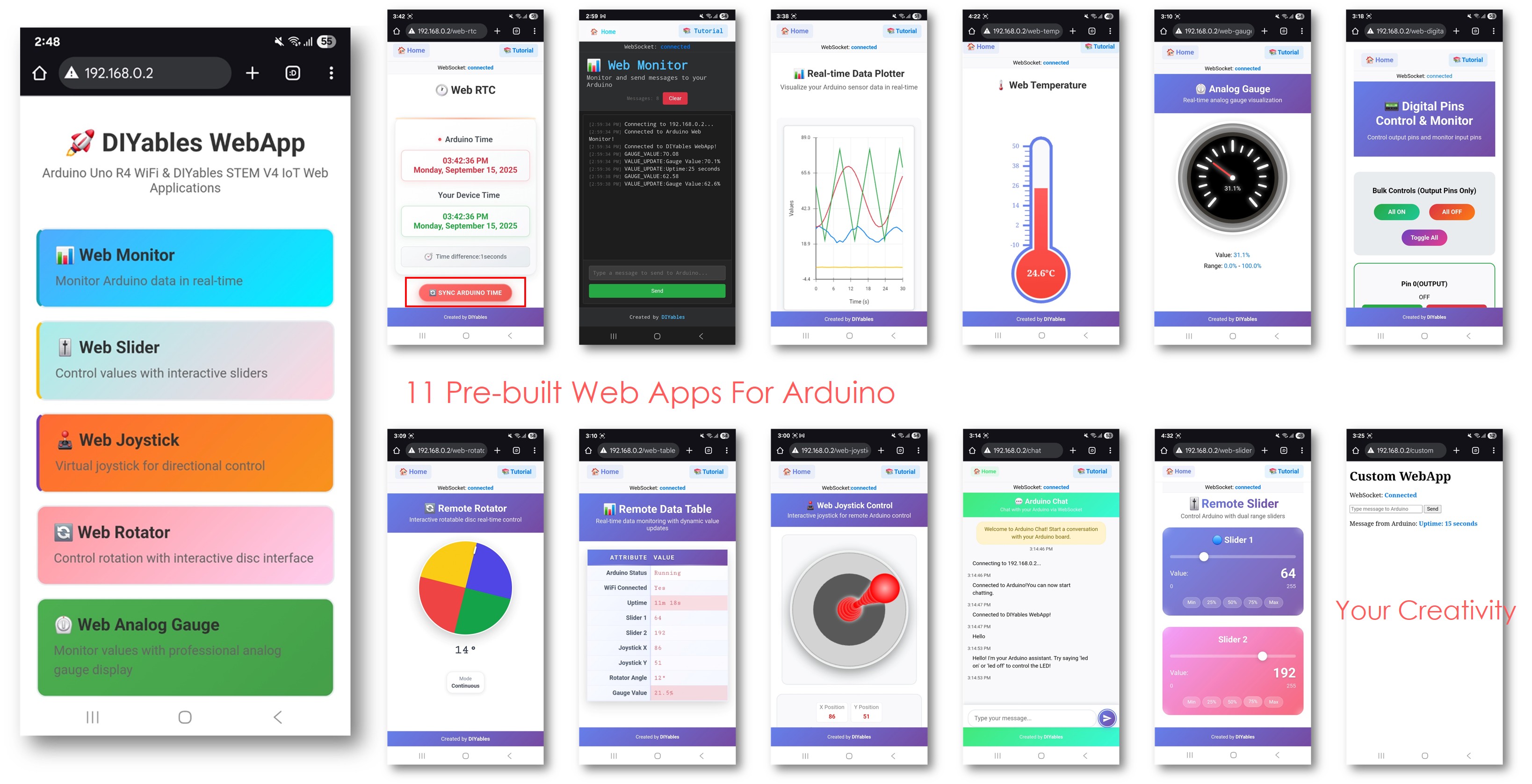
This example showcases how to use multiple web applications simultaneously with the DIYables WebApps library. It demonstrates the integration of several interactive web interfaces—such as monitoring, control, and communication—within a single project. Designed for the Arduino Uno R4 WiFi and DIYables STEM V4 IoT platform, this example is ideal for learning how to combine and manage multiple web-based features at the same time, providing a robust foundation for advanced IoT projects.
