Raspberry Pi - RFID
This tutorial instructs you how to use RFID/NFC with Raspberry Pi. The RFID/NFC system consists of two components: a reader and a tag. Two of the most popular RFID/NFC readers are the RC522 and PN532. This tutorial will uses the RC522 RFID/NFC reader, which is cheap and easy to use.
The RC522 RFID/NFC reader can:
- Obtains the UID of an RFID/NFC tag
- Changes the UID of an RFID/NFC tag (only if the tag supports this)
- Stores data onto an RFID/NFC tag
- Retrieves data from an RFID/NFC tag
This tutorial focuses on:
- How to connect RC522 module to Raspberry Pi
- How to program Raspberry Pi to communicate with RC522 module to read UID of RFID tag.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of RFID-RC522 Module
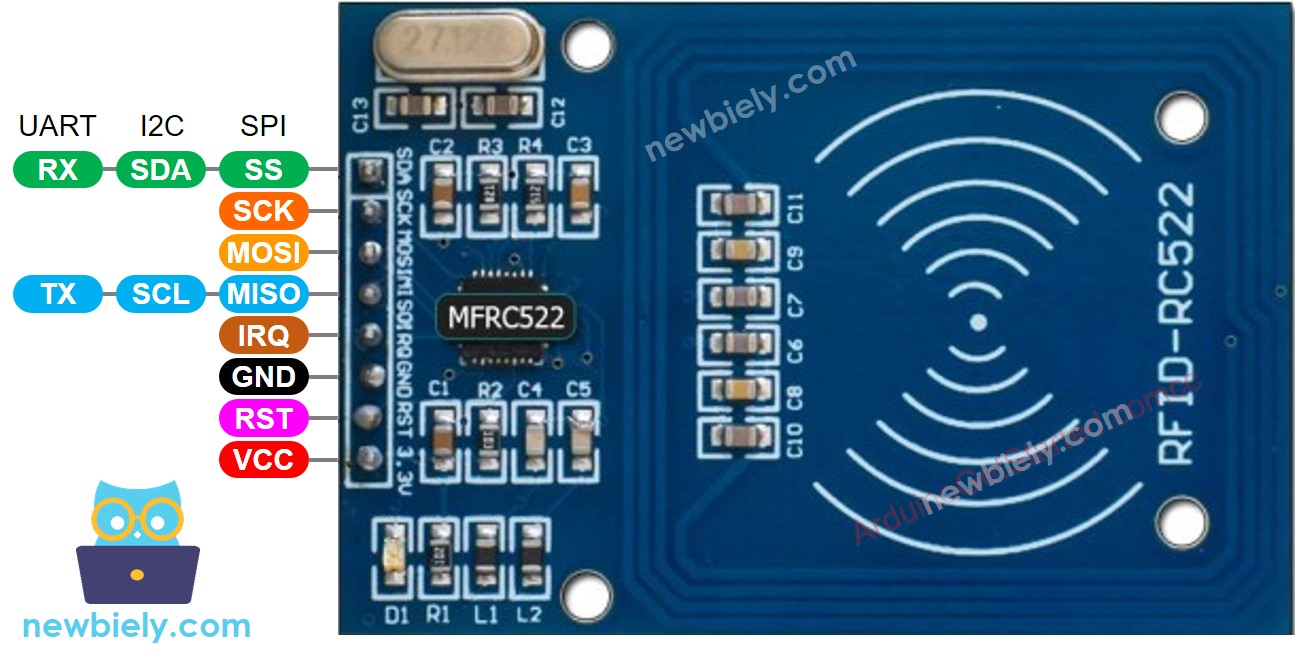
RFID-RC522 Module Pinout
The RFID-RC522 has 8 pins, some of which are common pins and the others are shared among three communication modes: SPI, I2C, and UART. Only one communication mode can be used at a time. The pins are:
- GND pin: This needs to be connected to GND (0V).
- VCC pin: This needs to be connected to VCC (3.3).
- RST pin: This is a pin for reset and power-down. When this pin goes low, hard power-down is enabled. On the rising edge, the module is reset.
- IRQ pin: This is an interrupt pin that can alert the microcontroller when an RFID tag comes into its vicinity.
- MISO/SCL/TX pin: This acts as MISO when SPI interface is enabled, acts as SCL when I2C interface is enabled and acts as TX when UART interface is enabled.
- MOSI pin: This acts as MOSI when SPI interface is enabled.
- SCK pin: This acts as SCK when SPI interface is enabled.
- SS/SDA/RX pin: This acts as SS when SPI interface is enabled, acts as SDA when I2C interface is enabled and acts as RX when UART interface is enabled.

※ NOTE THAT:
- The pins of the module may be arranged differently depending on the manufacturer. It is important to use the labels printed on the module, as seen in the image above from DIYables.
- Do not make the mistake of connecting the VCC pin to the 5V pin, as this could damage the module.
- The MFRC522 library only supports SPI mode, so this tutorial will focus on SPI communication.
How RFID/NFC Works
RFID/NFC consists of two components: reader and tag:
- The reader is made up of a radio frequency module and an antenna which produces a high frequency electromagnetic field.
- The tag is generally a passive device, not requiring a power source. It has a microchip that stores and processes information, as well as an antenna to send and receive signals. The tag is used to store the information including UID (Unique ID) and data.
The tag must be close to the reader in order to read the information it contains. The process of reading is as follows:
- The reader generates an electromagnetic field that causes electrons to flow through the antenna of the tag, powering the chip.
- The chip inside the tag then responds by sending the requested information back to the reader in the form of a radio signal.
- The reader detects the signal and converts it into data.
- Raspberry Pi reads the data from the reader.
