Raspberry Pi - Heating System
This tutorial instructs you how to use Raspberry Pi, heating element and DS18B20 temperature sensor to regulate the room temperature.
- If the temperature is too low, the heating element will be activated by Raspberry Pi.
- If the temperature is warm enough, the heating element will be deactivated by Raspberry Pi.
Additionally, the code can be adapted for other temperature sensors such as DHT11 or DHT22, LM35 in place of the DS18B20 sensor.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Buy Note: Many DS18B20 sensors available in the market are unreliable. We strongly recommend buying the sensor from the DIYables brand using the link provided above. We tested it, and it worked reliably.
Overview of Heating Element and DS18B20 Temperature Sensor
The heating element used in this tutorial requires a 12v power supply. When power is supplied to the heating element, it will generate heat. To be able to control the heating element with a Raspberry Pi, a relay needs to be inserted between them.
If you are unfamiliar with temperature sensors and heating elements (pinouts, how they work, how to program them, etc.), the following tutorials can help:
Wiring Diagram
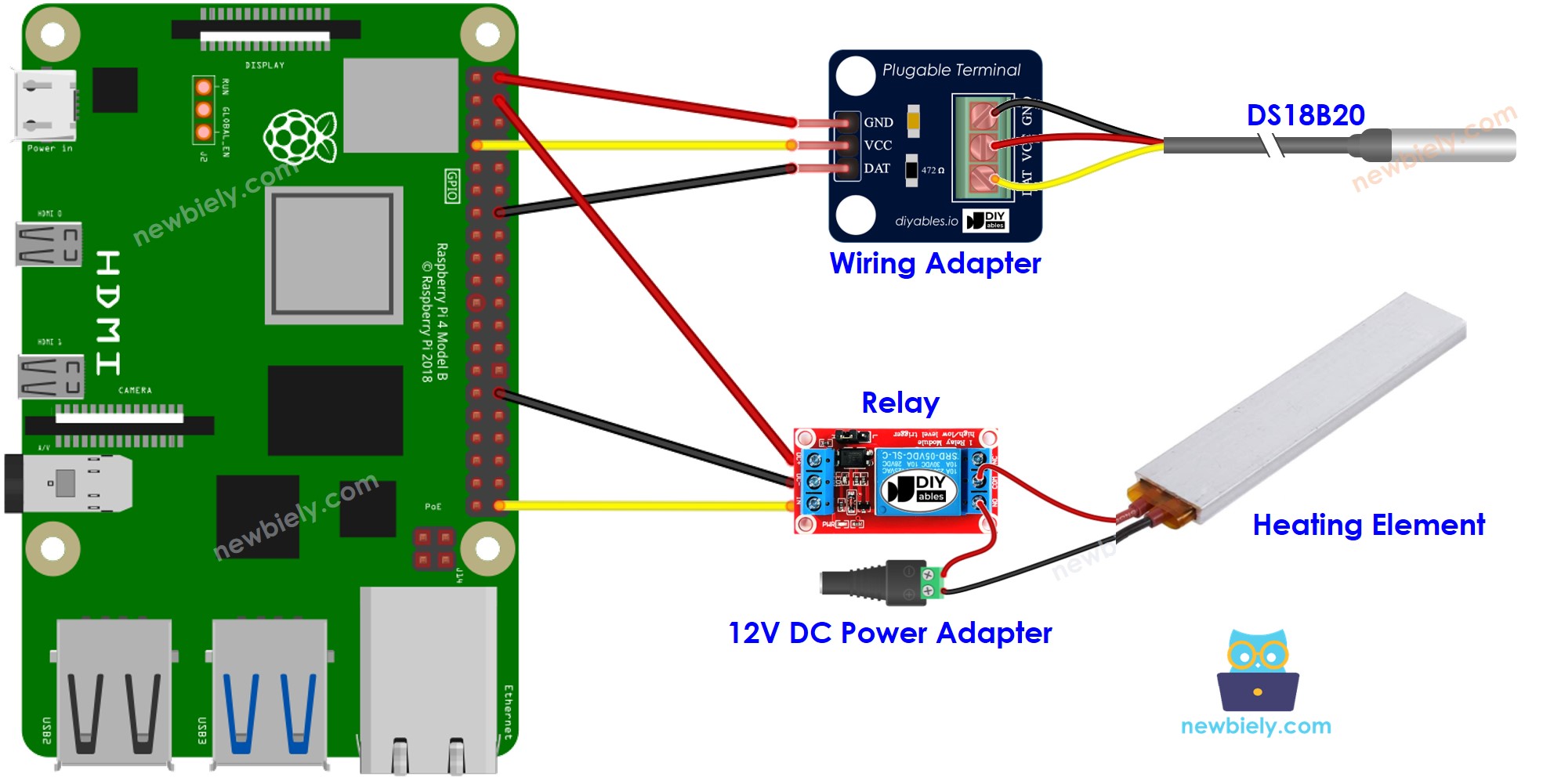
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
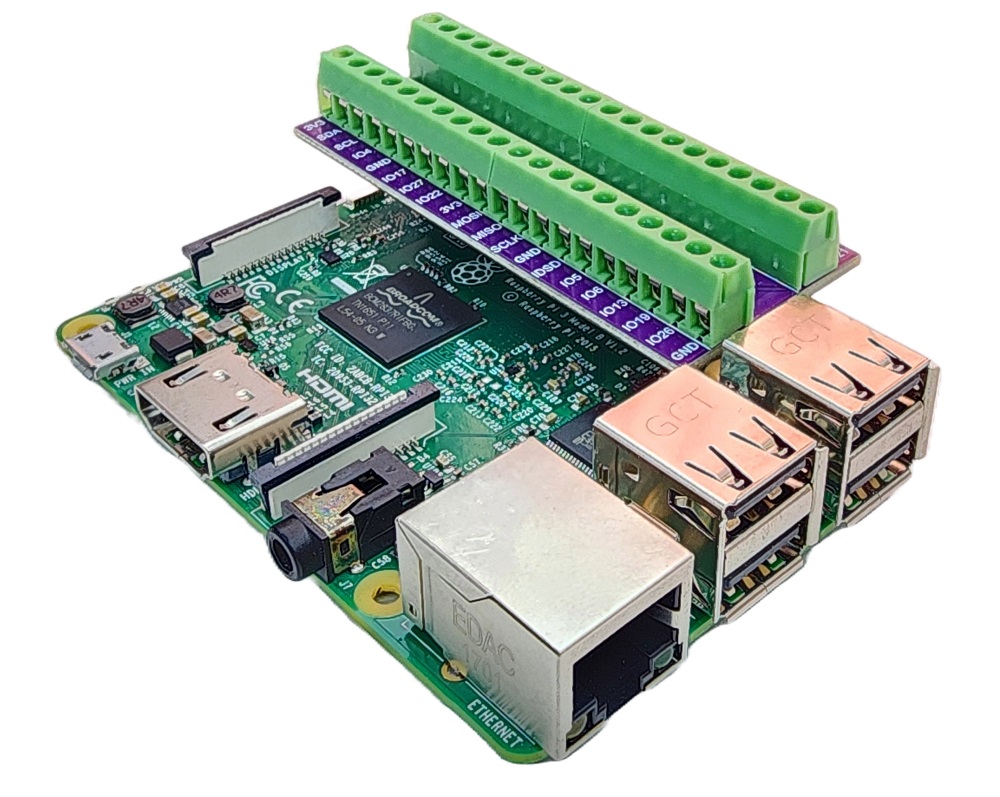
To simplify and organize your wiring setup, we recommend using a Screw Terminal Block Shield for Raspberry Pi. This shield ensures more secure and manageable connections, as shown below:
How System Works
- Raspberry Pi obtains the temperature from the temperature sensor.
- If the temperature drops below a certain lower limit, Raspberry Pi activates the heating elements.
- When the temperature exceeds a certain upper limit, Raspberry Pi deactivates the heating element.
The loop is repeated endlessly.
Raspberry Pi Code for Cooling System with DS18B20 sensor
