Arduino Nano 33 IoT - DHT22
This guide shows you how to use the Arduino Nano 33 IoT to measure the temperature and humidity using a DHT22 sensor, and display the readings on the Serial Monitor. It includes steps for both the DHT22 sensor and module.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of DHT22 Temperature and Humidity Sensor
| DHT22 | |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3 to 5V |
| The humidity range | 0% to 100% |
| The humidity accuracy | ± 2% to 5% |
| The temperature range | -40°C to 80°C |
| The temperature accuracy | ± 0.5°C |
| The reading rate | 0.5Hz (one time per 2 seconds) |
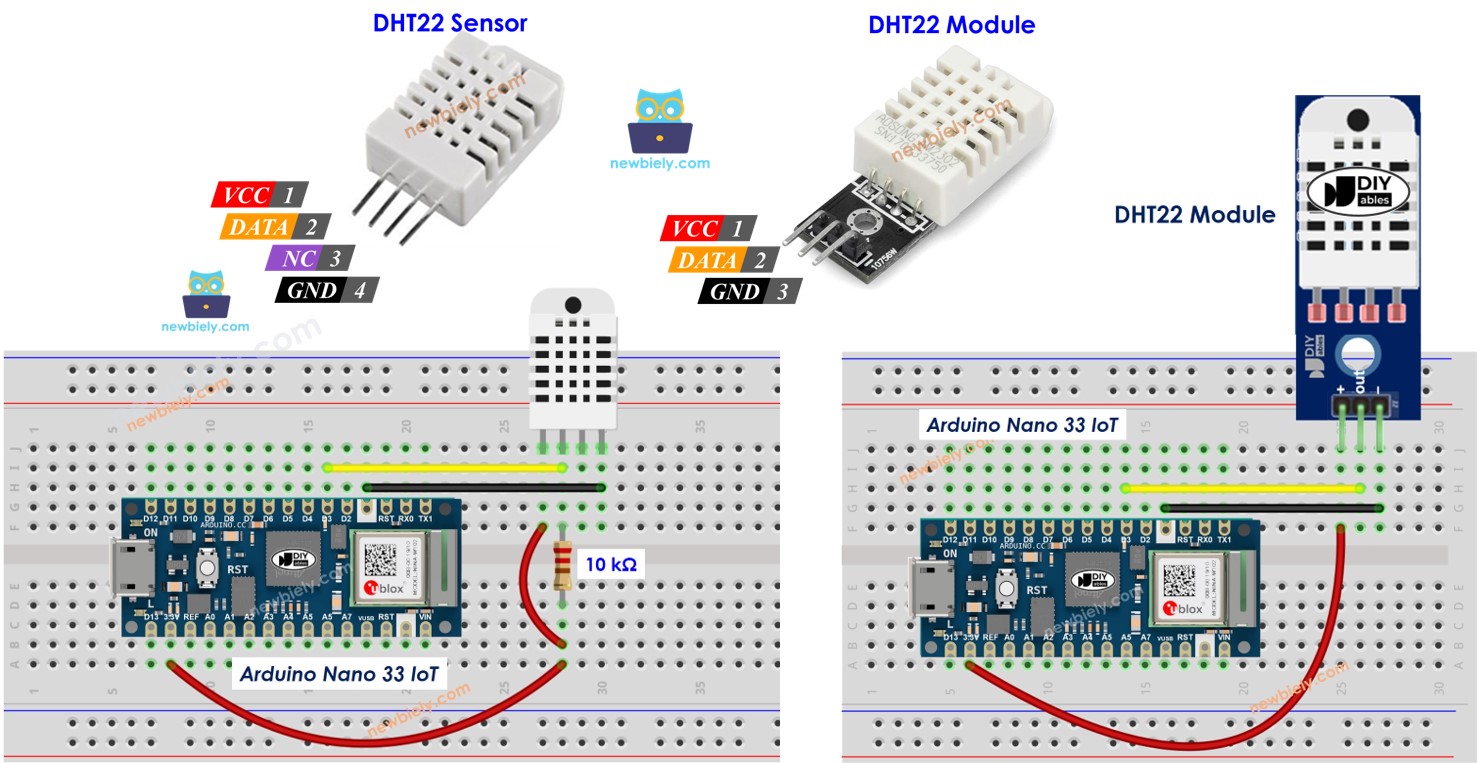
DHT22 Pinout
The DHT22 comes in two versions: one as a raw sensor and the other as a module.
