Arduino Nano ESP32 - LM35 Temperature Sensor
This tutorial provides instructions on how to use Arduino Nano ESP32 to read temperature value from LM35 temperature sensor, and print it to Serial Monitor.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of LM35 Temperature Sensor
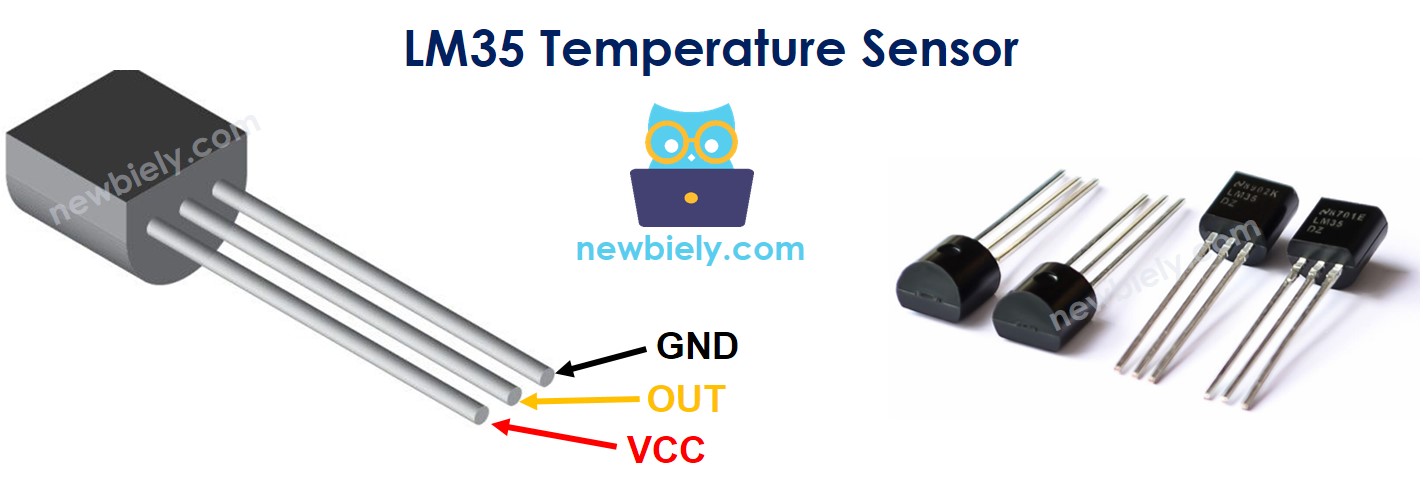
LM35 Temperature Sensor Pinout
LM35 temperature sensor has three pins:
- VCC pin: connect this pin to VCC (3.3V)
- GND pin: connect this pin to GND (0V)
- OUT pin: This pin outputs voltage in proportion to the temperature value.
How LM35 Temperature Sensor Works
The LM35 sensor outputs the voltage in linearly proportion to the Celsius temperature. The output scale factor of the LM35 is 10 mV/°C. By measuring the voltage on the LM32's OUT pin, we can calculate the temperature value.
