Arduino Nano 33 IoT - Obstacle Sensor
This guide shows you how to use the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board with an infrared sensor to detect obstacles.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
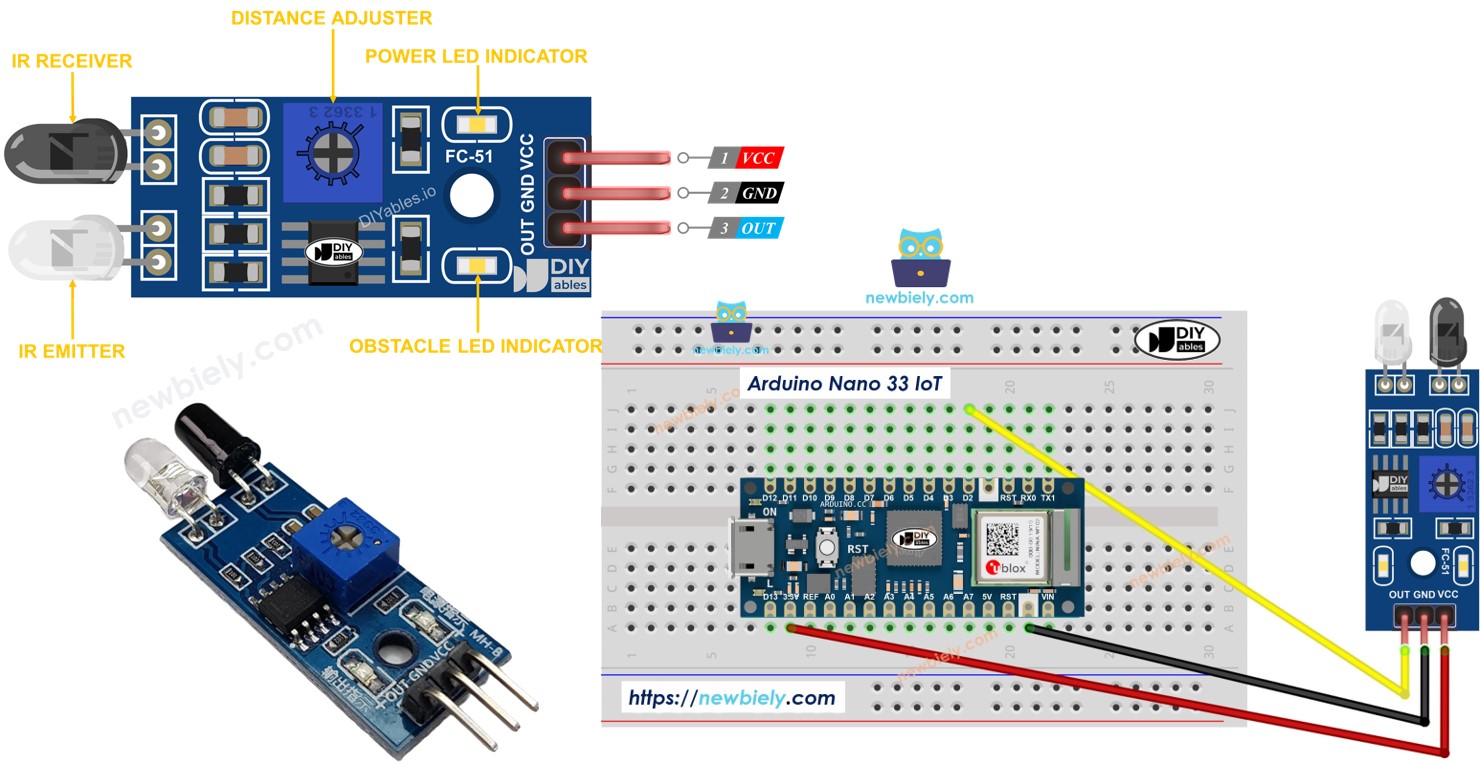
Overview of IR Obstacle Avoidance Sensor
The infrared obstacle sensor checks if anything is in front of it using infrared light. It can sense objects from 2cm to 30cm away, and you can adjust this range with the built-in knob.
Pinout
An infrared sensor used to avoid obstacles has three pins:
- GND Pin: Connect this pin to the ground (0 volts).
- VCC Pin: Connect this pin to the power supply (5V or 3.3V).
- OUT Pin: This is an output pin. It shows LOW when there is an obstacle and HIGH when there is no obstacle. Connect this pin to an input pin on the Arduino Nano 33 IoT.