Follow these instructions step by step:
Connect the Arduino Uno R4/DIYables STEM V4 IoT board to your computer using a USB cable.
Launch the Arduino IDE on your computer.
Select the appropriate Arduino Uno R4 board (e.g., Arduino Uno R4 WiFi) and COM port.
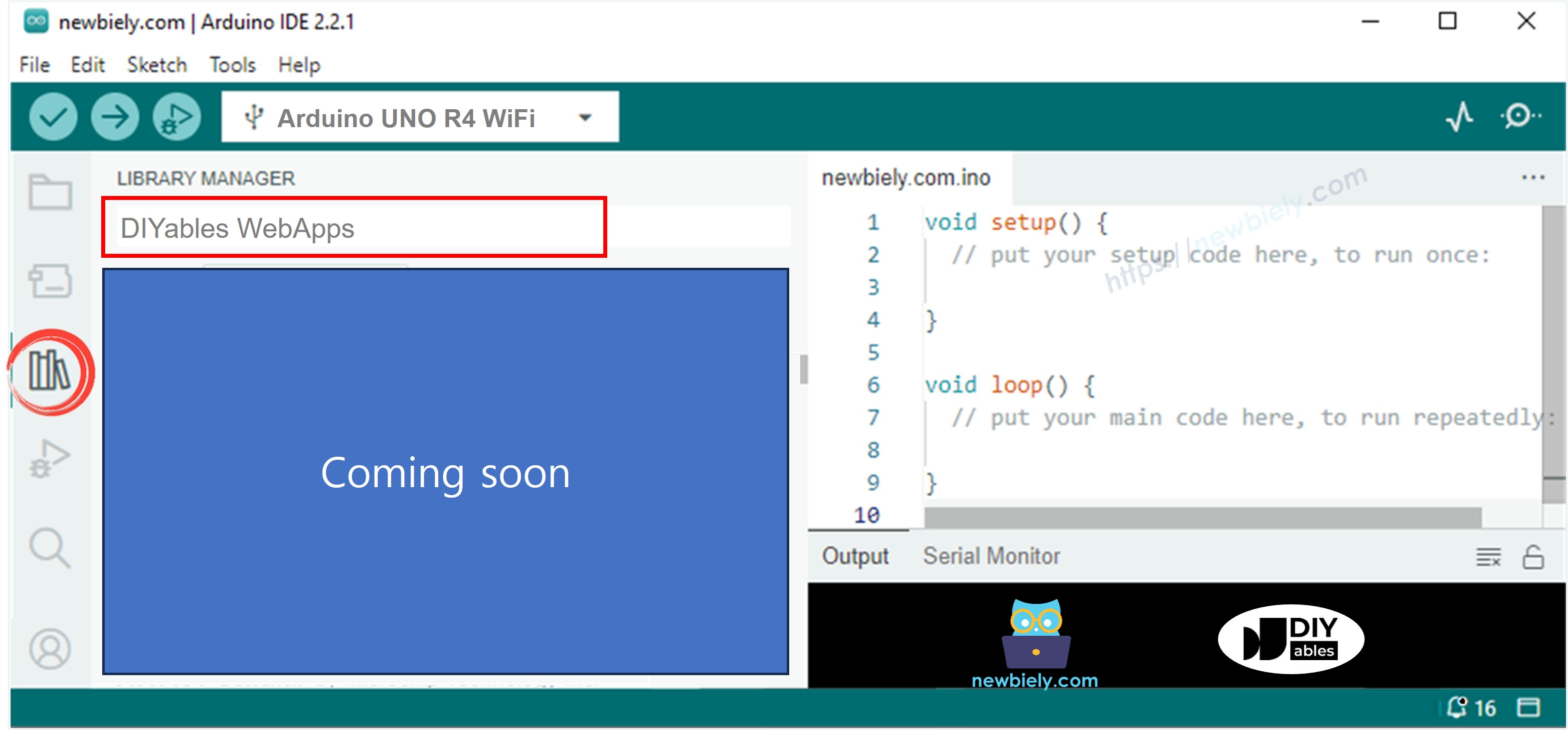
Navigate to the Libraries icon on the left bar of the Arduino IDE.
