Arduino Nano 33 IoT - Temperature Humidity Sensor - LCD
This guide shows you how to use the Arduino Nano 33 IoT to measure humidity and temperature with DHT11 or DHT22 sensors and display the results on an I2C LCD screen.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of DHT11, DHT22 and LCD
If you're new to using the DHT11, DHT22, LCD, and Arduino Nano 33 IoT, please check out these tutorials:
These tutorials explain how DHT11, DHT22 and LCD work, their pinouts, how to connect them to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT, and how to program Arduino Nano 33 IoT to work with the DHT11, DHT22 and LCD.
Wiring Diagram
Sometimes the Arduino Nano 33 IoT does not give enough power to the LCD display. If you see nothing on the LCD, use an external power source for it. Below are wiring diagrams for different cases. Remember, the DHT22 sensor works with 5V or 3.3V, so you can connect the VCC pin of the DHT22 to either a 3.3V pin or a 5V pin.
Arduino Nano 33 IoT - DHT11 Module LCD I2C Wiring
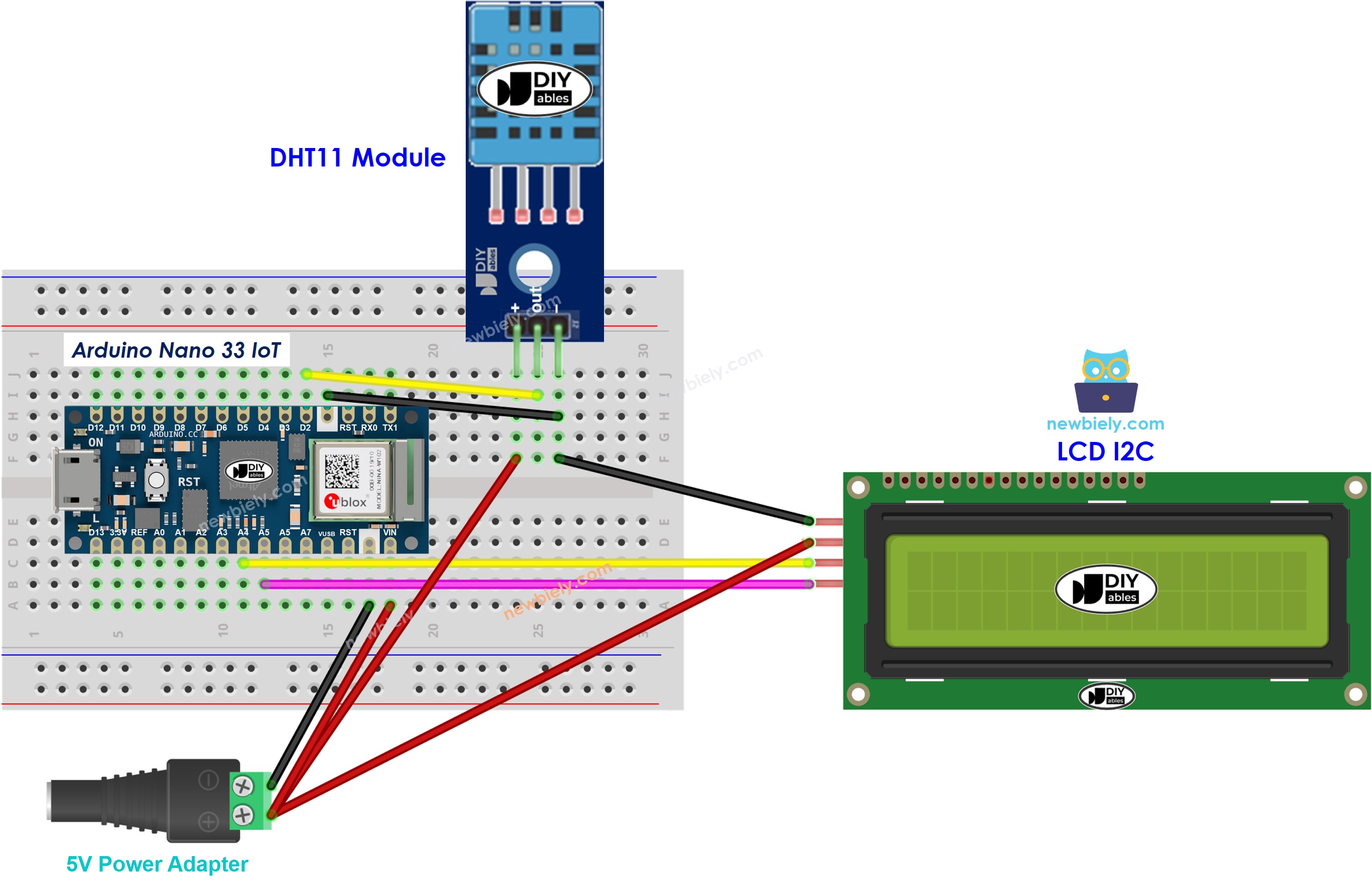
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino Nano 33 IoT - DHT22 Module LCD I2C Wiring
- Wiring plan using a breadboard. Power the Arduino Nano 33 IoT with a USB cable, and use the Arduino board to power the LCD screen.