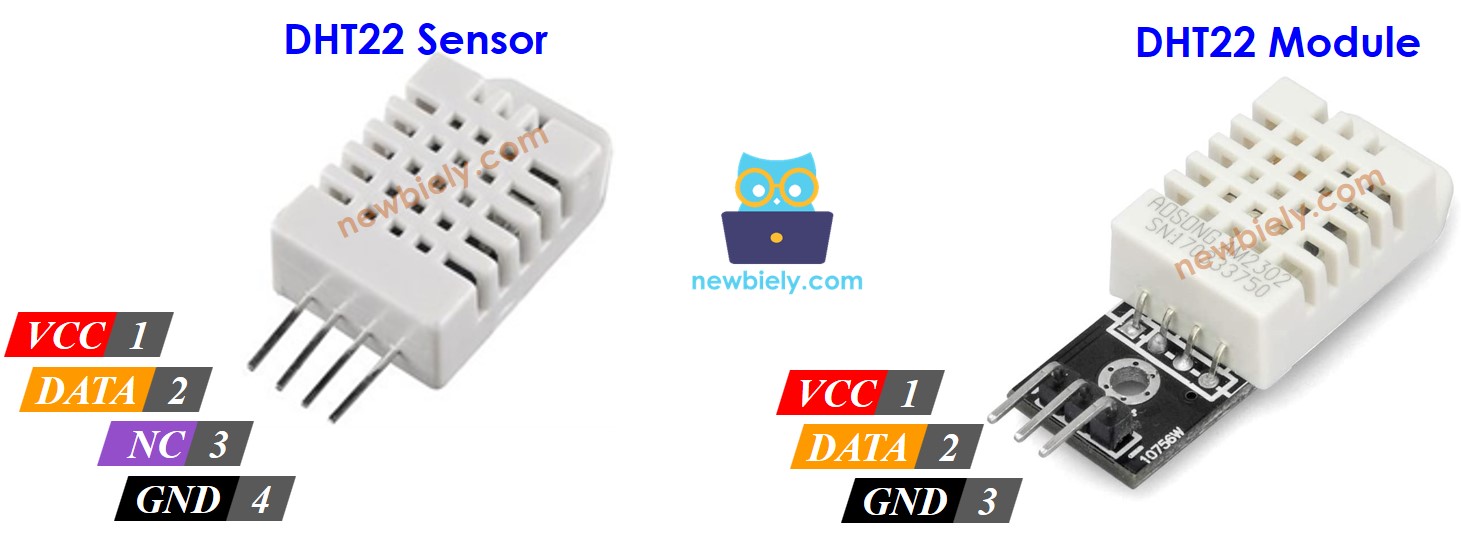
The DHT22 sensor has four pins:
- GND pin: Connect this pin to ground (0V)
- VCC pin: Connect this pin to power (3.3V or 5V)
- DATA pin: This pin lets the sensor talk with the Arduino Nano 33 IoT
- NC pin: Do not connect anything to this pin
We strongly recommend using the DHT22 module. This module has a built-in resistor and only three pins: VCC, GND, and DATA (or alternatively: +, -, and OUT).
Wiring Diagram between DHT22 and Arduino Nano 33 IoT
Wiring the Arduino Nano 33 IoT is the same for both sensors. In its original design, you need a resistor between 5K and 10K ohms to keep the data line high and allow communication between the sensor and the Arduino Nano 33 IoT.
