DIYables Web Apps Web Joystick
Overview
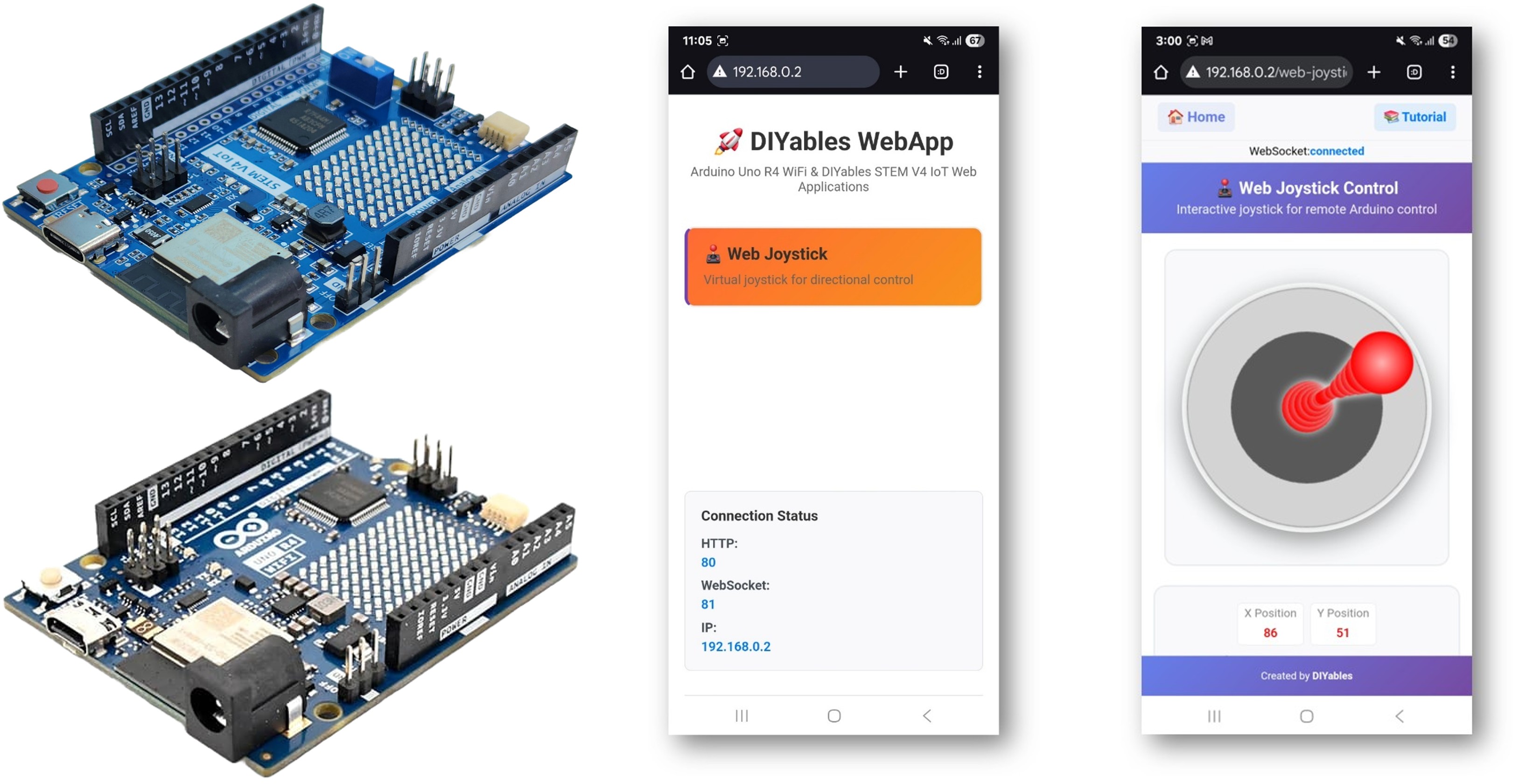
The WebJoystick example creates a virtual joystick interface accessible from any web browser. Designed for Arduino Uno R4 WiFi and DIYables STEM V4 IoT educational platform with enhanced robotics capabilities, built-in motor control features, and seamless integration with robotics educational modules. Perfect for controlling robots, vehicles, or any system requiring 2D position input.