Search "DIYables WebApps", then find the DIYables WebApps library by DIYables
Click Install button to install the library.
#include <DIYablesWebApps.h>
const char WIFI_SSID[] = "YOUR_WIFI_SSID";
const char WIFI_PASSWORD[] = "YOUR_WIFI_PASSWORD";
UnoR4ServerFactory factory;
DIYablesWebAppServer webAppsServer(factory, 80, 81);
DIYablesHomePage homePage;
DIYablesWebMonitorPage webMonitorPage;
DIYablesWebSliderPage webSliderPage;
DIYablesWebJoystickPage webJoystickPage(false, 5);
DIYablesWebRotatorPage webRotatorPage(ROTATOR_MODE_CONTINUOUS);
DIYablesWebAnalogGaugePage webAnalogGaugePage(0.0, 100.0, "%");
DIYablesWebTablePage webTablePage;
int currentSlider1 = 64;
int currentSlider2 = 128;
int currentJoystickX = 0;
int currentJoystickY = 0;
int currentRotatorAngle = 0;
float currentGaugeValue = 50.0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(1000);
Serial.println("DIYables WebApp - Multiple Apps Example");
webAppsServer.addApp(&homePage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webMonitorPage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webSliderPage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webJoystickPage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webRotatorPage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webAnalogGaugePage);
webAppsServer.addApp(&webTablePage);
webAppsServer.setNotFoundPage(DIYablesNotFoundPage());
webTablePage.addRow("Arduino Status");
webTablePage.addRow("WiFi Connected");
webTablePage.addRow("Uptime");
webTablePage.addRow("Slider 1");
webTablePage.addRow("Slider 2");
webTablePage.addRow("Joystick X");
webTablePage.addRow("Joystick Y");
webTablePage.addRow("Rotator Angle");
webTablePage.addRow("Gauge Value");
if (!webAppsServer.begin(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASSWORD)) {
while (1) {
Serial.println("Failed to start WebApp server!");
delay(1000);
}
}
setupCallbacks();
}
void setupCallbacks() {
webMonitorPage.onWebMonitorMessage([](const String& message) {
Serial.println("Web Monitor: " + message);
webMonitorPage.sendToWebMonitor("Arduino received: " + message);
});
webSliderPage.onSliderValueFromWeb([](int slider1, int slider2) {
currentSlider1 = slider1;
currentSlider2 = slider2;
Serial.print("Slider 1: ");
Serial.print(slider1);
Serial.print(", Slider 2: ");
Serial.println(slider2);
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Slider 1", String(slider1));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Slider 2", String(slider2));
currentGaugeValue = map(slider1, 0, 255, 0, 100);
webAnalogGaugePage.sendToWebAnalogGauge(currentGaugeValue);
char gaugeStr[16];
snprintf(gaugeStr, sizeof(gaugeStr), "%.1f%%", currentGaugeValue);
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Gauge Value", String(gaugeStr));
});
webSliderPage.onSliderValueToWeb([]() {