Arduino Nano 33 IoT - DHT22 Sensor Wiring
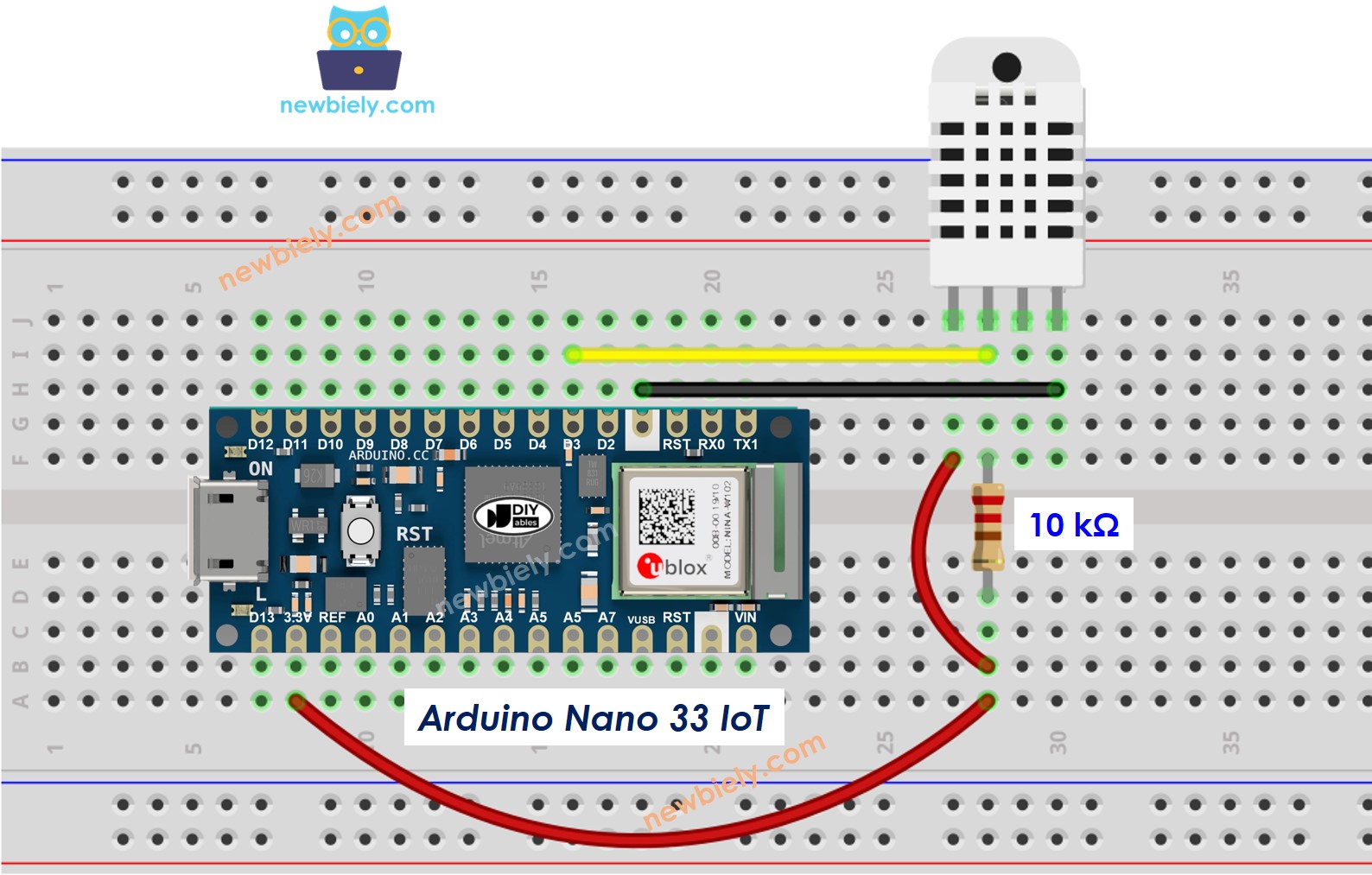
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino Nano 33 IoT - DHT22 Module Wiring
Most DHT22 sensor modules already include a resistor, so you don’t have to add one. This means less wiring and soldering work.