Wiring Diagram between RFID-RC522 Module and Raspberry Pi
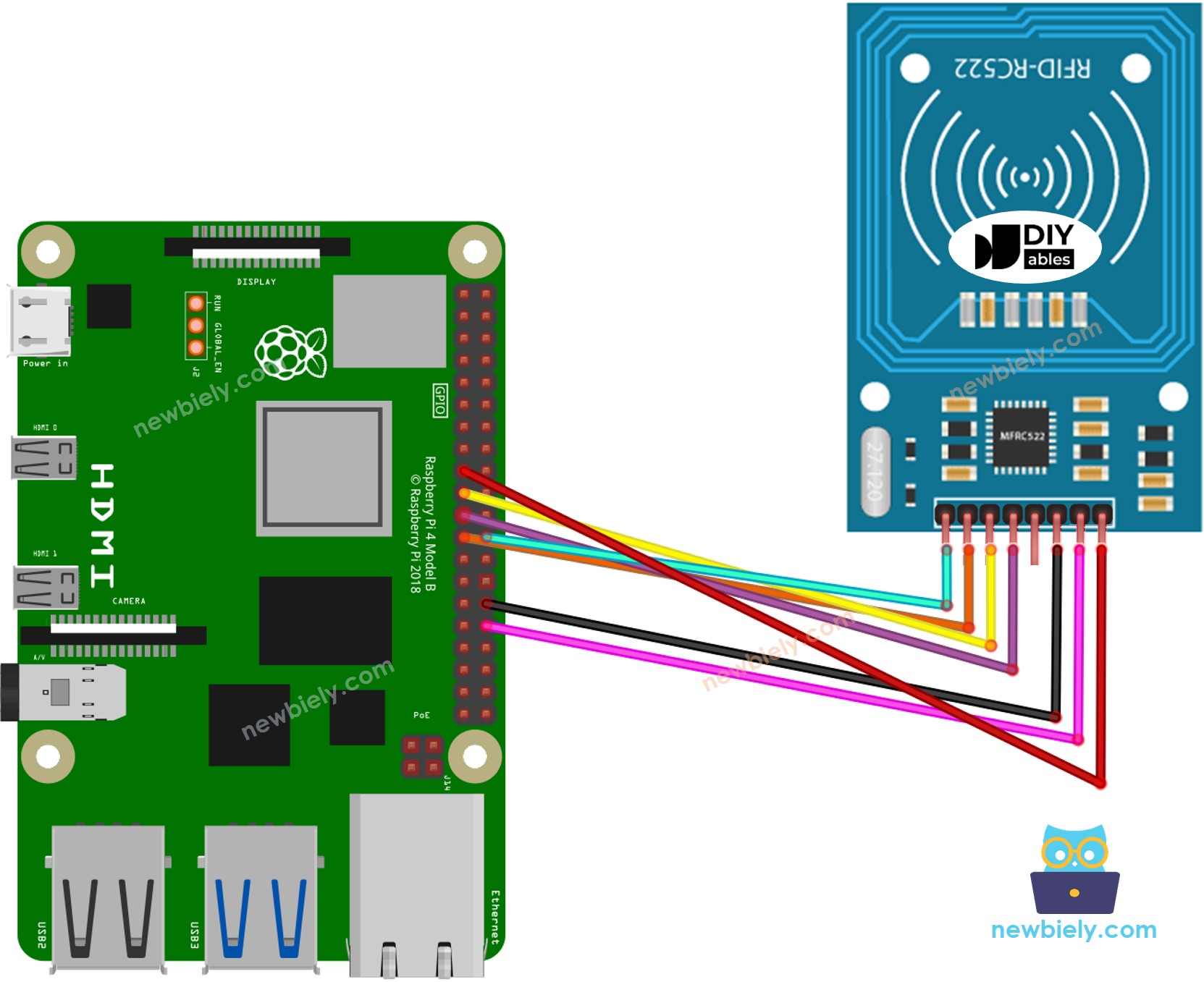
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
To simplify and organize your wiring setup, we recommend using a Screw Terminal Block Shield for Raspberry Pi. This shield ensures more secure and manageable connections, as shown below:
Wiring table of RFID/NFC RC522 Module and Raspberry Pi
| RC522 RFID Reader | Raspberry Pi |
|---|---|
| SS | Pin 24 (GPIO8) |
| SCK | Pin 23 (GPIO11) |
| MOSI | Pin 19 (GPIO10) |
| MISO | Pin 21 (GPIO9) |
| IRQ | Not connected (can be left unconnected) |
| GND | Any GND Pin |
| RST | Pin 31 (GPIO12) |
| VCC | Pin 1 or Pin 16 (3.3V) |
Raspberry Pi RFID/NFC Code
Detailed Instructions
- Make sure you have Raspbian or any other Raspberry Pi compatible operating system installed on your Pi.
- Make sure your Raspberry Pi is connected to the same local network as your PC.
- Make sure your Raspberry Pi is connected to the internet if you need to install some libraries.
- If this is the first time you use Raspberry Pi, See how to set up the Raspberry Pi
- Connect your PC to the Raspberry Pi via SSH using the built-in SSH client on Linux and macOS or PuTTY on Windows. See to how connect your PC to Raspberry Pi via SSH.
- Make sure you have the RPi.GPIO library installed. If not, install it using the following command:
- Enable the SPI interface on Raspberry Pi by following the instruction on Raspberry Pi - how to enable SPI inteface
- Make sure you have the spidev library installed. If not, install it using the following command:
- Make sure you have the mfrc522 library installed. If not, install it using the following command:
- Create a Python script file rc522_rfid.py and add the following code:
- Save the file and run the Python script by executing the following command in the terminal:
- Tap various RFID/NFC tags to the RFID-RC522 module.
- Check the UID on the Serial Monitor.
The script runs in an infinite loop continuously until you press Ctrl + C in the terminal.
