Arduino Nano ESP32 - Soil Moisture Sensor Pump
In this tutorial, We are going to learn how to use the Arduino Nano ESP32 to control the pump according to the value read from the capacitive soil moisture sensor.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Buy Note: Many soil moisture sensors available in the market are unreliable, regardless of their version. We strongly recommend buying the sensor with TLC555I Chip from the DIYables brand using the link provided above. We tested it, and it worked reliably.
Overview of soil moisture sensor and Pump
If you do not know about pump and soil moisture sensor (pinout, how it works, how to program ...), learn about them in the following tutorials:
- Arduino Nano ESP32 - Controls Pump tutorial
How It Works
Arduino Nano ESP32 periodically reads the value from the capacitive soil moisture sensor. Based on the soil moisture value, it will take the following actions:
- If the soil moisture value is below a threshold, Arduino Nano ESP32 automatically activates a relay to turn a pump on.
- Otherwise, Arduino Nano ESP32 automatically deactivates a relay to turn a pump off.
Wiring Diagram
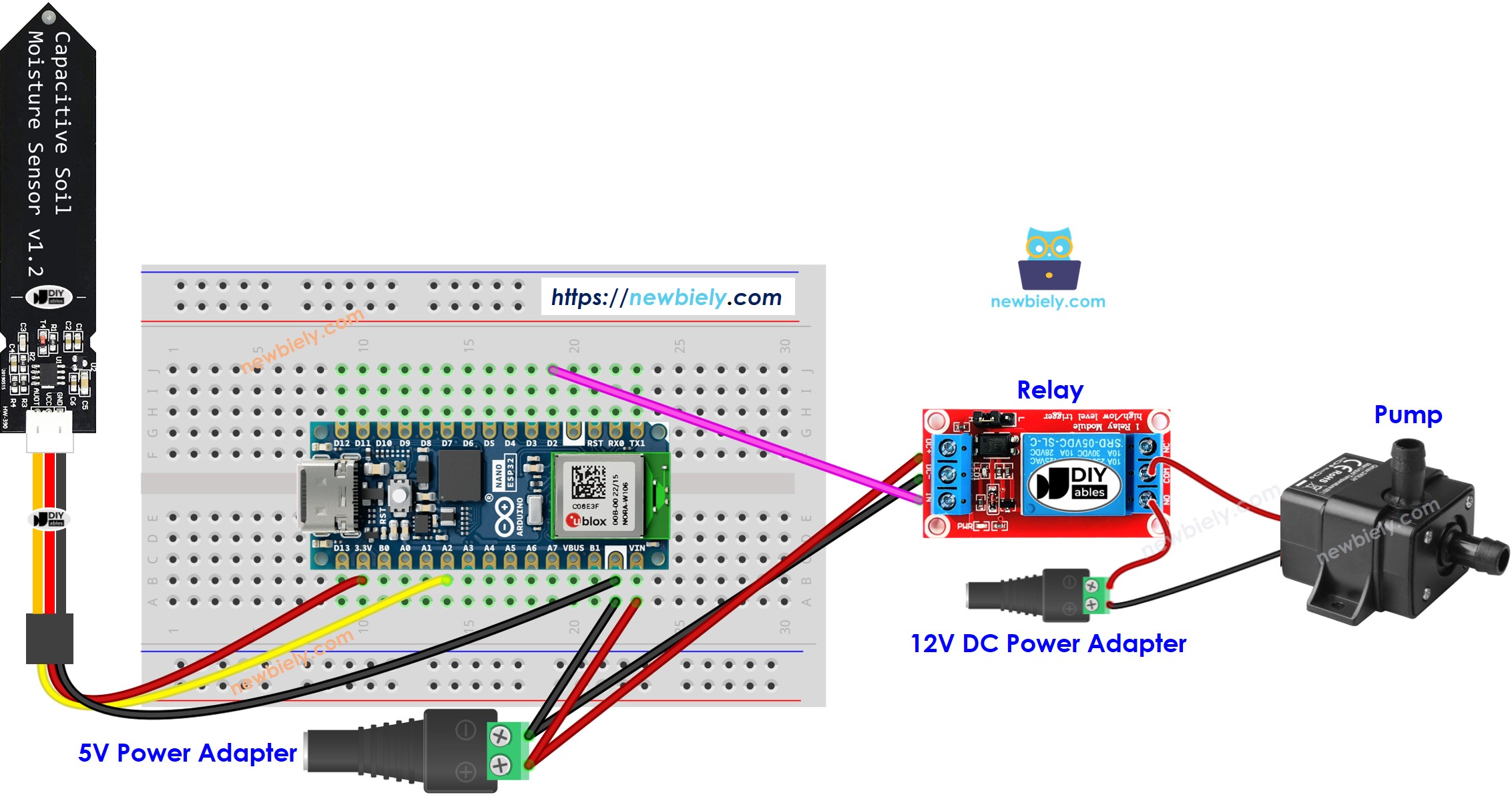
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Arduino Nano ESP32 Code
Detailed Instructions
- If you are new to Arduino Nano ESP32, refer to the tutorial on how to set up the environment for Arduino Nano ESP32 in the Arduino IDE.
- Do calibration to determine the wet-dry THRESHOLD, see Arduino Nano ESP32 - Calibrates Soil Moisture Sensor
- Update the calibrated value to THRESHOLD in the code
- Open Serial Monitor on Arduino IDE
- Upload the code to Arduino Nano ESP32
- Check out the result on Serial Monitor.
Code Explanation
Read the line-by-line explanation in the comment lines of the source code!
※ NOTE THAT:
This tutorial uses the analogRead() function to read values from an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) connected to a sensor or component. The Arduino Nano ESP32's ADC is suitable for projects that do not require high accuracy. However, for projects needing precise measurements, keep the following in mind:
- The Arduino Nano ESP32's ADC is not perfectly accurate and might require calibration for correct results. Each Arduino Nano ESP32 board can vary slightly, so calibration is necessary for each individual board.
- Calibration can be challenging, especially for beginners, and might not always yield the exact results you want.
For projects requiring high precision, consider using an external ADC (e.g ADS1115) with the Arduino Nano ESP32 or using another Arduino, such as the Arduino Uno R4 WiFi, which has a more reliable ADC. If you still want to calibrate the Arduino Nano ESP32's ADC, refer to the ESP32 ADC Calibration Driver.
