Arduino UNO R4 - Actuator with Feedback
This Arduino UNO R4 tutorial shows how to use a *feedback linear actuator* in your DIY projects.
In the previous lesson, we used a linear actuator without feedback. That type only moves in or out, but doesn’t tell us its position.
Now, we’ll learn about a feedback linear actuator. It can tell us where it is while moving, so we can control its exact position.
In this simple guide, you’ll learn:
- How a feedback linear actuator works – What it is and what it does
- How to know its position – Get its location in millimeters
- How to move it to the right spot – Control it to stop exactly where you want
This simple Arduino project is good for beginners. Follow this easy guide to learn Arduino programming and make a smart moving system!
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables STEM V4 IoT Starter Kit (Arduino included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Feedback Linear Actuator
A feedback linear actuator is a type of linear actuator that includes a feedback signal to monitor and control its position. This feedback comes from a potentiometer that provides a voltage output corresponding to the actuator's position.
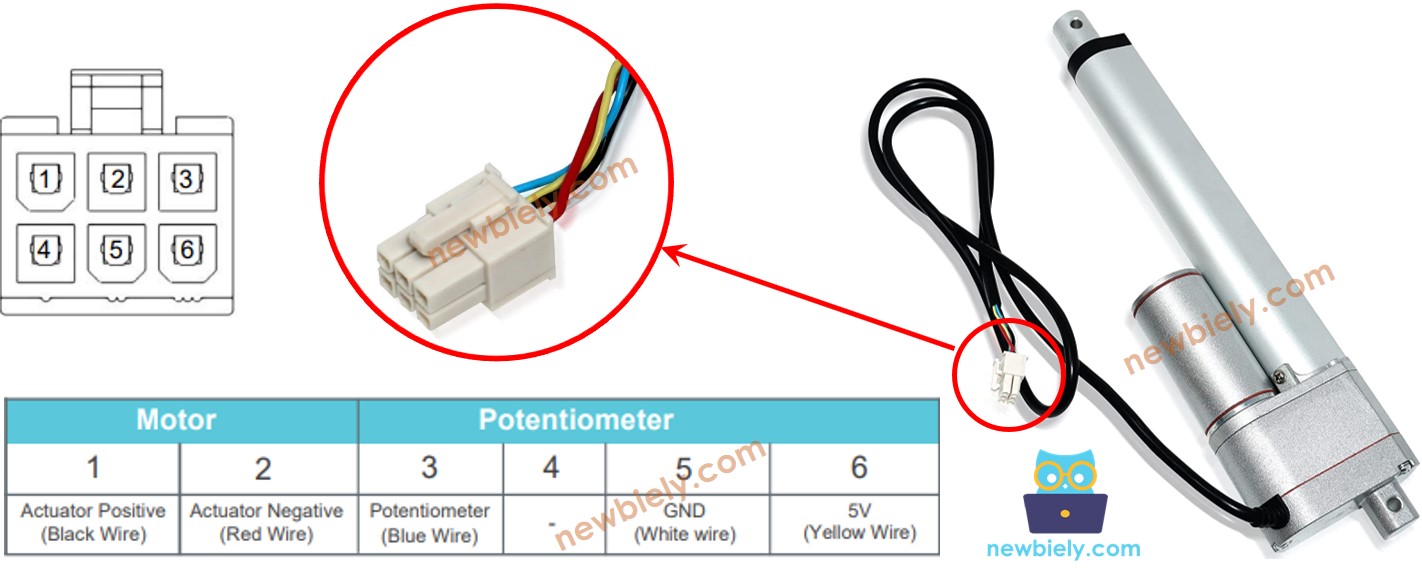
Feedback Linear Actuator Pinout
A Feedback Linear Actuator has five wires:
- Actuator Positive Wire: This wire controls the linear actuator using high voltage (12V, 24V, 48V).
- 5V Wire: This wire connects to the feedback potentiometer. Attach it to 5V or 3.3V.
- GND Wire: This wire connects to the feedback potentiometer. Attach it to the ground (GND).
- Potentiometer Wire: Also known as the feedback or output wire, this wire sends out a voltage value that changes based on the position of the stroke.
How It Works
When we supply a high voltage to the positive and negative wires, the actuator will either extend or retract. Specifically, if we connect:
- Connect 12V (like 12V, 24V, 48V...) and GND to the positive and negative wires respectively: the linear actuator extends at full speed until it stops at the end.
- Connect 12V (like 12V, 24V, 48V...) and GND to the negative and positive wires respectively: the linear actuator retracts at full speed until it stops at the end.
- If power is cut off from the actuator (GND connected to both positive and negative wires) while it is extending or retracting, the actuator will stop moving.
※ NOTE THAT:
- The voltage needed to control the actuator varies based on its specifications. Check the datasheet or manual to find out the right voltage.
- The actuator can maintain its position without power, even if it is holding a weight.