Features
- Virtual Joystick: Interactive joystick control via web interface
- Real-time Coordinates: X/Y values from -100 to +100 for precise control
- Touch & Mouse Support: Works on desktop, tablet, and mobile devices
- Configurable Auto-Return: Option for joystick to return to center when released
- Sensitivity Control: Adjustable sensitivity to prevent excessive updates
- Visual Feedback: Real-time position display and coordinate values
- WebSocket Communication: Instant response without page refresh
- Center Position: Clear center position indicator for neutral control
- Platform Extensible: Currently implemented for Arduino Uno R4 WiFi, but can be extended for other hardware platforms. See DIYables_WebApps_ESP32
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables STEM V4 IoT Starter Kit (Arduino included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Setup Instructions
Detailed Instructions
Follow these instructions step by step:
- If this is your first time using the Arduino Uno R4 WiFi/DIYables STEM V4 IoT, refer to the tutorial on setting up the environment for Arduino Uno R4 WiFi/DIYables STEM V4 IoT in the Arduino IDE.
- Connect the Arduino Uno R4/DIYables STEM V4 IoT board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Launch the Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Select the appropriate Arduino Uno R4 board (e.g., Arduino Uno R4 WiFi) and COM port.
- Navigate to the Libraries icon on the left bar of the Arduino IDE.
- Search "DIYables WebApps", then find the DIYables WebApps library by DIYables
- Click Install button to install the library.
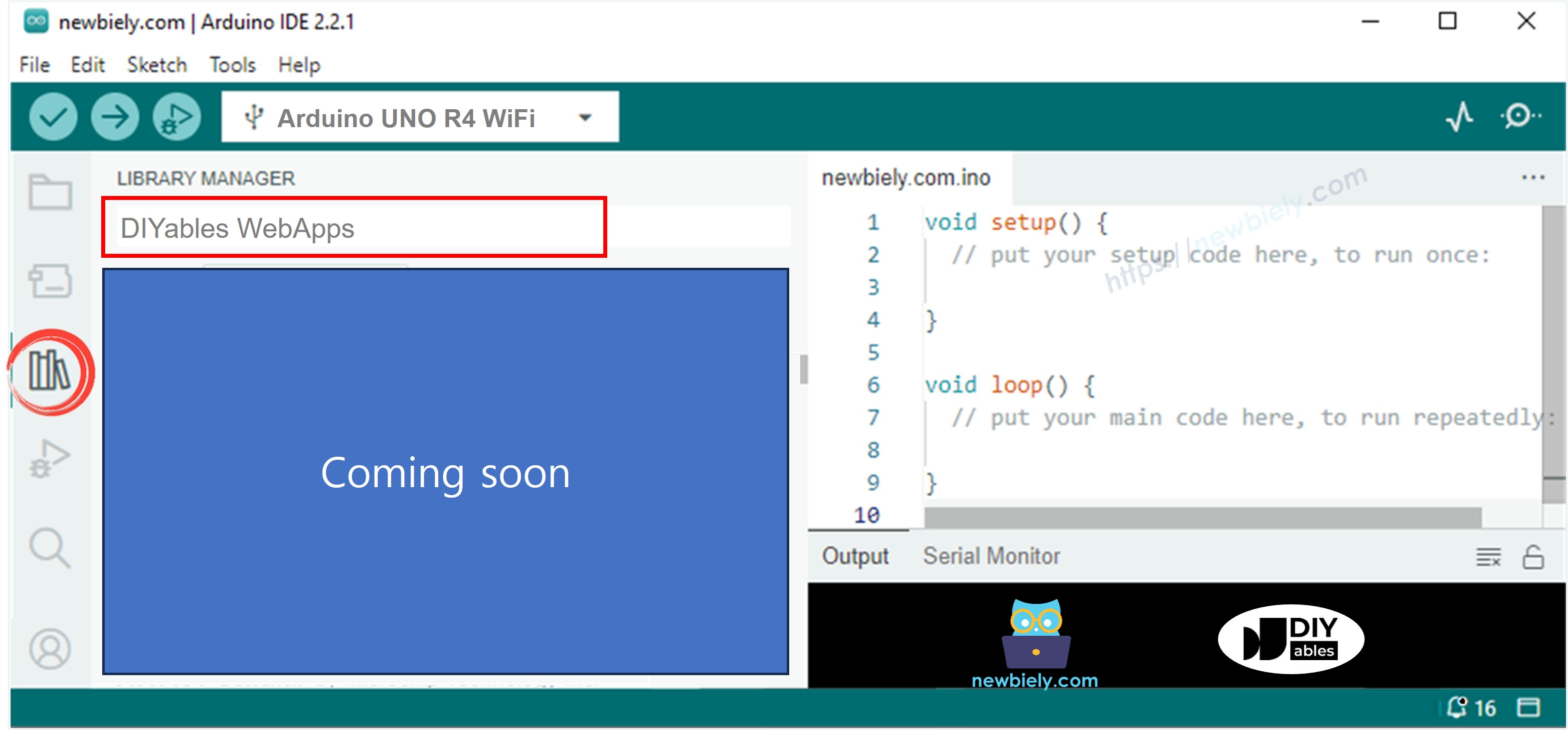
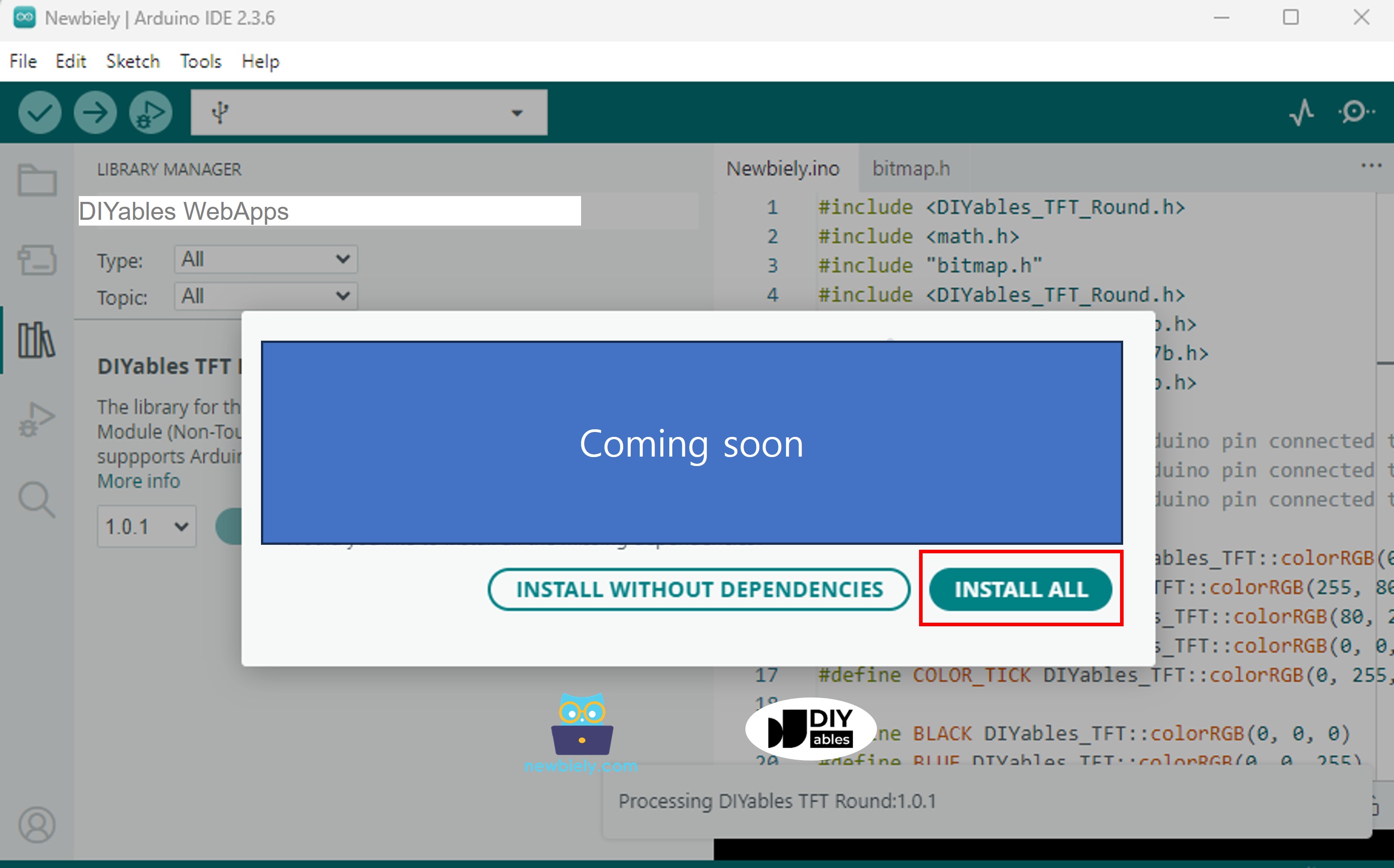
- You will be asked for installing some other library dependencies
- Click Install All button to install all library dependencies.