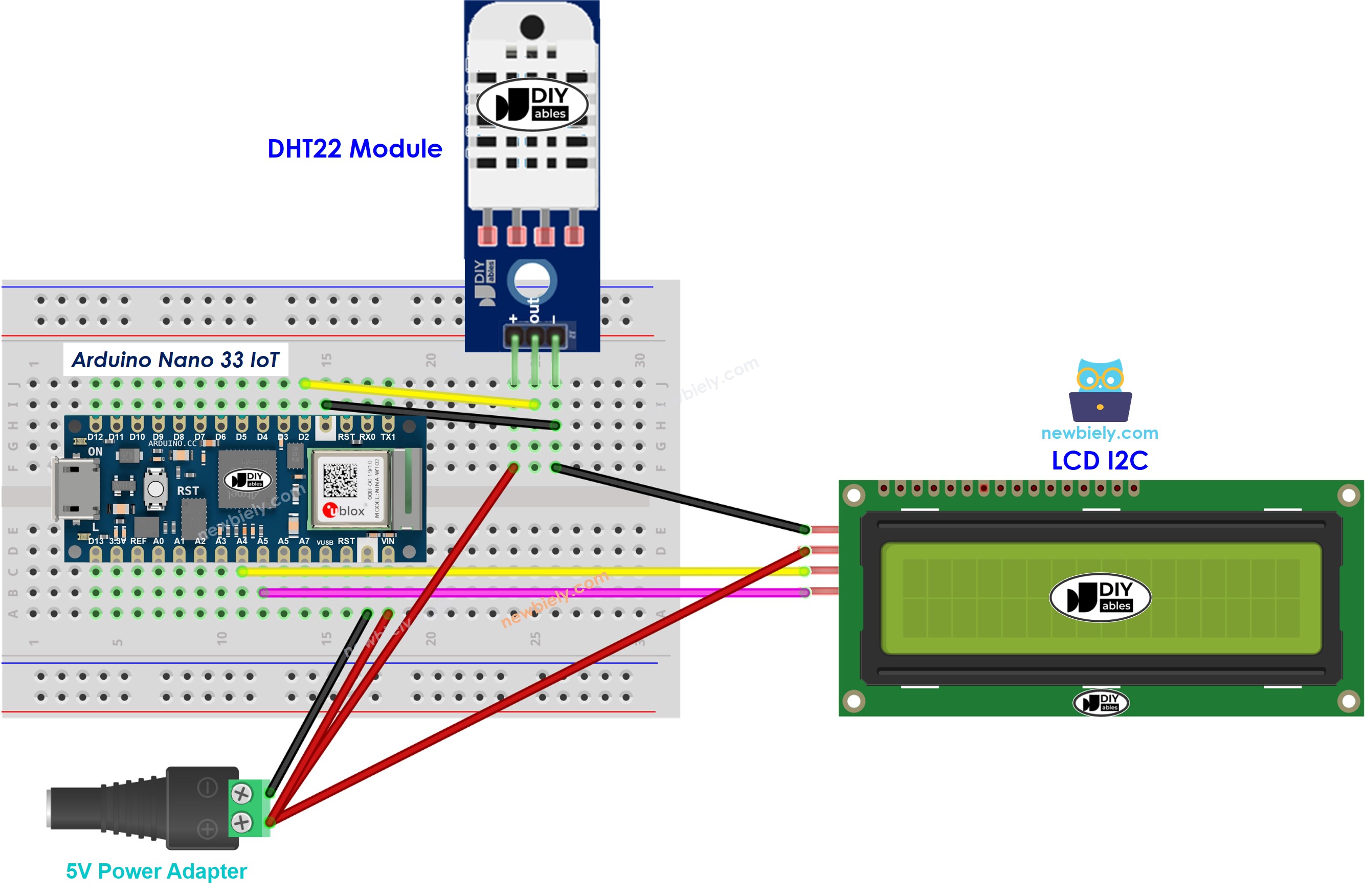
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino Nano 33 IoT Code - DHT11 Sensor - LCD I2C
※ NOTE THAT:
The LCD I2C address might be different for each maker. In our code, we used the address 0x27 as provided by the DIYables company.