In the code above, when the temperature drops below 15°C, the Raspberry Pi will activate the heating element. It will remain active until the temperature rises above 20°C.
Detailed Instructions
- Make sure you have Raspbian or any other Raspberry Pi compatible operating system installed on your Pi.
- Make sure your Raspberry Pi is connected to the same local network as your PC.
- Make sure your Raspberry Pi is connected to the internet if you need to install some libraries.
- If this is the first time you use Raspberry Pi, See how to set up the Raspberry Pi
- Connect your PC to the Raspberry Pi via SSH using the built-in SSH client on Linux and macOS or PuTTY on Windows. See to how connect your PC to Raspberry Pi via SSH.
- Make sure you have the RPi.GPIO library installed. If not, install it using the following command:
- Prior to utilizing the DS18B20 temperature sensor with a Raspberry Pi, we need to enable 1-Wire interface on Raspberry Pi. See How to enable 1-Wire interface on Raspberry Pi
- Install the library for DS18B20 temperature sensor by running the following command:
- Create a Python script file heating.py and add the following code:
- Save the file and run the Python script by executing the following command in the terminal:
The script runs in an infinite loop continuously until you press Ctrl + C in the terminal.
- Change the temperature of the area surrounding the sensor.
- Check out the temperature of the heating element and the room.
Advanced Knowledge
The above technique for controlling is the on-off controller, which is also referred to as a signaller or "bang-bang" controller. This method is quite easy to put into practice.
An alternative approach known as the PID controller exists. This method of temperature control is more stable, however it is complicated and not widely used. Consequently, the PID controller is not a popular choice for temperature regulation.