- On Arduino IDE, Go to File Examples DIYables WebApps WebJoystick example, or copy the above code and paste it to the editor of Arduino IDE
- Configure WiFi credentials in the code by updating these lines:
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to Arduino UNO R4/DIYables STEM V4 IoT
- Open the Serial Monitor
- Check out the result on Serial Monitor. It looks like the below
- If you do not see anything, reboot Arduino board.
- Take note of the IP address displayed, and enter this address into the address bar of a web browser on your smartphone or PC.
- Example: http://192.168.0.2
- You will see the home page like below image:
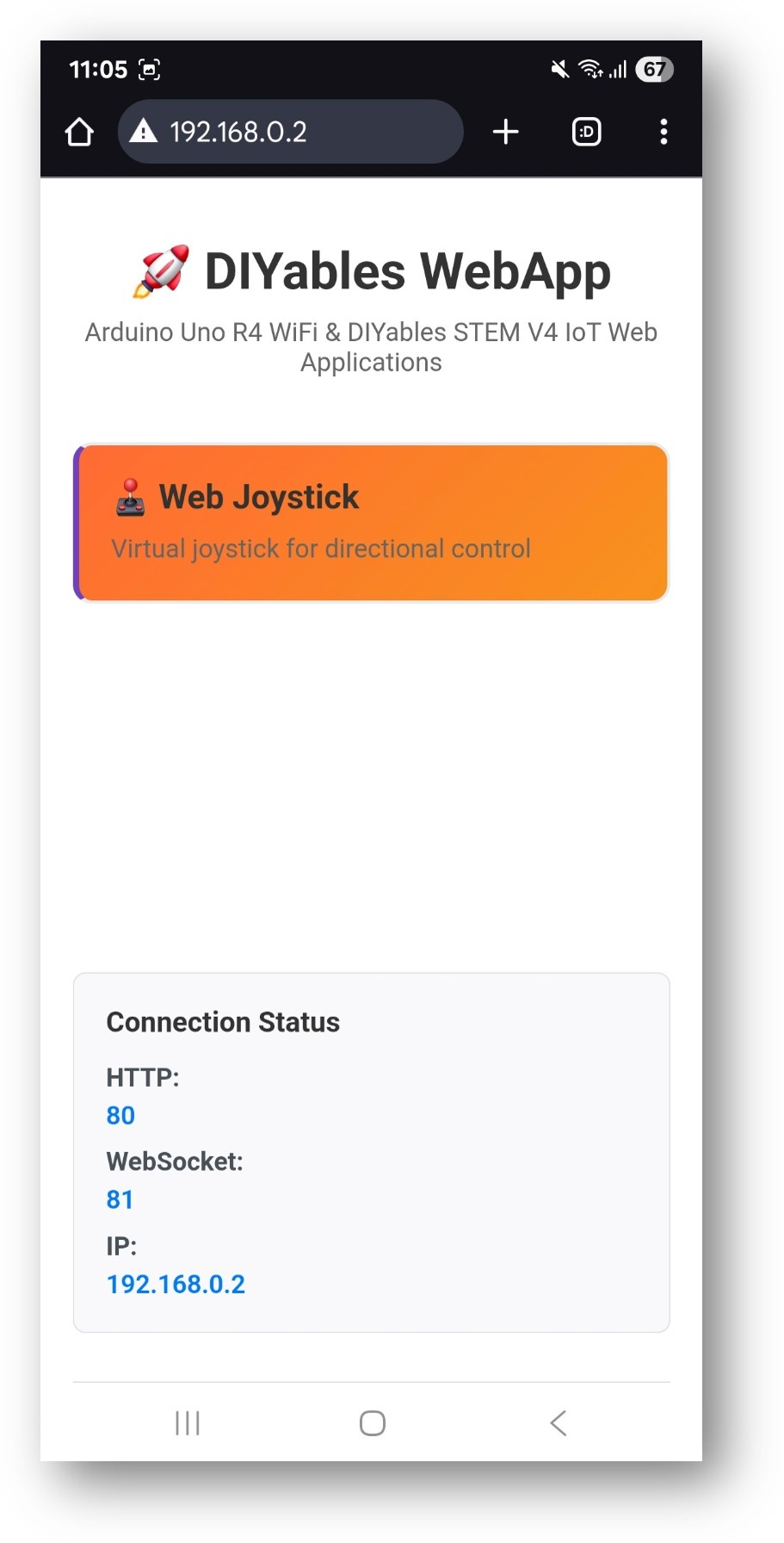
- Click to the Web Joystick link, you will see the Web Joystick app's UI like the below:
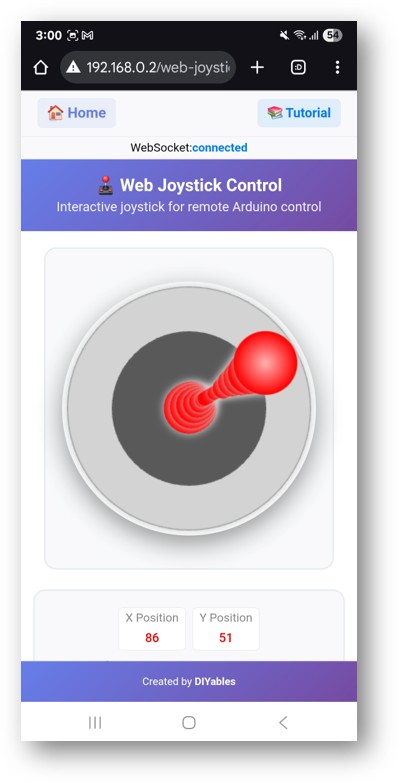
- Or you can also access the page directly by IP address followed by /web-joystick. For example: http://192.168.0.2/web-joystick
- Try controlling the virtual joystick by clicking and dragging on the joystick area and observe the X/Y coordinate values (-100 to +100) in the Serial Monitor.