The voltage in the wire of the potentiometer changes according to where the actuator moves. By checking this voltage, we can find out where the stroke is positioned.
Wiring Diagram
Before wiring, take off all three jumpers from the L298N module.
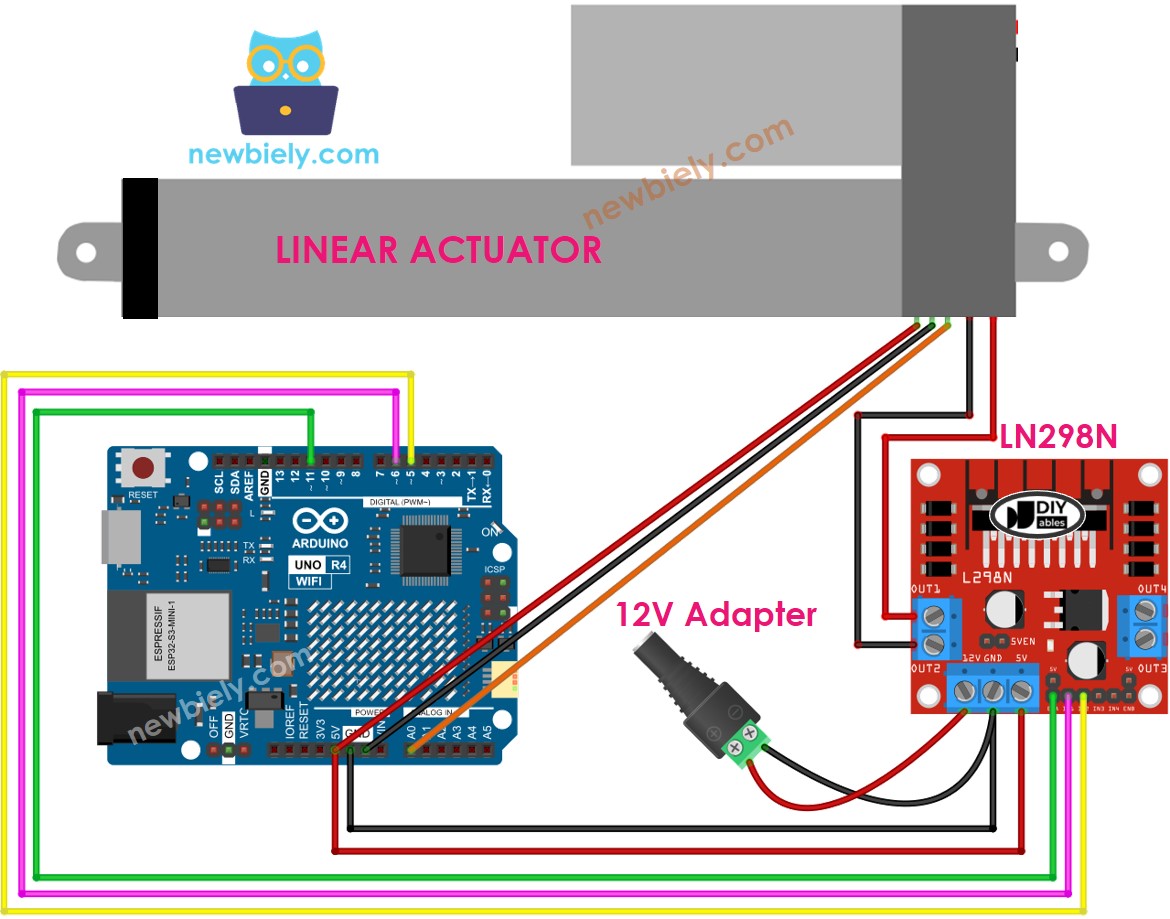
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See The best way to supply power to the Arduino Uno R4 and other components.
How to control extend/retract a linear actuator
Visit the tutorial for the Arduino UNO R4 Actuator here.
How to find the position of the linear actuator
Here's how to find the stroke position on a linear actuator:
Calibration
- Measure the length of the actuator's stroke (in millimeters) with a ruler or check the datasheet.
- Find the output values when the linear actuator is fully extended and retracted by executing the following code.
- You will see the log on the Serial Monitor as shown in the example below.
- Write down these values.
- If the minimum and maximum values are reversed, switch IN1_PIN with IN2_PIN.
- Update three values in the code below.
Arduino UNO R4 code that calculate the position of the actuator
- Change the three adjusted values in the code
- Load the code onto Arduino UNO R4
- Check the outcome on the Serial Monitor
How to control a linear actuator to a specific position
Video Tutorial
Summary
In this Arduino UNO R4 tutorial, you learned how to use a feedback linear actuator for DIY projects. This easy guide taught you how the actuator works, how to find its position in millimeters, and how to move it to the right spot with Arduino programming. After our lesson on a linear actuator without feedback, this simple Arduino project shows you how to make a smart moving system. Now you can build your own movement control projects with Arduino UNO R4!