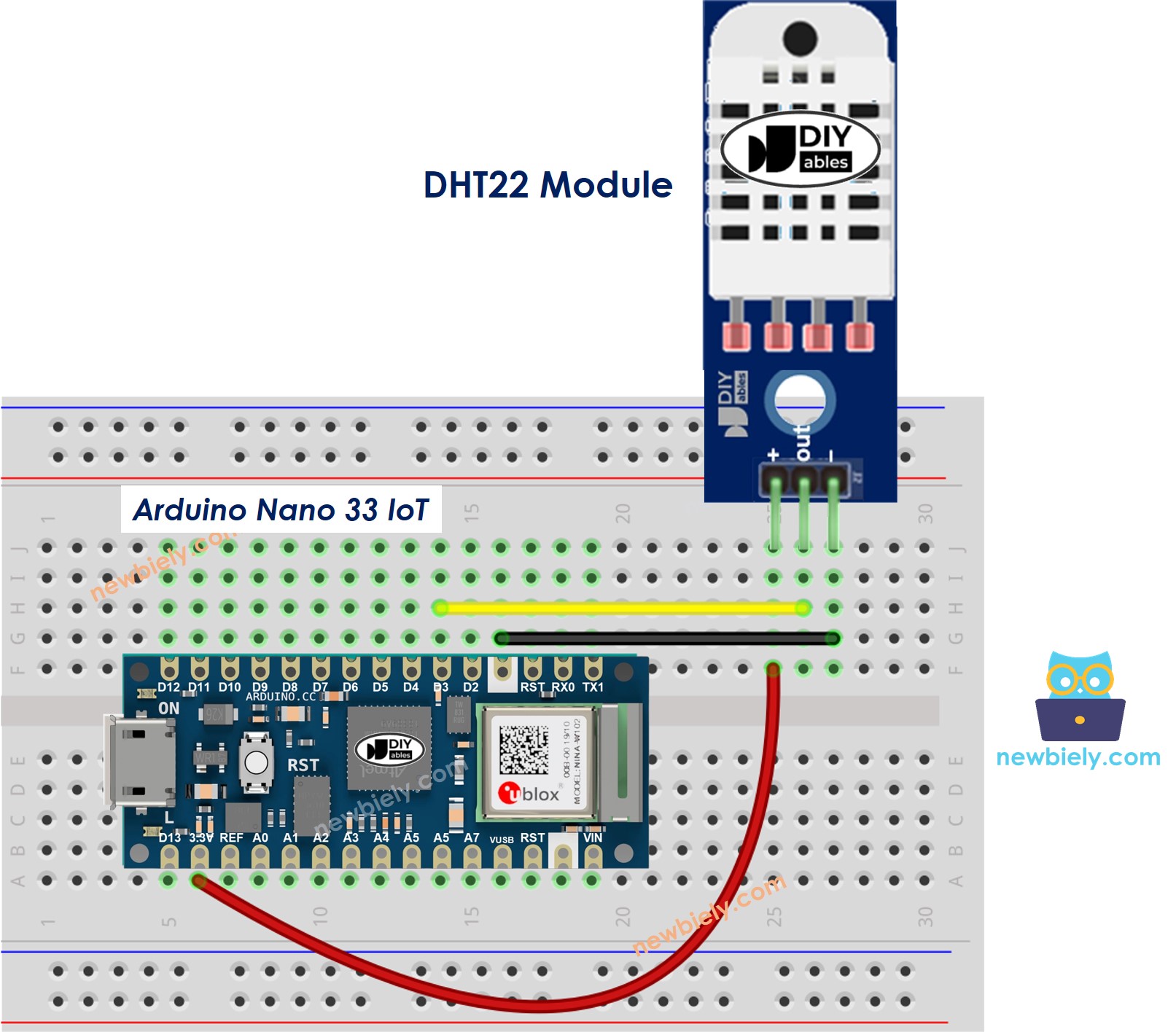
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino Nano 33 IoT Code - DHT22
Detailed Instructions
If you are new to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT, be sure to check out our Getting Started with Arduino Nano 33 IoT tutorial. Then, follow these steps:
- Connect the components to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board as depicted in the diagram.