webSliderPage.sendToWebSlider(currentSlider1, currentSlider2);
});
webJoystickPage.onJoystickValueFromWeb([](int x, int y) {
currentJoystickX = x;
currentJoystickY = y;
Serial.print("Joystick - X: ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(", Y: ");
Serial.println(y);
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(", Y: ");
Serial.println(y);
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Joystick X", String(x));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Joystick Y", String(y));
}
});
webJoystickPage.onJoystickValueToWeb([]() {
webJoystickPage.sendToWebJoystick(currentJoystickX, currentJoystickY);
});
webRotatorPage.onRotatorAngleFromWeb([](float angle) {
currentRotatorAngle = (int)angle;
Serial.println("Rotator angle: " + String(angle) + "°");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Rotator Angle", String(angle, 0) + "°");
});
webAnalogGaugePage.onGaugeValueRequest([]() {
webAnalogGaugePage.sendToWebAnalogGauge(currentGaugeValue);
});
webTablePage.onTableValueRequest([]() {
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Arduino Status", "Running");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("WiFi Connected", "Yes");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Uptime", "0 seconds");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Slider 1", String(currentSlider1));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Slider 2", String(currentSlider2));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Joystick X", String(currentJoystickX));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Joystick Y", String(currentJoystickY));
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Rotator Angle", String(currentRotatorAngle) + "°");
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Gauge Value", String(currentGaugeValue, 1) + "%");
});
}
void loop() {
webAppsServer.loop();
static unsigned long lastUptimeUpdate = 0;
if (millis() - lastUptimeUpdate > 5000) {
lastUptimeUpdate = millis();
unsigned long uptimeSeconds = millis() / 1000;
String uptimeStr = String(uptimeSeconds) + " seconds";
if (uptimeSeconds >= 60) {
uptimeStr = String(uptimeSeconds / 60) + "m " + String(uptimeSeconds % 60) + "s";
}
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Uptime", uptimeStr);
}
static unsigned long lastSensorUpdate = 0;
if (millis() - lastSensorUpdate > 3000) {
lastSensorUpdate = millis();
float sensorValue = 50.0 + 30.0 * sin(millis() / 10000.0);
currentGaugeValue = sensorValue;
webAnalogGaugePage.sendToWebAnalogGauge(currentGaugeValue);
webTablePage.sendValueUpdate("Gauge Value", String(currentGaugeValue, 1) + "%");
}
delay(10);
}
const char WIFI_SSID[] = "YOUR_WIFI_NETWORK";
const char WIFI_PASSWORD[] = "YOUR_WIFI_PASSWORD";
DIYables WebApp - Multiple Apps Example
INFO: Added app /
INFO: Added app /web-monitor