Creative Customization - Adapt the Code to Your Project
2. Configure Joystick Settings
The joystick can be configured with different parameters:
Basic Configuration
Advanced Configuration
How to Use the Joystick
Web Interface Controls
The joystick interface provides:
- Joystick Pad: Circular control area for touch/mouse input
- Position Indicator: Shows current joystick position
- Coordinate Display: Real-time X/Y values (-100 to +100)
- Center Point: Visual reference for neutral position
Operating the Joystick
Desktop (Mouse Control)
- Click and Drag: Click on joystick and drag to move
- Release: Joystick returns to center (if autoReturn=true)
- Click Position: Direct click to set joystick position
Mobile/Tablet (Touch Control)
- Touch and Drag: Touch joystick and drag finger to move
- Multi-touch: Single finger for precise control
- Release: Automatic return to center (if enabled)
Coordinate System
The joystick provides coordinates in a standard Cartesian system:
- X-axis: -100 (full left) to +100 (full right)
- Y-axis: -100 (full down) to +100 (full up)
- Center: X=0, Y=0 (neutral position)
- Corners: Diagonal positions provide combined X/Y values
Programming Examples
Basic Joystick Handler
Motor Control Example
Servo Control Example
LED Position Indicator
Advanced Configuration
Runtime Configuration Changes
Dead Zone Implementation
Speed Ramping
Hardware Integration Examples
Robot Car Control
Camera Gimbal Control
RGB LED Color Control
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
1. Joystick not responding
- Check WebSocket connection status in browser console
- Verify network connectivity
- Refresh browser page
- Check Serial Monitor for errors
2. Jerky or inconsistent movement
- Increase sensitivity value to reduce update frequency
- Implement dead zone filtering
- Add speed ramping for smooth transitions
- Check for network latency issues
3. Auto-return not working
- Verify autoReturn setting: webJoystickPage.setAutoReturn(true)
- Check browser compatibility (some touch devices vary)
- Test with different input methods (mouse vs touch)
4. Values not reaching full range
- Check joystick calibration in web interface
- Verify coordinate calculations in callback
- Test with different browser/device combinations
Debug Tips
Add comprehensive debugging:
Project Ideas
Robotics Projects
- Remote-controlled robot car
- Robotic arm control
- Drone flight control (basic movements)
- Pet robot navigation
Home Automation
- Smart curtain control (open/close/position)
- Camera pan/tilt control
- Light brightness and color control
- Fan speed and direction control
Educational Projects
- Coordinate system teaching tool
- Motor control demonstrations
- Servo positioning experiments
- Gaming controller interfaces
Art and Creative Projects
- LED matrix pattern control
- Music visualization control
- Drawing robot control
- Interactive art installations
Integration with Other Examples
Combine with WebSlider
Use joystick for direction and sliders for speed/intensity:
Combine with WebDigitalPins
Use joystick positions to trigger digital pin states:
Next Steps
After mastering the WebJoystick example, try:
- WebSlider - For additional analog control
- WebDigitalPins - For discrete on/off control
- WebMonitor - For debugging joystick values
- MultipleWebApps - Combining joystick with other controls
Support
For additional help:
- Check the API Reference documentation
- Visit DIYables tutorials: https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-uno-r4/arduino-uno-r4-diyables-webapps
- Arduino community forums
