Raspberry Pi - Button - LED
This tutorial instructs you how to use the Raspberry Pi and button to control the LED. We will learn two different applications:
Application 1 - The LED state is synchronized with the button state. In detail:
Application 2 - The LED state is toggled each time the button is pressed. More specifically:
If Raspberry Pi detects that the button has been pressed (changing from a HIGH state to a LOW state), it will turn ON the LED if it's currently OFF, or turn OFF the LED if it's currently ON.
Releasing the button does not affect to the LED state.
In the Application 2, We need to debounce the button to make sure it works properly. We'll figure out why it's important by comparing how the LED behaves when we use the Raspberry Pi code with and without debouncing the button.
Or you can buy the following kits:
Disclosure: Some of the links provided in this section are Amazon affiliate links. We may receive a commission for any purchases made through these links at no additional cost to you.
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand,
DIYables .
Buy Note: Use the LED Module for easier wiring. It includes an integrated resistor.
If you are unfamiliar with LED and button (including pinout, operation, and programming), the following tutorials can help:
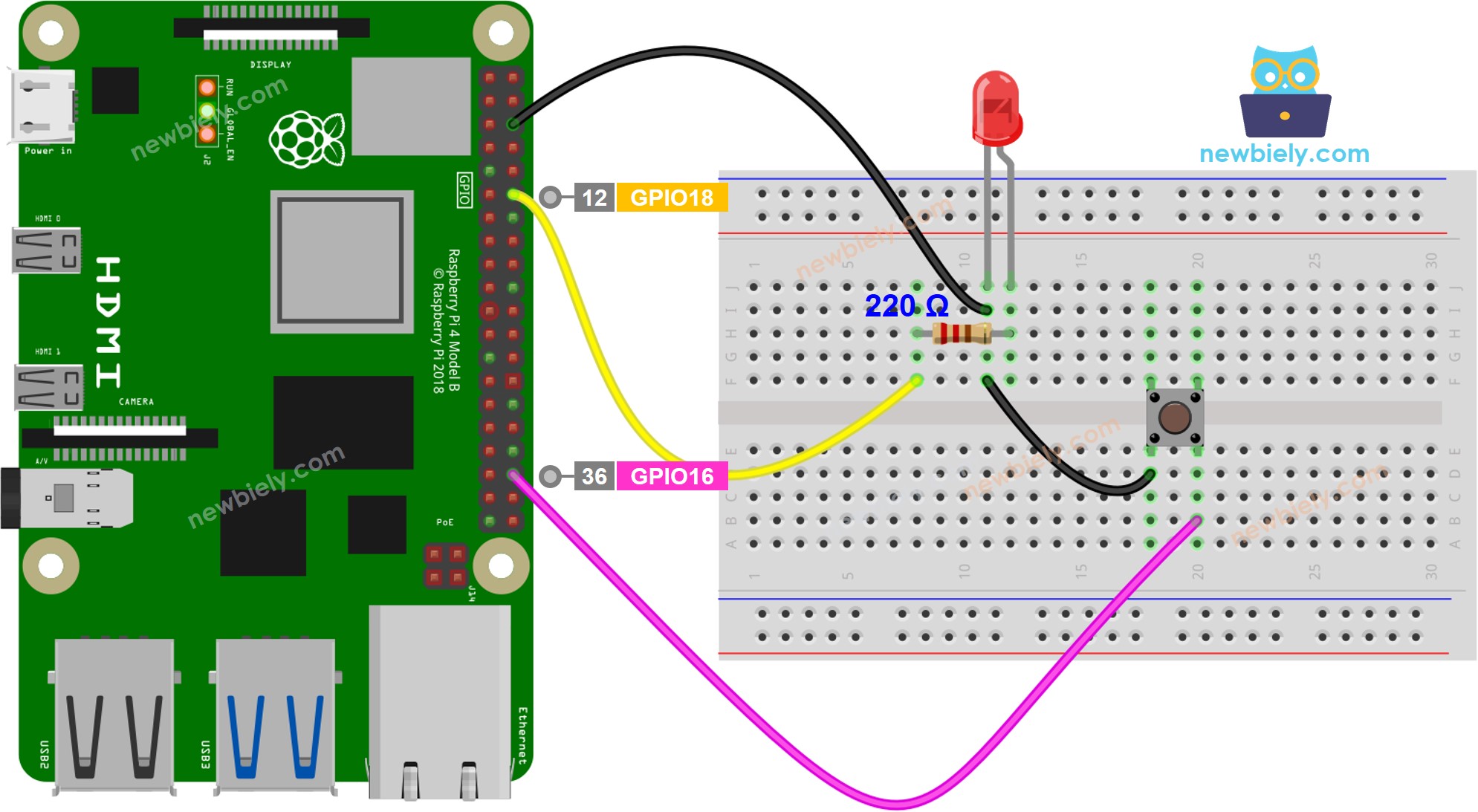
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
To simplify and organize your wiring setup, we recommend using a Screw Terminal Block Shield for Raspberry Pi. This shield ensures more secure and manageable connections, as shown below:
Make sure you have Raspbian or any other Raspberry Pi compatible operating system installed on your Pi.
Make sure your Raspberry Pi is connected to the same local network as your PC.
Make sure your Raspberry Pi is connected to the internet if you need to install some libraries.
Make sure you have the RPi.GPIO library installed. If not, install it using the following command:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python3-rpi.gpio
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
BUTTON_PIN = 16
LED_PIN = 18
button_state = 0
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(LED_PIN, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(BUTTON_PIN, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
try:
while True:
button_state = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN)
if button_state == GPIO.LOW:
GPIO.output(LED_PIN, GPIO.HIGH)
else:
GPIO.output(LED_PIN, GPIO.LOW)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
GPIO.cleanup()
The script runs in an infinite loop continuously until you press Ctrl + C in the terminal.
Check out the line-by-line explanation contained in the comments of the source code!
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
BUTTON_PIN = 16
LED_PIN = 18
led_state = GPIO.LOW
prev_button_state = GPIO.LOW
button_state = GPIO.LOW
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(LED_PIN, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(BUTTON_PIN, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
try:
while True:
prev_button_state = button_state
button_state = GPIO.input(BUTTON_PIN)
if prev_button_state == GPIO.HIGH and button_state == GPIO.LOW:
time.sleep(0.1)
print("The button is pressed")
if led_state == GPIO.LOW:
led_state = GPIO.HIGH
else:
led_state = GPIO.LOW
GPIO.output(LED_PIN, led_state)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
GPIO.cleanup()
python3 button_toggle_led.py
Check out the line-by-line explanation contained in the comments of the source code!