP32
- How to write MicroPython code for ESP32 to read data from the force sensor
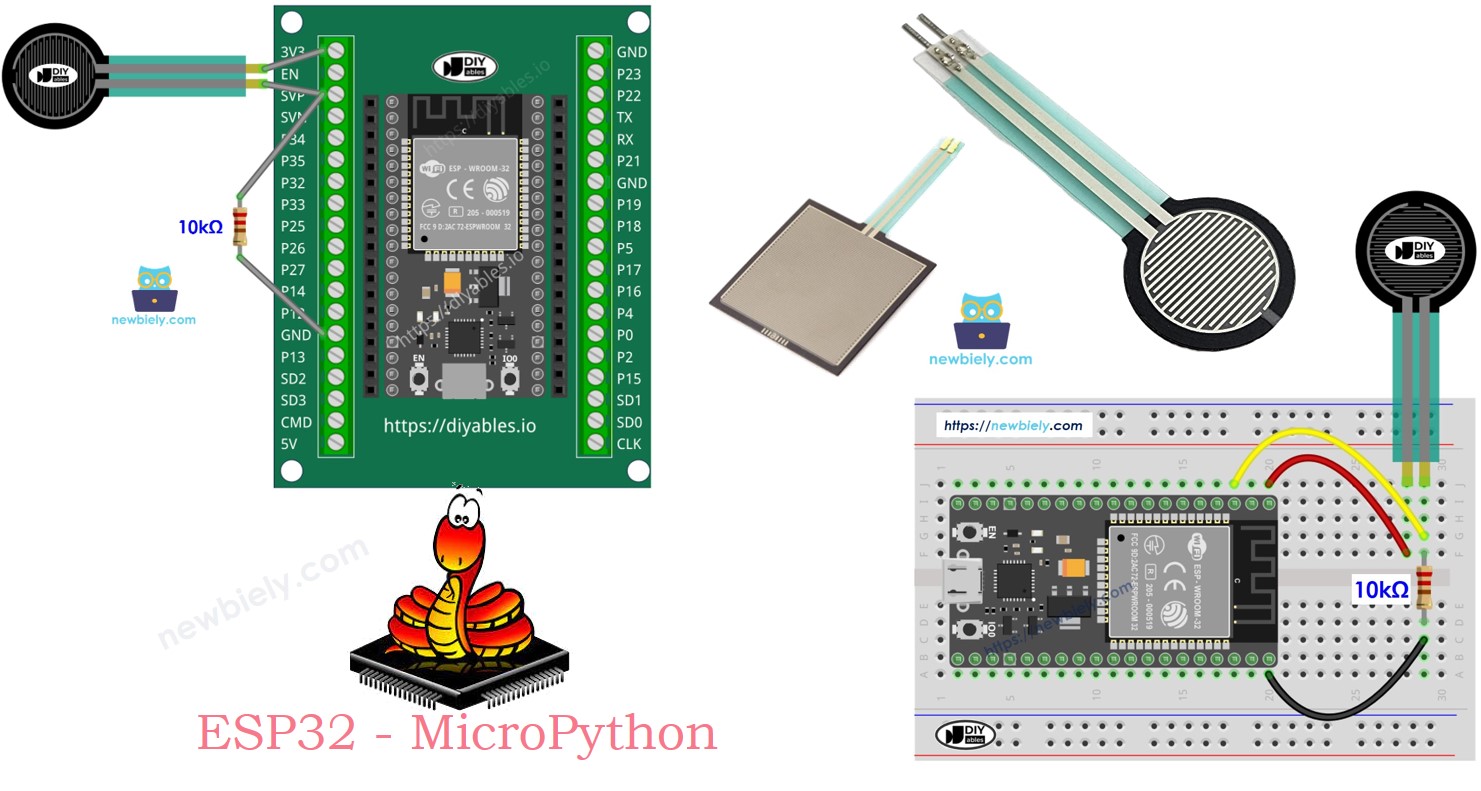
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Force Sensor
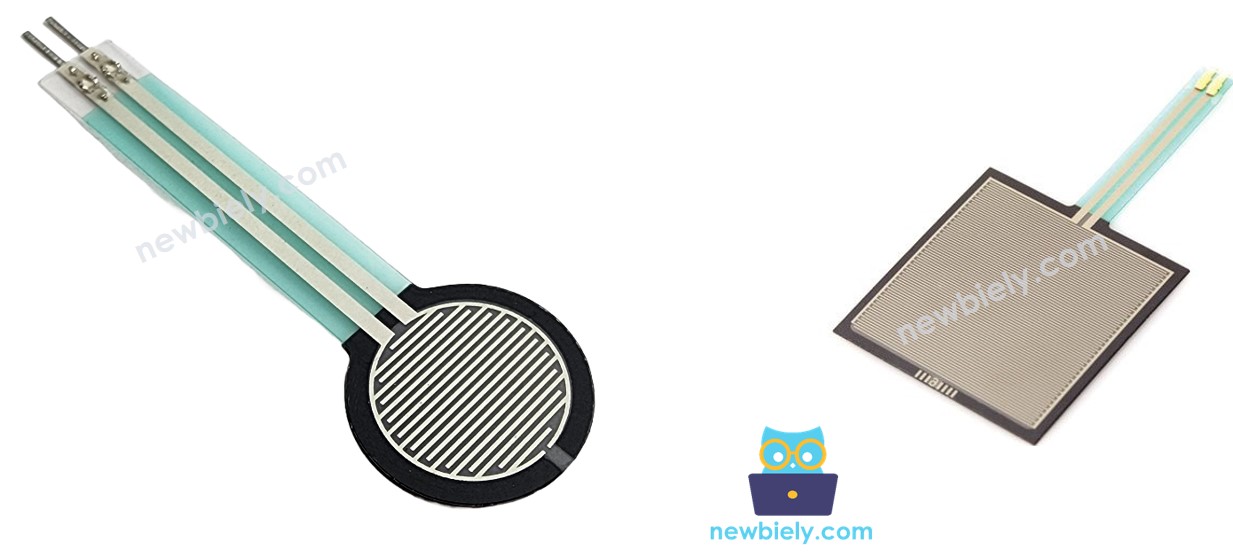

The force sensor, also called a force sensing resistor (FSR), changes its resistance when pressure is applied.
- Affordable and simple to use.
- Great for detecting physical pressure or compression.
- Not suitable for measuring weight in pounds.
You can find force sensors in electronic drums, mobile phones, handheld gaming devices, and many other small electronic gadgets.
Pinout
A force sensor has only two wires. Because it works like a resistor, it doesn't matter which wire goes where. They're both the same.
How It Works
Imagine the force sensor as a special kind of knob that changes its resistance based on how hard you push it. The harder you press, the closer the two ends of the knob get, which means lower resistance.
