Raspberry Pi - LM35 Temperature Sensor
This tutorial instructs you how to use Raspberry Pi to read the temperature from LM35 sensor. In detail, we will learn:
- How to connect Raspberry Pi to LM35 temperature sensor.
- How to program Raspberry Pi to get the temperature from LM35 sensor.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of LM35 Temperature Sensor
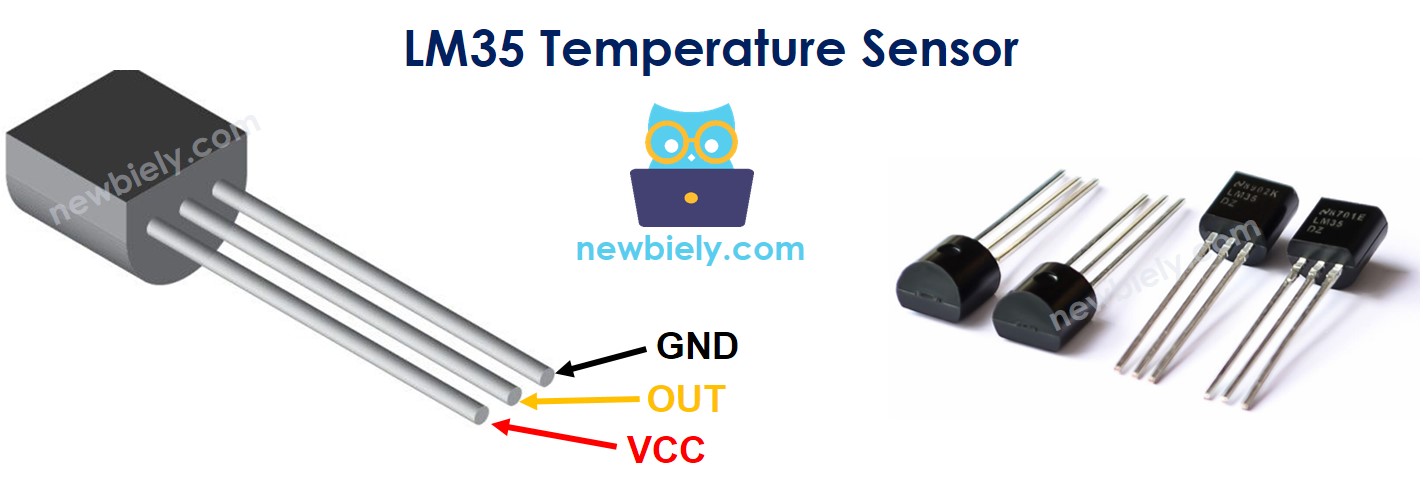
The LM35 Temperature Sensor Pinout
The LM35 temperature sensor has three pins:
- GND pin: This should be linked to GND (0V)
- VCC pin: This should be linked to VCC (5V)
- OUT pin: This signal pin provides an output voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature, and should be connected to an analog pin on the Raspberry Pi.
How It Works
The LM35 produces an output voltage that is linearly proportional to the Centigrade temperature. The scale factor of the LM35 is 10 mV/°C, meaning that the temperature can be determined by dividing the voltage (in mV) at the output pin by 10.
Since Raspberry Pi does not have an analog input pin, we need to use the ADC module such as ADS1115 ADC Module
Wiring Diagram
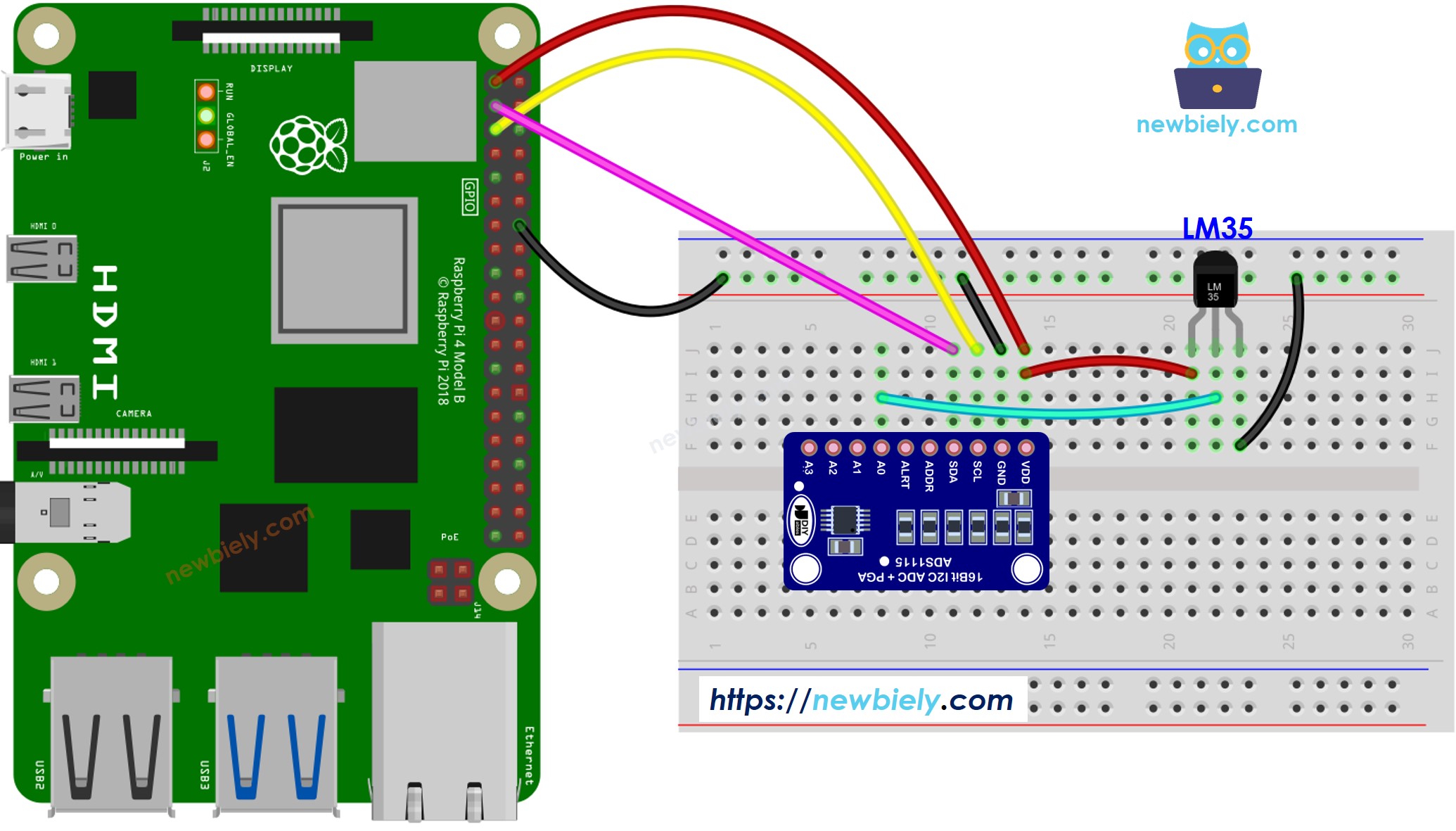
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
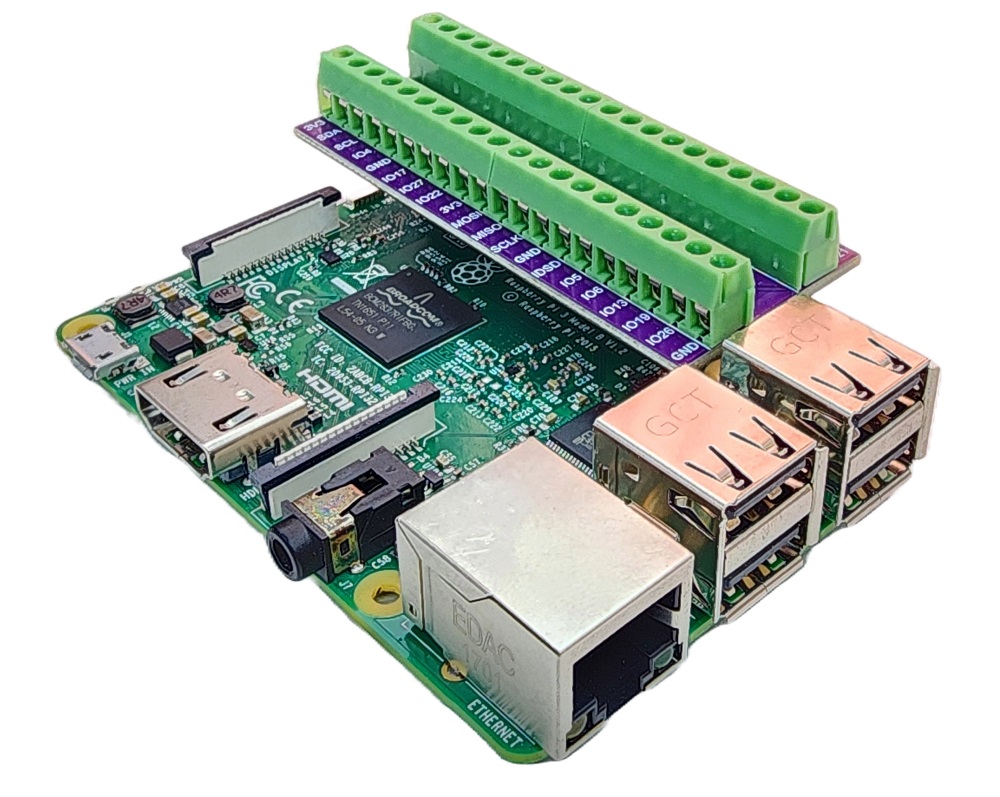
To simplify and organize your wiring setup, we recommend using a Screw Terminal Block Shield for Raspberry Pi. This shield ensures more secure and manageable connections, as shown below:
Raspberry Pi Code
Detailed Instructions
- Make sure you have Raspbian or any other Raspberry Pi compatible operating system installed on your Pi.
- Make sure your Raspberry Pi is connected to the same local network as your PC.
- Make sure your Raspberry Pi is connected to the internet if you need to install some libraries.
- If this is the first time you use Raspberry Pi, See how to set up the Raspberry Pi
- Connect your PC to the Raspberry Pi via SSH using the built-in SSH client on Linux and macOS or PuTTY on Windows. See to how connect your PC to Raspberry Pi via SSH.
- Make sure you have the RPi.GPIO library installed. If not, install it using the following command:
- Install the Adafruit_ADS1x15 library by running the following commands on your Raspberry Pi terminal:
- Create a Python script file LM35.py and add the following code:
- Save the file and run the Python script by executing the following command in the terminal:
- Hold the sensor in your hand.
- Check the output in the Terminal.
The script runs in an infinite loop continuously until you press Ctrl + C in the terminal.