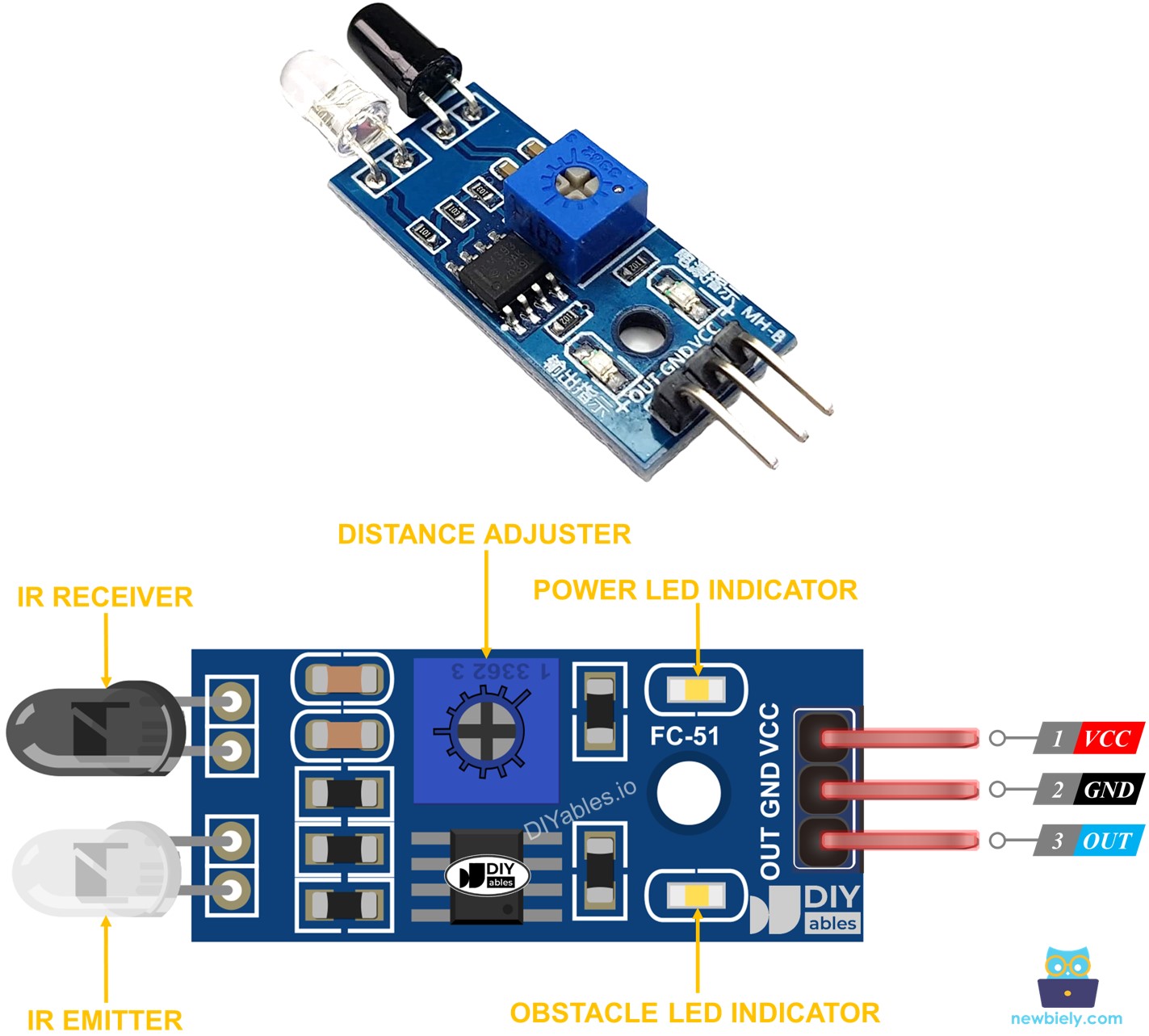
How It Works
An infrared obstacle sensor module has an IR transmitter and an IR receiver. The IR transmitter sends out an infrared signal while the IR receiver looks for the signal that bounces back. If an object is present, the OUT pin shows it.
- If something is blocking the sensor, its OUT pin shows LOW.
- If nothing is blocking the sensor, its OUT pin shows HIGH.
※ NOTE THAT:
During delivery, the sensor might get bent, which can make it work incorrectly. If the sensor is not working well, adjust the IR sender and receiver to make sure they are straight and face the same way.
