Arduino Nano 33 IoT - Multiple Button
This lesson shows you how to program an Arduino Nano 33 IoT to work with several buttons at once without using the delay() function. The lesson provides code in two different ways.
We are using three buttons as examples. You can easily change it to work with two, four, or even more buttons.
Or you can buy the following kits:
Disclosure: Some of the links provided in this section are Amazon affiliate links. We may receive a commission for any purchases made through these links at no additional cost to you.
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand,
DIYables .
If you are not familiar with the button (its pin layout, how it works, or how to program it), these tutorials will give you more details.
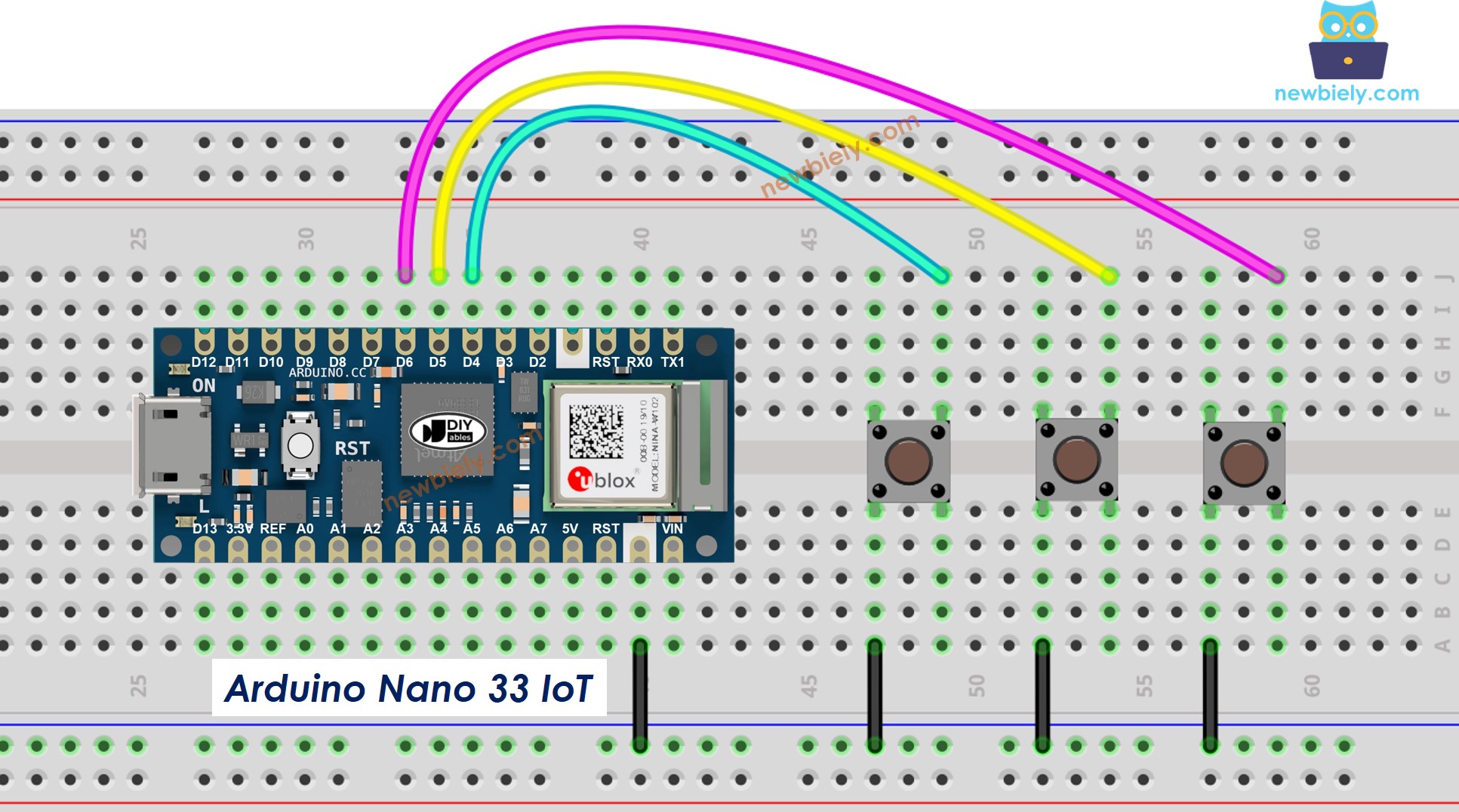
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
※ NOTE THAT:
Please note that the Arduino Nano 33 IoT pins A4 and A5 have built-in pull-up resistors for I2C communication. Although these pins can be used as digital input pins, it is recommended to avoid using them for digital input. If you must use them, do NOT use internal or external pull-down resistors for these pins
When you use many buttons, some situations may become confusing:
For projects that need to clear extra signals when a button is pressed (see this explanation: https://arduinogetstarted.com/faq/why-needs-debounce-for-button)
For projects that need to notice when the button is pressed or released
Fortunately, the ezButton library makes this process easier by taking care of button bounce and events itself. This means you don't have to worry about managing time stamps or extra variables when using the library. Also, using a list of buttons can make your code clearer and shorter.