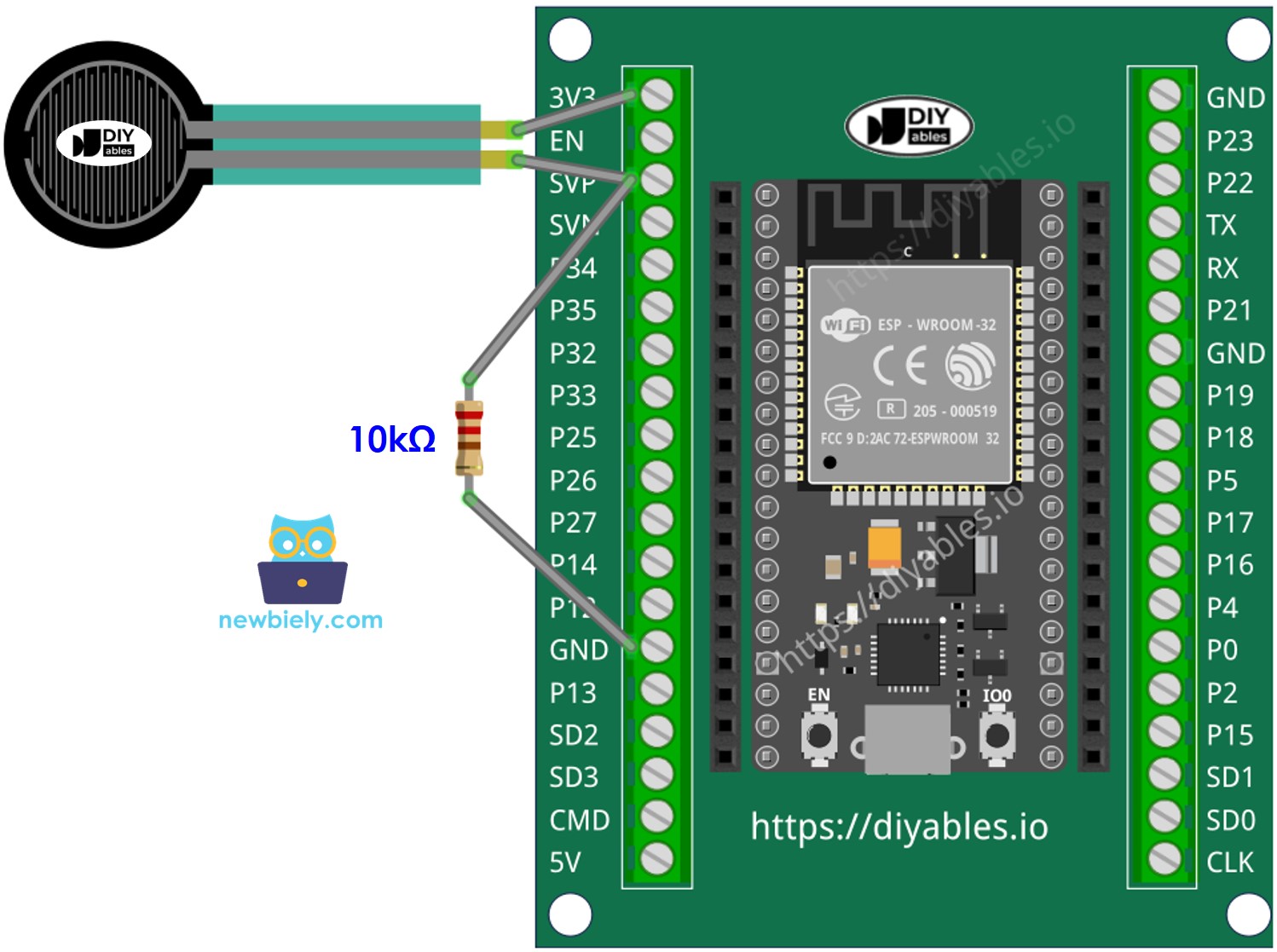
Wiring Diagram
- How to connect ESP32 and force sensor using breadboard
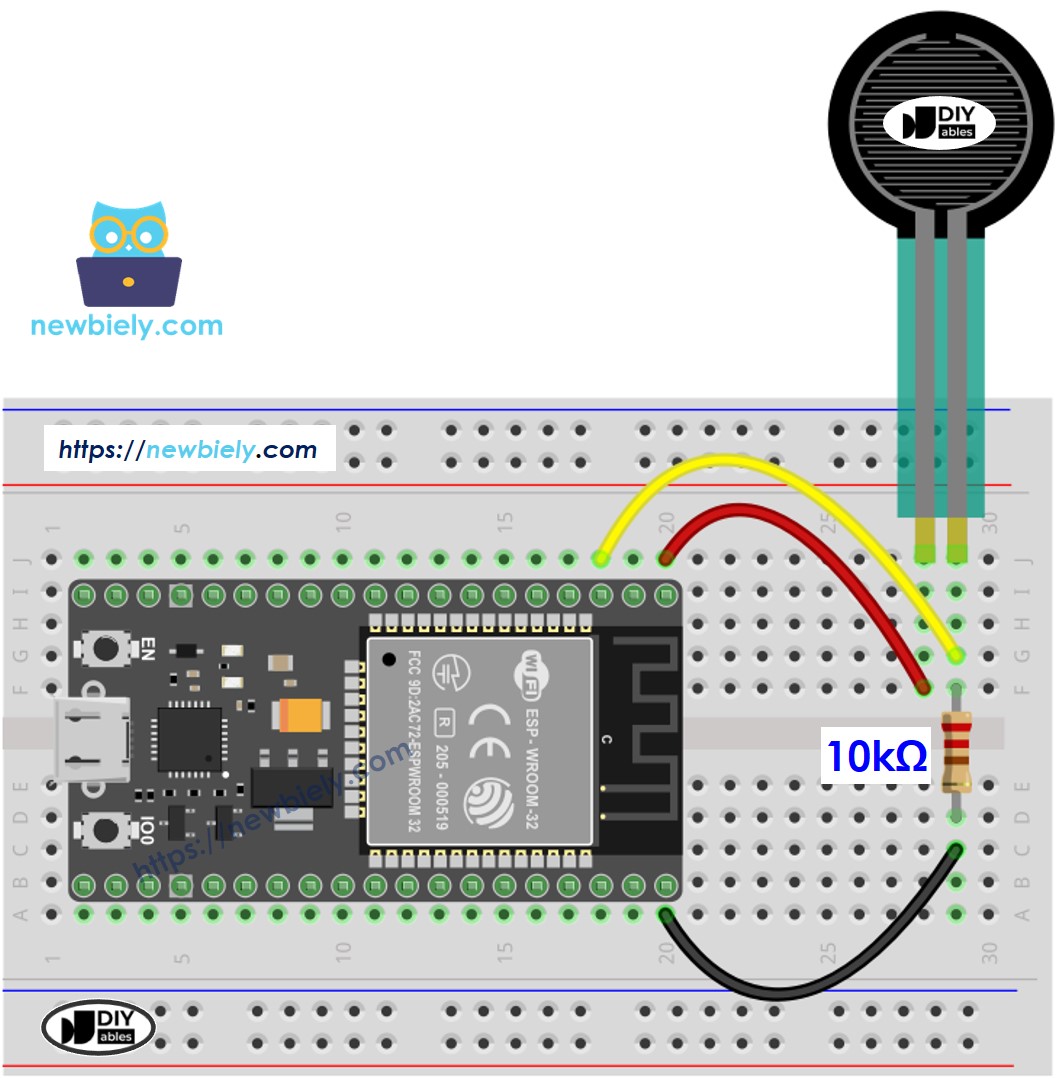
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
- How to connect ESP32 and force sensor using screw terminal block breakout board (powered via USB cable)
ESP32 MicroPython Code for Force Sensor
Detailed Instructions
Here’s instructions on how to set up and run your MicroPython code on the ESP32 using Thonny IDE:
- Make sure Thonny IDE is installed on your computer.
- Confirm that MicroPython firmware is loaded on your ESP32 board.
- If this is your first time using an ESP32 with MicroPython, check out the ESP32 MicroPython Getting Started guide for step-by-step instructions.
- Connect the force sensor to the ESP32 according to the provided diagram.
- Connect the ESP32 board to your computer with a USB cable.
