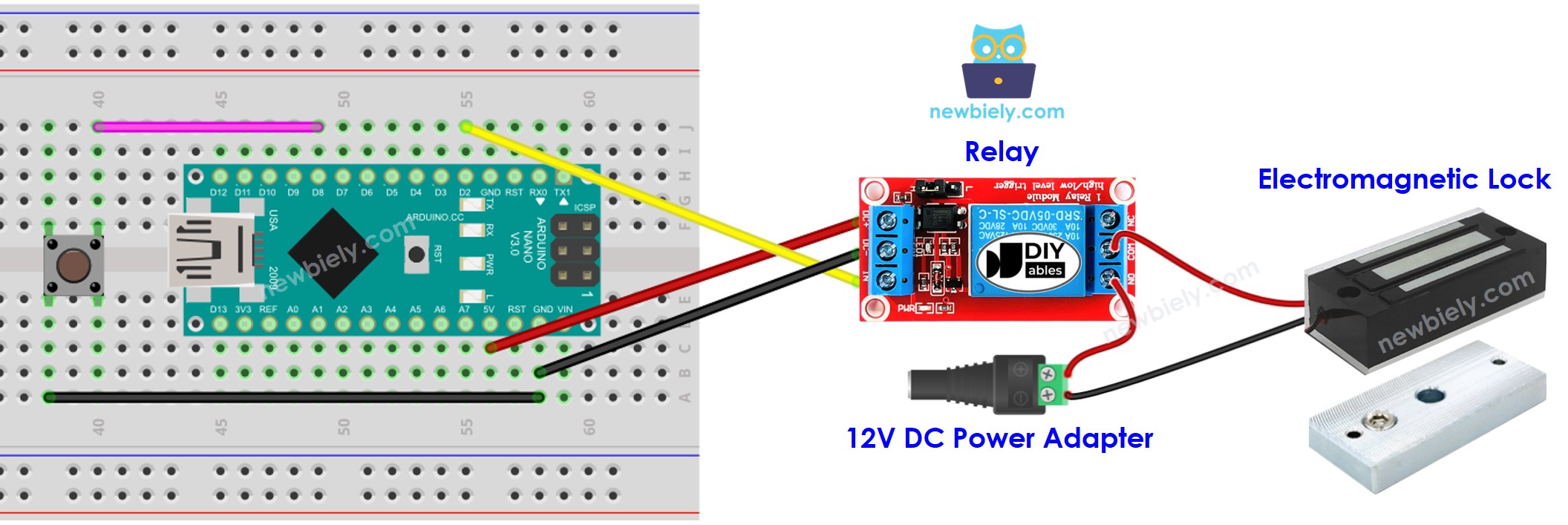
Arduino Nano - Button Control Electromagnetic Lock
The tutorial instructs you how to use Arduino Nano and button to control the door lock by using an electromagnetic lock. When the button is pressed, the door will be unlocked for a specific time (e.g. 10 seconds). After that, it will be locked again.
We will progress by two steps from easy to difficult:
Or you can buy the following kits:
Disclosure: Some of the links provided in this section are Amazon affiliate links. We may receive a commission for any purchases made through these links at no additional cost to you.
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand,
DIYables .
If you are unfamiliar with electromagnetic locks and buttons (including pinouts, functionality, and programming), the following tutorials can help:
#define BUTTON_PIN 8
#define RELAY_PIN 2
int prev_button_state;
int button_state;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(BUTTON_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(RELAY_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, HIGH);
button_state = digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN);
}
void loop() {
prev_button_state = button_state;
button_state = digitalRead(BUTTON_PIN);
if(prev_button_state == HIGH && button_state == LOW) {
Serial.println("The button is pressed");
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, LOW);
delay(10000);
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, HIGH);
}
}
Connect an Arduino Nano to a PC using a USB cable.
Open the Arduino IDE, select the appropriate board and port.
Copy the code above and open it in the Arduino IDE.
Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to upload the code to the Arduino Nano.
Place the armature plate near the electromagnet.
Press the button once.
Check out the attraction between the armature plate and the electromagnet for 10 seconds.
Check out the line-by-line explanation contained in the comments of the source code!
※ NOTE THAT:
In practice, the code mentioned above may not always work correctly. To guarantee its proper functioning, we need to debounce for the button. Debouncing for the button is not a straightforward task for beginners. However, thanks to the ezButton library, it can be done easily.
Why is debouncing necessary?. See the Arduino Nano - Button Debounce tutorial for more information.
#include <ezButton.h>
#define BUTTON_PIN 8
#define RELAY_PIN 2
ezButton button(BUTTON_PIN);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(RELAY_PIN, OUTPUT);
button.setDebounceTime(50);
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
button.loop();
if(button.isPressed()) {
Serial.println("The button is pressed");
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, LOW);
delay(10000);
digitalWrite(RELAY_PIN, HIGH);
}
}
Install the ezButton library. Refer to
How To for instructions.
Open the code in the Arduino IDE and click the Upload button to upload it to the Arduino Nano.
Bring the armature plate close to the electromagnet and press the button once.
Check out the attraction between the armature plate and the electromagnet for 10 seconds.
※ NOTE THAT:
In the code above, we utilized the delay function. Consequently, we do not need to implement debouncing for the button. Nevertheless, we still offer the code with debouncing just in case you would like to execute additional tasks without using the delay function. Refer to How to use millis() instead of delay() for more information.