#include <ezButton.h>
#define BUTTON_PIN_1 4
#define BUTTON_PIN_2 5
#define BUTTON_PIN_3 6
ezButton button1(BUTTON_PIN_1);
ezButton button2(BUTTON_PIN_2);
ezButton button3(BUTTON_PIN_3);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
button1.setDebounceTime(100);
button2.setDebounceTime(100);
button3.setDebounceTime(100);
}
void loop() {
button1.loop();
button2.loop();
button3.loop();
int button1_state = button1.getState();
int button2_state = button2.getState();
int button3_state = button3.getState();
if (button1.isPressed())
Serial.println("The button 1 is pressed");
if (button1.isReleased())
Serial.println("The button 1 is released");
if (button2.isPressed())
Serial.println("The button 2 is pressed");
if (button2.isReleased())
Serial.println("The button 2 is released");
if (button3.isPressed())
Serial.println("The button 3 is pressed");
if (button3.isReleased())
Serial.println("The button 3 is released");
}
If you are new to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT, be sure to check out our Getting Started with Arduino Nano 33 IoT tutorial. Then, follow these steps:
Connect the components to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board as depicted in the diagram.
Use a USB cable to connect the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board to your computer.
Launch the Arduino IDE on your computer.
Select the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board and choose its corresponding COM port.
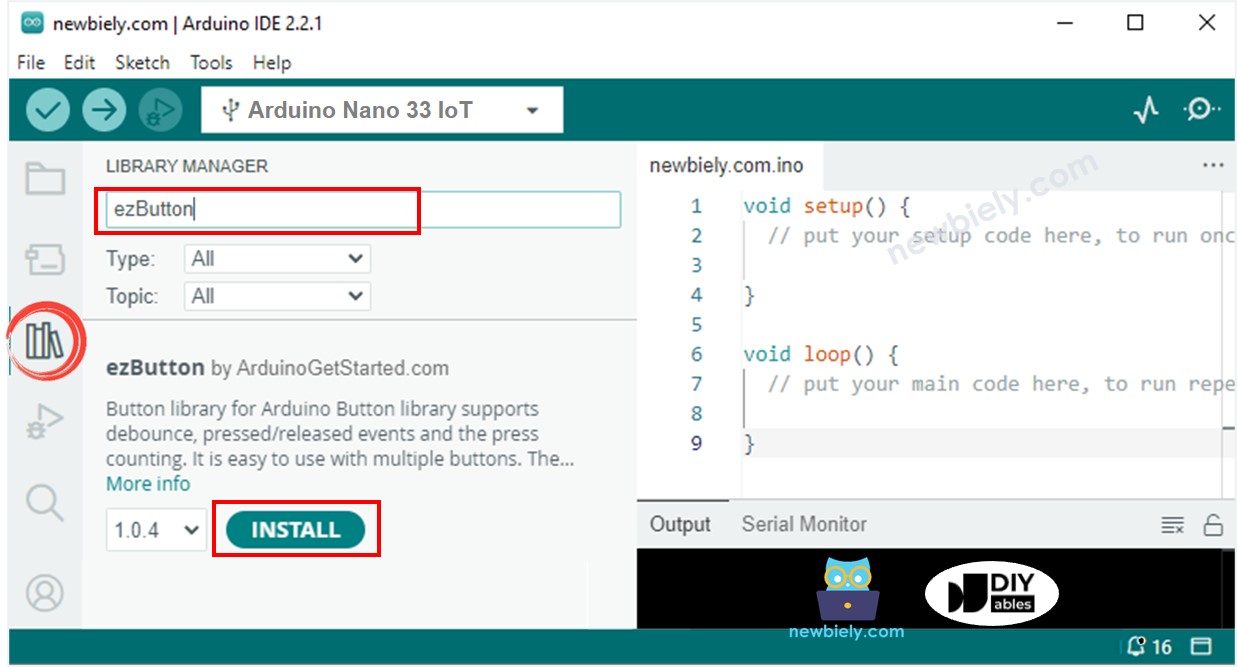
Click on the Libraries icon on the left side of the Arduino IDE.
Search for ezButton and find the button library by ArduinoGetStarted.
Click the Install button to add the ezButton library.