- Open Thonny IDE on your computer.
- In Thonny IDE, go to Tools Options.
- Under the Interpreter tab, choose MicroPython (ESP32) from the dropdown menu.
- Make sure the correct port is selected. Thonny IDE usually detects it automatically, but you might need to select it manually (like COM12 on Windows or /dev/ttyACM0 on Linux).
- Copy the provided MicroPython code and paste it into Thonny's editor.
- Save the code to your ESP32 by:
- Clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
- In the save dialog, choose MicroPython device.
- Name the file main.py.
- Click the green Run button (or press F5) to execute the script.
- Press on the force sensor.
- Check out the message in the Shell at the bottom of Thonny.
Keep in mind that the sensor's values aren't always exactly the same. It's a good idea to adjust the sensor's settings for each specific force level you want to measure.
※ NOTE THAT:
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the adc.read() function to read values from an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) connected to a force sensor. The ESP32's ADC is suitable for projects that do not require high precision. However, if your project needs accurate measurements, keep the following in mind:
- The ESP32 ADC is not perfectly accurate and may require calibration for precise results. Each ESP32 board may vary slightly, so calibration is necessary for each individual board.
- Calibration can be challenging, especially for beginners, and might not always yield the exact results you desire.
For projects requiring high precision, consider using an external ADC (e.g., ADS1115) with the ESP32 or opt for an Arduino, which has a more reliable ADC. If you still wish to calibrate the ESP32 ADC, refer to the ESP32 ADC Calibration Driver.