INFO: Added app /web-slider
INFO: Added app /web-joystick
INFO: Added app /web-rotator
INFO: Added app /web-gauge
INFO: Added app /web-table
DIYables WebApp Library
Platform: Arduino Uno R4 WiFi
Network connected!
IP address: 192.168.0.2
HTTP server started on port 80
Configuring WebSocket server callbacks...
WebSocket server started on port 81
WebSocket URL: ws://192.168.0.2:81
WebSocket server started on port 81
==========================================
DIYables WebApp Ready!
==========================================
📱 Web Interface: http://192.168.0.2
🔗 WebSocket: ws://192.168.0.2:81
📋 Available Applications:
🏠 Home Page: http://192.168.0.2/
📊 Web Monitor: http://192.168.0.2/web-monitor
🎚️ Web Slider: http://192.168.0.2/web-slider
🕹️ Web Joystick: http://192.168.0.2/web-joystick
🔄 Web Rotator: http://192.168.0.2/web-rotator
⏲️ Web Analog Gauge: http://192.168.0.2/web-gauge
📊 Web Table: http://192.168.0.2/web-table
==========================================
If you do not see anything, reboot Arduino board.
Take note of the IP address displayed, and enter this address into the address bar of a web browser on your smartphone or PC.
Example: http://192.168.0.2
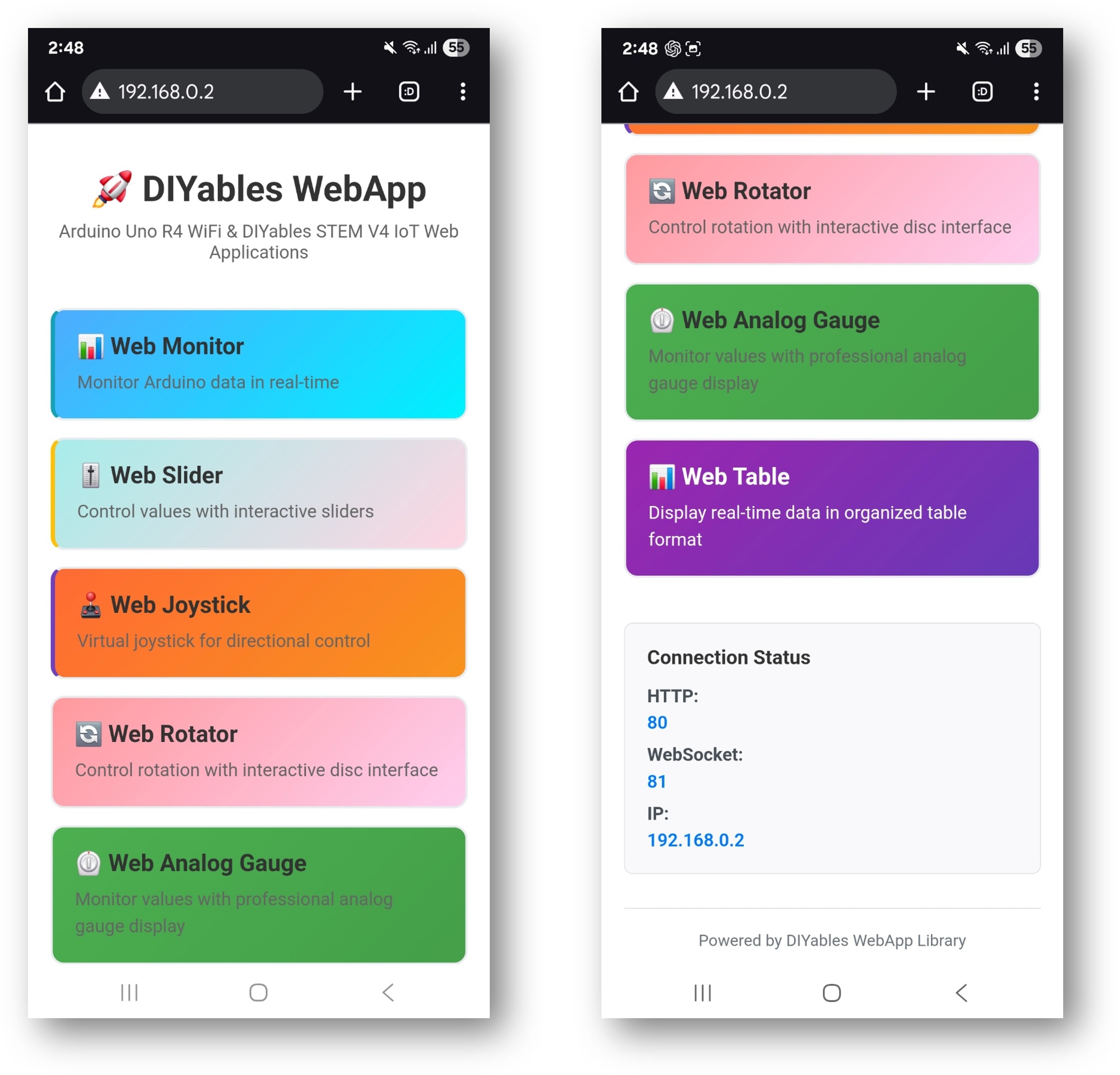
You will see the home page with all web applications like below image:
Click to any web application link (Chat, Web Monitor, Web Digital Pins, Web Slider, Web Joystick, etc.), you will see the corresponding web app's UI.
Or you can also access each page directly by IP address followed by the app path. For example: http://192.168.0.2/chat, http://192.168.0.2/web-monitor, etc.
Explore all the web applications: try chatting with Arduino, monitor serial output, control digital pins, adjust sliders, and use the virtual joystick to experience the full capabilities of the integrated web interface.
The home page serves as your control center with links to all applications:
Web Monitor: /webmonitor - Serial communication interface
Chat: /chat - Interactive messaging with Arduino
Digital Pins: /digital-pins - Pin control and monitoring
Web Slider: /webslider - Dual analog control sliders
Web Joystick: /webjoystick - 2D position control interface
Access each interface directly:
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/ # Home page
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/webmonitor # Serial monitor interface
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/chat # Chat interface
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/digital-pins # Pin control
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/webslider # Slider controls
http://[ARDUINO_IP]/webjoystick # Joystick control
This comprehensive example provides a foundation for your creative projects. Modify and adapt the configurations below to build amazing IoT applications that match your unique vision.