- Use a USB cable to connect the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board to your computer.
- Launch the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Select the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board and choose its corresponding COM port.
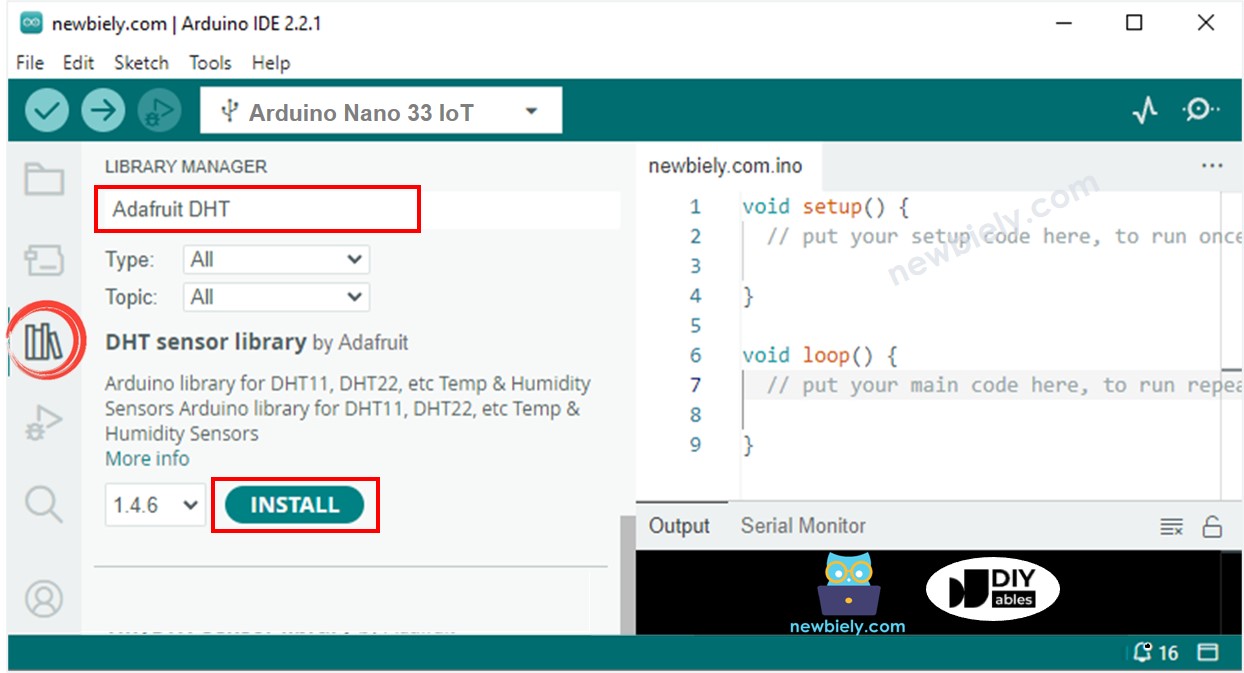
- Open the Library Manager by clicking on the Library Manager icon on the left side of the Arduino software.
- Type DHT in the search box and find the DHT sensor library made by Adafruit.
- Click on the Install button to add the library.