Detailed Instructions
If you are new to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT, be sure to check out our Getting Started with Arduino Nano 33 IoT tutorial. Then, follow these steps:
- Connect the components to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board as depicted in the diagram.
- Use a USB cable to connect the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board to your computer.
- Launch the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Select the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board and choose its corresponding COM port.
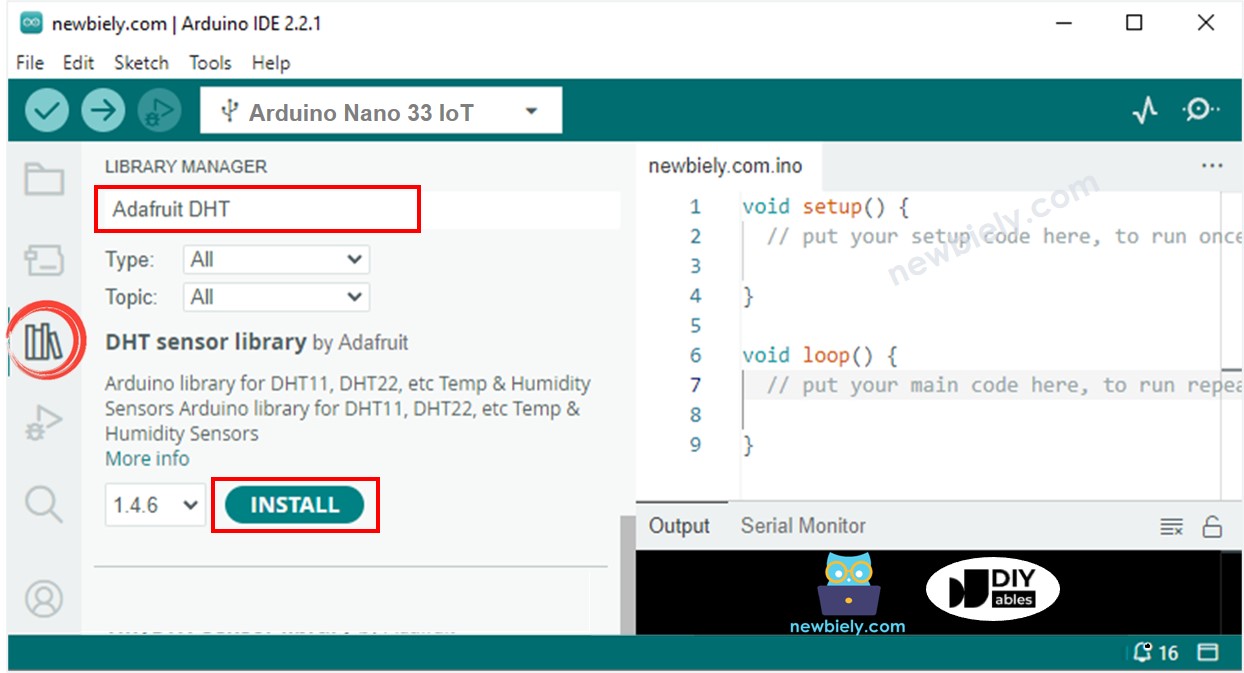
- Click on the Libraries icon on the left side of the Arduino IDE.
- Type DHT into the search box and find the DHT sensor library by Adafruit.
- Click the Install button to add the library.