The example pre-configures specific pins for different purposes:
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(2, WEB_PIN_OUTPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(3, WEB_PIN_OUTPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(4, WEB_PIN_OUTPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(13, WEB_PIN_OUTPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(8, WEB_PIN_INPUT);
webDigitalPinsPage.enablePin(9, WEB_PIN_INPUT);
DIYablesWebJoystickPage webJoystickPage(false, 5);
The example maintains synchronized state across all interfaces:
int pinStates[16] = { LOW };
int currentSlider1 = 64;
int currentSlider2 = 128;
int currentJoystickX = 0;
int currentJoystickY = 0;
The chat interface includes several pre-programmed commands:
hello - Friendly greeting response
time - Shows Arduino uptime in seconds
status - Reports Arduino status and LED state
help - Lists available commands
User: hello
Arduino: Hello! I'm your Arduino. How can I help you?
User: led on
Arduino: Built-in LED is now ON!
User: time
Arduino: I've been running for 1245 seconds.
User: status
Arduino: Status: Running smoothly! LED is ON
#include <Servo.h>
const int MOTOR_LEFT_PWM = 9;
const int MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM = 10;
const int SERVO_PAN = 11;
const int SERVO_TILT = 12;
const int LED_STRIP_PIN = 6;
Servo panServo, tiltServo;
void setup() {
panServo.attach(SERVO_PAN);
tiltServo.attach(SERVO_TILT);
pinMode(MOTOR_LEFT_PWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM, OUTPUT);
setupRobotCallbacks();
}
void setupRobotCallbacks() {
webJoystickPage.onJoystickValueFromWeb([](int x, int y) {
int leftSpeed = y + (x / 2);
int rightSpeed = y - (x / 2);
leftSpeed = constrain(leftSpeed, -100, 100);
rightSpeed = constrain(rightSpeed, -100, 100);
leftSpeed = map(leftSpeed, -100, 100, -currentSlider1, currentSlider1);
rightSpeed = map(rightSpeed, -100, 100, -currentSlider1, currentSlider1);
analogWrite(MOTOR_LEFT_PWM, abs(leftSpeed));
analogWrite(MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM, abs(rightSpeed));
Serial.println("Robot - Left: " + String(leftSpeed) + ", Right: " + String(rightSpeed));
});
webSliderPage.onSliderValueFromWeb([](int slider1, int slider2) {
int panAngle = map(currentJoystickX, -100, 100, 0, 180);
int tiltAngle = map(slider2, 0, 255, 0, 180);
panServo.write(panAngle);
tiltServo.write(tiltAngle);
Serial.println("Camera - Pan: " + String(panAngle) + "°, Tilt: " + String(tiltAngle) + "°");
});
webDigitalPinsPage.onPinWrite([](int pin, int state) {
switch (pin) {
case 2:
digitalWrite(pin, state);
Serial.println("Headlights " + String(state ? "ON" : "OFF"));
break;
case 3:
if (state) {
digitalWrite(pin, HIGH);
delay(200);
digitalWrite(pin, LOW);
}
break;
case 4:
if (state) {
analogWrite(MOTOR_LEFT_PWM, 0);
analogWrite(MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM, 0);
Serial.println("EMERGENCY STOP ACTIVATED");
}
break;
}
});
chatPage.onChatMessage([](const String& message) {
String msg = message;
msg.toLowerCase();
if (msg.indexOf("stop") >= 0) {
analogWrite(MOTOR_LEFT_PWM, 0);
analogWrite(MOTOR_RIGHT_PWM, 0);
chatPage.sendToChat("Robot stopped!");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("center camera") >= 0) {
panServo.write(90);
tiltServo.write(90);
chatPage.sendToChat("Camera centered!");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("speed") >= 0) {
String response = "Current max speed: " + String(map(currentSlider1, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%";
chatPage.sendToChat(response);
return;
}
chatPage.sendToChat("Robot commands: stop, center camera, speed");
});
}
const int LIVING_ROOM_LIGHTS = 2;
const int BEDROOM_LIGHTS = 3;
const int KITCHEN_LIGHTS = 4;
const int FAN_CONTROL = 9;
const int AC_CONTROL = 10;
const int MOTION_SENSOR = 8;
const int DOOR_SENSOR = 9;
void setupHomeAutomation() {
pinMode(LIVING_ROOM_LIGHTS, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BEDROOM_LIGHTS, OUTPUT);