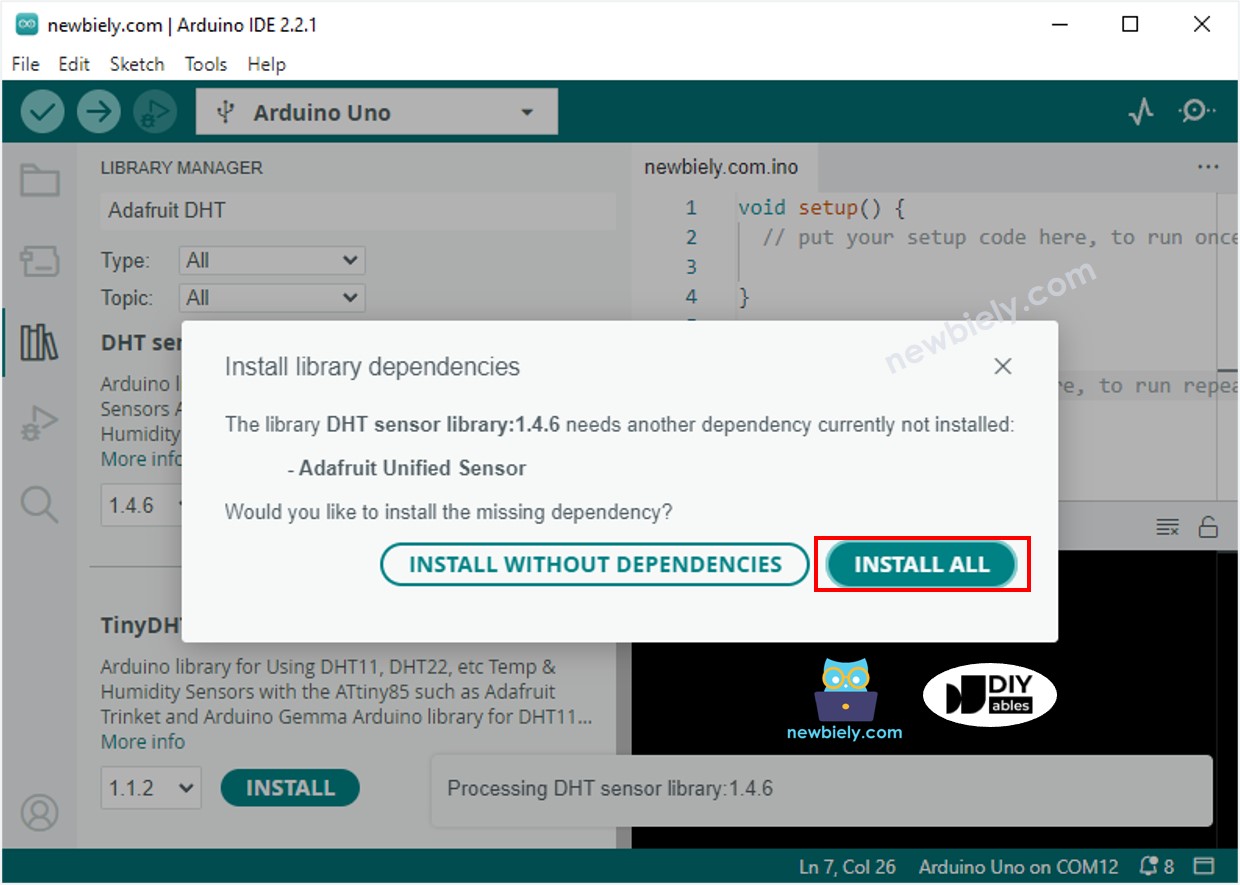
- A window will open asking if you want to install extra software needed by the library.
- To install all the extra software, just click the Install All button.
- Copy one of the code examples above and open it in the Arduino program.
- Compile and send the code to your Arduino Nano 33 IoT board by clicking the Upload button.
- Change the sensor's temperature by making it colder or warmer, for example, by placing it near a hot cup of coffee.
- See the result on the Serial Monitor. It should look like the picture shown below.