The button 1 is pressed
The button 1 is released
The button 2 is pressed
The button 2 is released
The button 3 is pressed
The button 3 is released
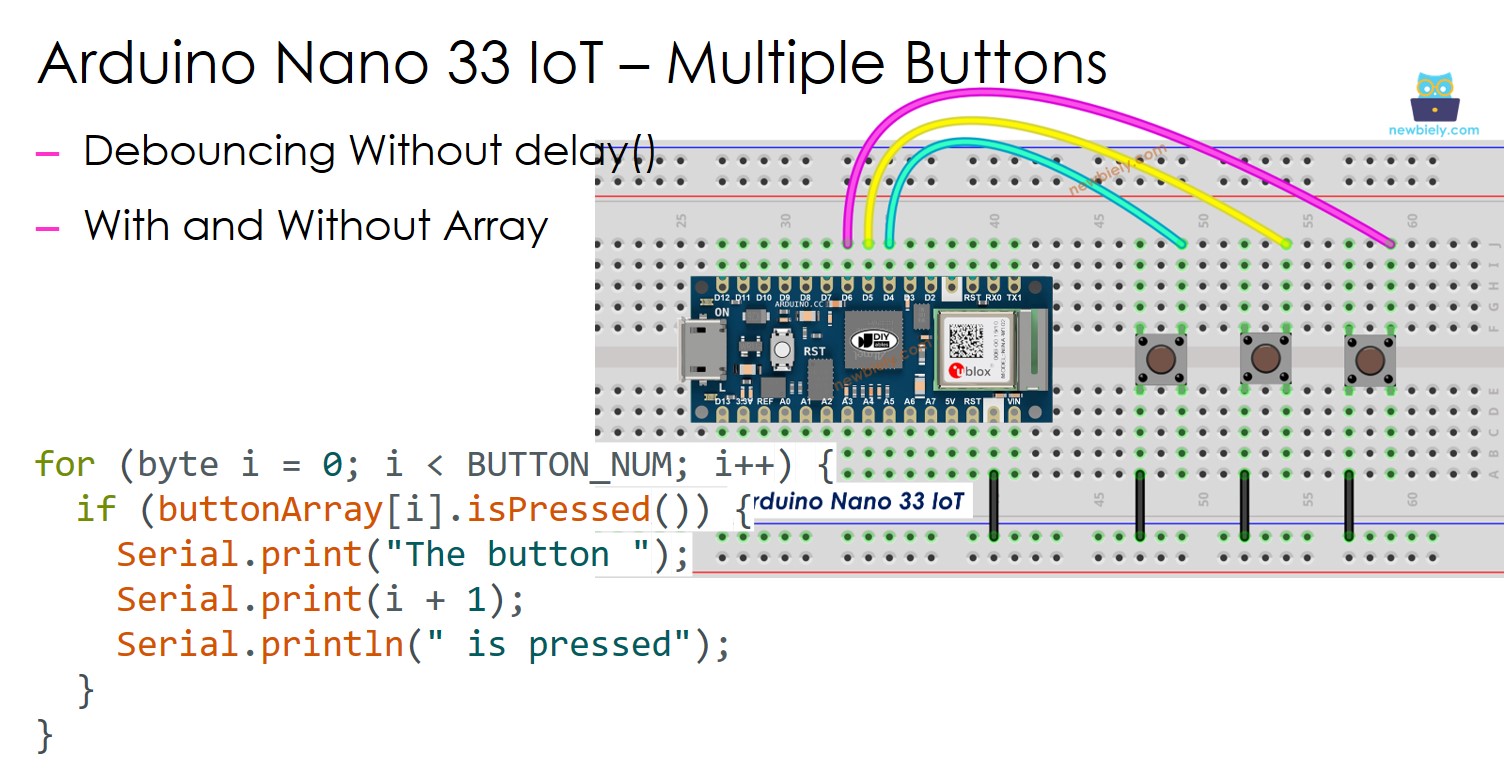
We can make the code better by using a list of buttons. The code below shows how this list is used to work with button objects.
#include <ezButton.h>
#define BUTTON_NUM 3
#define BUTTON_PIN_1 4
#define BUTTON_PIN_2 5
#define BUTTON_PIN_3 6
ezButton buttonArray[] = {
ezButton(BUTTON_PIN_1),
ezButton(BUTTON_PIN_2),
ezButton(BUTTON_PIN_3)
};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
for (byte i = 0; i < BUTTON_NUM; i++) {
buttonArray[i].setDebounceTime(100);
}
}
void loop() {
for (byte i = 0; i < BUTTON_NUM; i++)
buttonArray[i].loop();
for (byte i = 0; i < BUTTON_NUM; i++) {
int button_state = buttonArray[i].getState();
if (buttonArray[i].isPressed()) {
Serial.print("The button ");
Serial.print(i + 1);
Serial.println(" is pressed");
}
if (buttonArray[i].isReleased()) {
Serial.print("The button ");
Serial.print(i + 1);
Serial.println(" is released");
}
}
}