pinMode(KITCHEN_LIGHTS, OUTPUT);
pinMode(FAN_CONTROL, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AC_CONTROL, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOTION_SENSOR, INPUT);
pinMode(DOOR_SENSOR, INPUT_PULLUP);
webDigitalPinsPage.onPinWrite([](int pin, int state) {
digitalWrite(pin, state);
String room;
switch (pin) {
case 2: room = "Living Room"; break;
case 3: room = "Bedroom"; break;
case 4: room = "Kitchen"; break;
default: room = "Pin " + String(pin); break;
}
Serial.println(room + " lights " + String(state ? "ON" : "OFF"));
String message = room + " lights turned " + String(state ? "ON" : "OFF");
chatPage.sendToChat(message);
});
webSliderPage.onSliderValueFromWeb([](int slider1, int slider2) {
analogWrite(FAN_CONTROL, slider1);
analogWrite(AC_CONTROL, slider2);
Serial.println("Fan: " + String(map(slider1, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%, " +
"AC: " + String(map(slider2, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%");
});
chatPage.onChatMessage([](const String& message) {
String msg = message;
msg.toLowerCase();
if (msg.indexOf("all lights on") >= 0) {
digitalWrite(LIVING_ROOM_LIGHTS, HIGH);
digitalWrite(BEDROOM_LIGHTS, HIGH);
digitalWrite(KITCHEN_LIGHTS, HIGH);
chatPage.sendToChat("All lights turned ON!");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("all lights off") >= 0) {
digitalWrite(LIVING_ROOM_LIGHTS, LOW);
digitalWrite(BEDROOM_LIGHTS, LOW);
digitalWrite(KITCHEN_LIGHTS, LOW);
chatPage.sendToChat("All lights turned OFF!");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("temperature") >= 0) {
String response = "Fan: " + String(map(currentSlider1, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%, " +
"AC: " + String(map(currentSlider2, 0, 255, 0, 100)) + "%";
chatPage.sendToChat(response);
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("security") >= 0) {
bool motion = digitalRead(MOTION_SENSOR);
bool door = digitalRead(DOOR_SENSOR);
String status = "Motion: " + String(motion ? "DETECTED" : "CLEAR") +
", Door: " + String(door ? "CLOSED" : "OPEN");
chatPage.sendToChat(status);
return;
}
chatPage.sendToChat("Home commands: all lights on/off, temperature, security");
});
}
void loop() {
server.loop();
static bool lastMotion = false;
static bool lastDoor = false;
bool currentMotion = digitalRead(MOTION_SENSOR);
bool currentDoor = digitalRead(DOOR_SENSOR);
if (currentMotion != lastMotion) {
if (currentMotion) {
chatPage.sendToChat("🚨 MOTION DETECTED!");
webMonitorPage.sendToWebMonitor("Security Alert: Motion detected");
}
lastMotion = currentMotion;
}
if (currentDoor != lastDoor) {
String status = currentDoor ? "CLOSED" : "OPENED";
chatPage.sendToChat("🚪 Door " + status);
webMonitorPage.sendToWebMonitor("Security: Door " + status);
lastDoor = currentDoor;
}
delay(10);
}
const int HEATING_ELEMENT = 9;
const int COOLING_FAN = 10;
const int STIRRER_MOTOR = 11;
const int TEMP_SENSOR_PIN = A0;
const int PH_SENSOR_PIN = A1;
void setupScienceExperiment() {
webSliderPage.onSliderValueFromWeb([](int slider1, int slider2) {
int targetTemp = map(slider1, 0, 255, 20, 80);
analogWrite(STIRRER_MOTOR, slider2);
int currentTemp = readTemperature();
if (currentTemp < targetTemp) {
analogWrite(HEATING_ELEMENT, 200);
analogWrite(COOLING_FAN, 0);
} else if (currentTemp > targetTemp + 2) {
analogWrite(HEATING_ELEMENT, 0);
analogWrite(COOLING_FAN, 255);
} else {
analogWrite(HEATING_ELEMENT, 0);
analogWrite(COOLING_FAN, 0);
}
Serial.println("Target: " + String(targetTemp) + "°C, Current: " + String(currentTemp) + "°C");
});
chatPage.onChatMessage([](const String& message) {
String msg = message;
msg.toLowerCase();
if (msg.indexOf("data") >= 0) {
int temp = readTemperature();
float ph = readPH();
String data = "Temperature: " + String(temp) + "°C, pH: " + String(ph, 2);
chatPage.sendToChat(data);
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("start") >= 0) {
chatPage.sendToChat("🔬 Experiment started! Monitoring conditions...");