Wiring Diagram
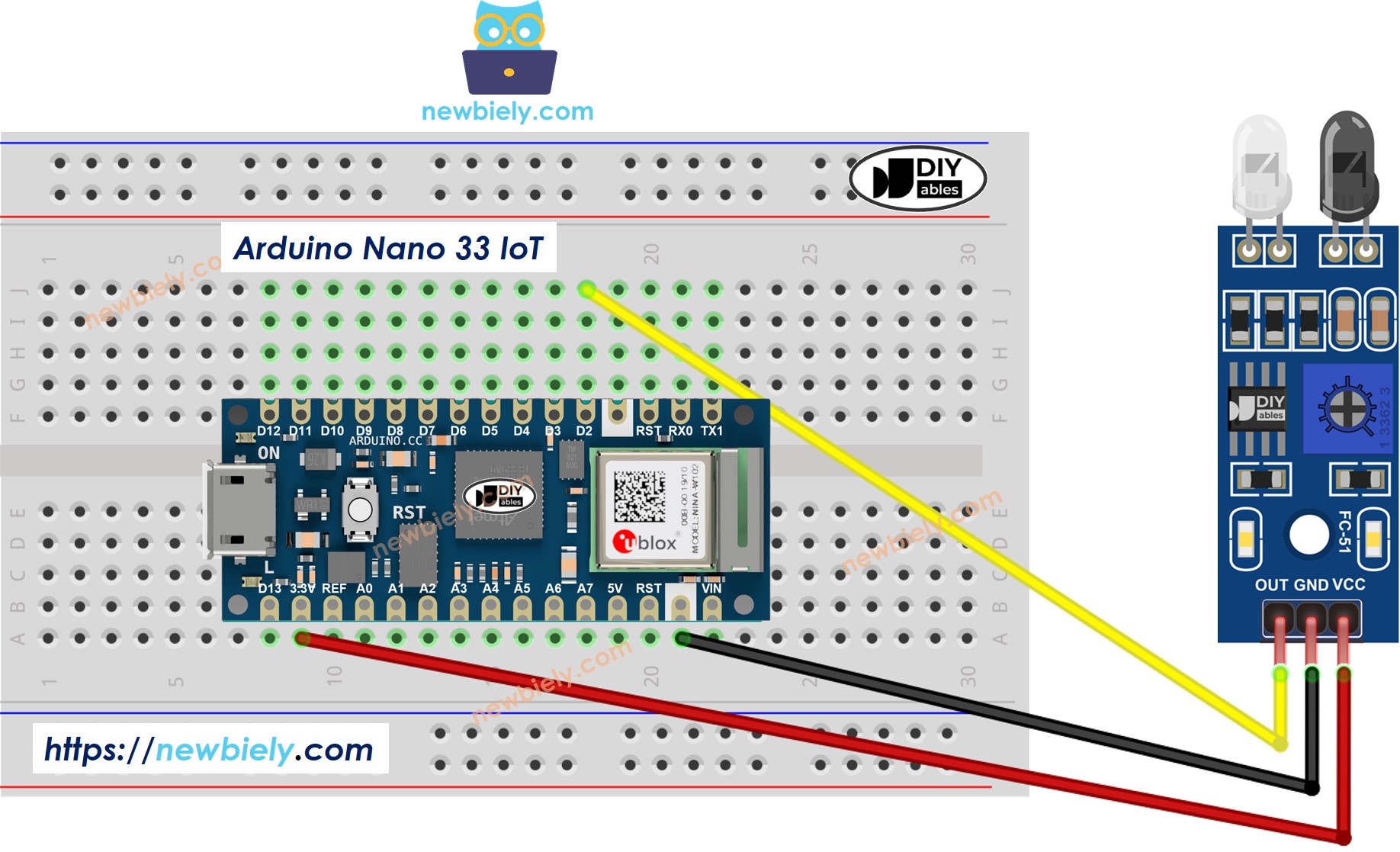
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
※ NOTE THAT:
Please note that the Arduino Nano 33 IoT pins A4 and A5 have built-in pull-up resistors for I2C communication. Although these pins can be used as digital input pins, it is recommended to avoid using them for digital input. If you must use them, do NOT use internal or external pull-down resistors for these pins
How To Program For IR Obstacle Avoidance Sensor
- This code sets up an Arduino Nano 33 IoT pin as a digital input using the [pinMode()] function. For example, it can change pin D2 into an input pin.
- It checks the Arduino Nano 33 IoT pin to see if it is on or off using the digitalRead() function.
Arduino Nano 33 IoT Code
There are two ways to create an app that helps avoid obstacles:
- Take action whether the obstacle is there or not.
- Take action when the obstacle is seen or when it goes away.
Arduino Nano 33 IoT code for checking if the obstacle is present
Detailed Instructions
If you are new to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT, be sure to check out our Getting Started with Arduino Nano 33 IoT tutorial. Then, follow these steps:
- Connect the components to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board as depicted in the diagram.
- Use a USB cable to connect the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board to your computer.
- Launch the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Select the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board and choose its corresponding COM port.
- Copy the code above and paste it into the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to compile and send the code to your Arduino Nano 33 IoT board.
- Put an object in front of the sensor for a short time, and then take it away.
- Open the Serial Monitor to see the result. It should look like the picture below.
Arduino Nano 33 IoT code for detecting obstacle
Detailed Instructions
- Copy the code above and paste it into the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to compile and send the code to the Arduino Nano 33 IoT board.
- Put an object in front of the sensor for a few seconds, then remove it.
- Look at the Serial Monitor to see the result. It should look like the image below.