Wiring Diagram between LM35 Temperature Sensor and Arduino Nano ESP32
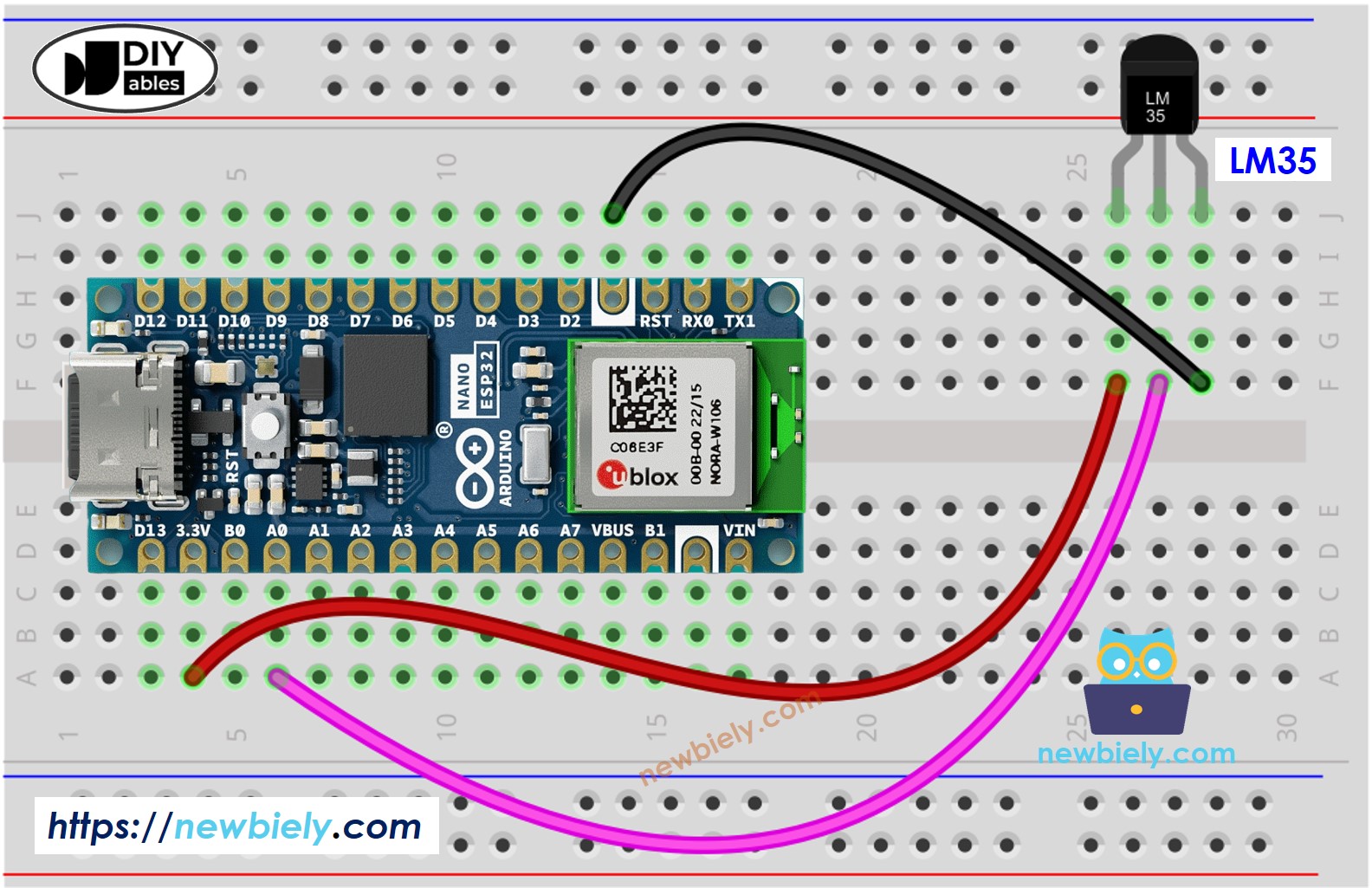
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino Nano ESP32 Code
Detailed Instructions
- If this is the first time you use Arduino Nano ESP32, see how to setup environment for Arduino Nano ESP32 on Arduino IDE.
- Copy the above code and paste it to Arduino IDE.
- Compile and upload code to Arduino Nano ESP32 board by clicking Upload button on Arduino IDE
- Make the sensor colder or hotter. For example, putting the sensor near an ice cup
- Check out the result on the Serial Monitor. It looks like the below:
※ NOTE THAT:
This tutorial uses the analogRead() function to read values from an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) connected to a sensor or component. The Arduino Nano ESP32's ADC is suitable for projects that do not require high accuracy. However, for projects needing precise measurements, keep the following in mind:
- The Arduino Nano ESP32's ADC is not perfectly accurate and might require calibration for correct results. Each Arduino Nano ESP32 board can vary slightly, so calibration is necessary for each individual board.
- Calibration can be challenging, especially for beginners, and might not always yield the exact results you want.
For projects requiring high precision, consider using an external ADC (e.g ADS1115) with the Arduino Nano ESP32 or using another Arduino, such as the Arduino Uno R4 WiFi, which has a more reliable ADC. If you still want to calibrate the Arduino Nano ESP32's ADC, refer to the ESP32 ADC Calibration Driver.