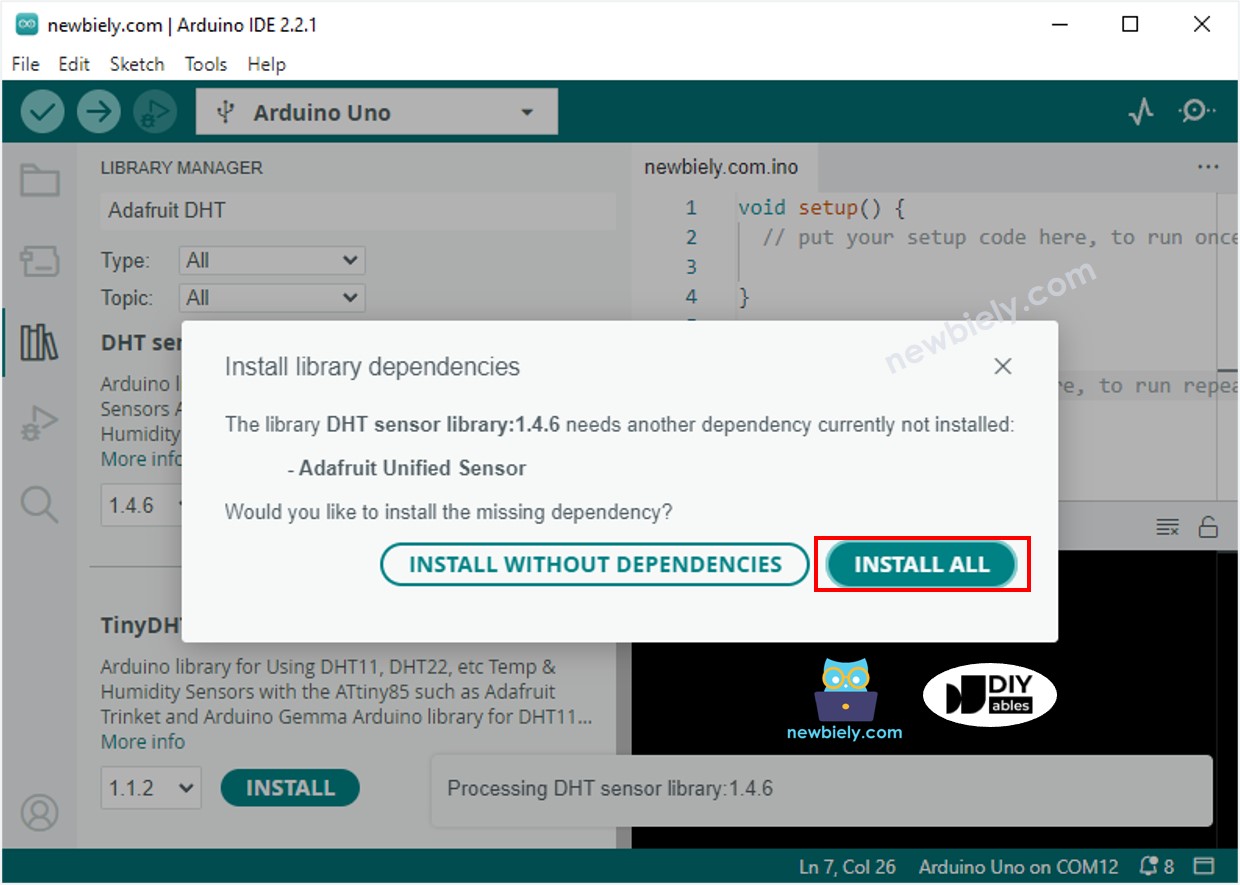
- A window appears asking if you want to add the necessary parts of the library. Click the Install All button to add everything you need.
- Type LiquidCrystal I2C in the search box, then look for the LiquidCrystal_I2C library by Frank de Brabander.
- Click the Install button to add the LiquidCrystal_I2C library.
- Copy the code from above and paste it into the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to compile the code and send it to your Arduino Nano 33 IoT board.
- Change the sensor's temperature by making it colder or hotter. For example, place the sensor near a hot cup of coffee.
- Check the results on the LCD screen.
If your LCD screen stays blank, check this guide for help: Troubleshooting on LCD I2C
Arduino Nano 33 IoT Code - DHT22 Sensor - LCD I2C
The two pieces of code above are the same except for one line.