return;
}
if (msg.indexOf("stop") >= 0) {
analogWrite(HEATING_ELEMENT, 0);
analogWrite(COOLING_FAN, 0);
analogWrite(STIRRER_MOTOR, 0);
chatPage.sendToChat("⚠️ Experiment stopped - all systems OFF");
return;
}
chatPage.sendToChat("Science commands: data, start, stop");
});
webMonitorPage.onWebMonitorMessage([](const String& message) {
if (message == "log") {
int temp = readTemperature();
float ph = readPH();
String logEntry = String(millis()) + "," + String(temp) + "," + String(ph, 2);
webMonitorPage.sendToWebMonitor(logEntry);
}
});
}
int readTemperature() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(TEMP_SENSOR_PIN);
return map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 100);
}
float readPH() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(PH_SENSOR_PIN);
return map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 14) / 10.0;
}
void synchronizeAllStates() {
webSliderPage.sendToWebSlider(currentSlider1, currentSlider2);
webJoystickPage.sendToWebJoystick(currentJoystickX, currentJoystickY);
for (int pin = 0; pin <= 13; pin++) {
if (webDigitalPinsPage.isPinEnabled(pin)) {
webDigitalPinsPage.updatePinState(pin, pinStates[pin]);
}
}
Serial.println("All interface states synchronized");
}
void setupCrossInterfaceCommunication() {
webJoystickPage.onJoystickValueFromWeb([](int x, int y) {
float distance = sqrt(x*x + y*y);
if (distance > 50) {
int maxValue = map(distance, 50, 100, 255, 128);
}
});
webDigitalPinsPage.onPinWrite([](int pin, int state) {
if (pin == 2 && state == HIGH) {
chatPage.sendToChat("📢 System armed - additional commands available");
} else if (pin == 2 && state == LOW) {
chatPage.sendToChat("📢 System disarmed - limited commands only");
}
});
}
1. Some interfaces not loading
Check that all applications are added to server in setup()
Verify WebSocket connections in browser console
Ensure sufficient memory for all interfaces
2. State inconsistencies between interfaces
Implement state synchronization callbacks
Use shared global variables for state tracking
Call synchronization functions after major state changes
3. Performance issues with multiple interfaces
Reduce update frequencies for non-critical interfaces
Implement selective updates based on active interface
Consider disabling unused interfaces for specific projects
4. Memory limitations
Monitor available RAM with Serial.print(freeMemory())
Disable unused interfaces if memory is tight
Optimize callback functions to minimize memory usage
void debugSystemState() {
Serial.println("=== System State Debug ===");
Serial.println("Free Memory: " + String(freeMemory()) + " bytes");
Serial.println("Digital Pins:");
for (int pin = 0; pin <= 13; pin++) {
if (webDigitalPinsPage.isPinEnabled(pin)) {
Serial.println(" Pin " + String(pin) + ": " + String(pinStates[pin] ? "HIGH" : "LOW"));
}
}
Serial.println("Sliders: " + String(currentSlider1) + ", " + String(currentSlider2));
Serial.println("Joystick: X=" + String(currentJoystickX) + ", Y=" + String(currentJoystickY));
Serial.println("========================");
}
After mastering the MultipleWebApps example:
Customize for Your Project: Remove unused interfaces and add project-specific logic
Add Sensors: Integrate real sensor readings for input monitoring
Implement Safety: Add emergency stops and safety interlocks
Create Custom Commands: Extend chat interface with project-specific commands
Add Data Logging: Use web monitor for permanent data storage
Mobile Optimization: Test and optimize for mobile device usage
For additional help:
Check individual example documentation (Chat_Example.txt, WebMonitor_Example.txt, etc.)
Review the API Reference documentation
Visit DIYables tutorials: https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-uno-r4/arduino-uno-r4-diyables-webapps
Arduino community forums
This comprehensive example provides the foundation for virtually any web-controlled Arduino project. Start with this template and customize it for your specific needs!