Arduino Nano - GPS
This tutorial instructs you how to use Arduino Nano with a NEO-6M GPS module. In detail, we will learn:
- How to connect Arduino Nano to a NEO-6M GPS module
- How to program Arduino Nano to read GPS coordinates (longitude, latitude, and altitude) from a NEO-6M GPS module
- How to program Arduino Nano to calculate the distance from the current GPS position to a predefined GPS coordinate (e.g. coordinates of London).
Apart from longitude, latitude, and altitude, Arduino Nano is also able to read GPS speed (km/h), and date time from a NEO-6M GPS module.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Disclosure: Some of the links provided in this section are Amazon affiliate links. We may receive a commission for any purchases made through these links at no additional cost to you.
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of NEO-6M GPS module
NEO-6M GPS module is a GPS module that can provide the following information:
- Longitude
- Latitude
- Altitude
- GPS speed (km/h)
- Date time
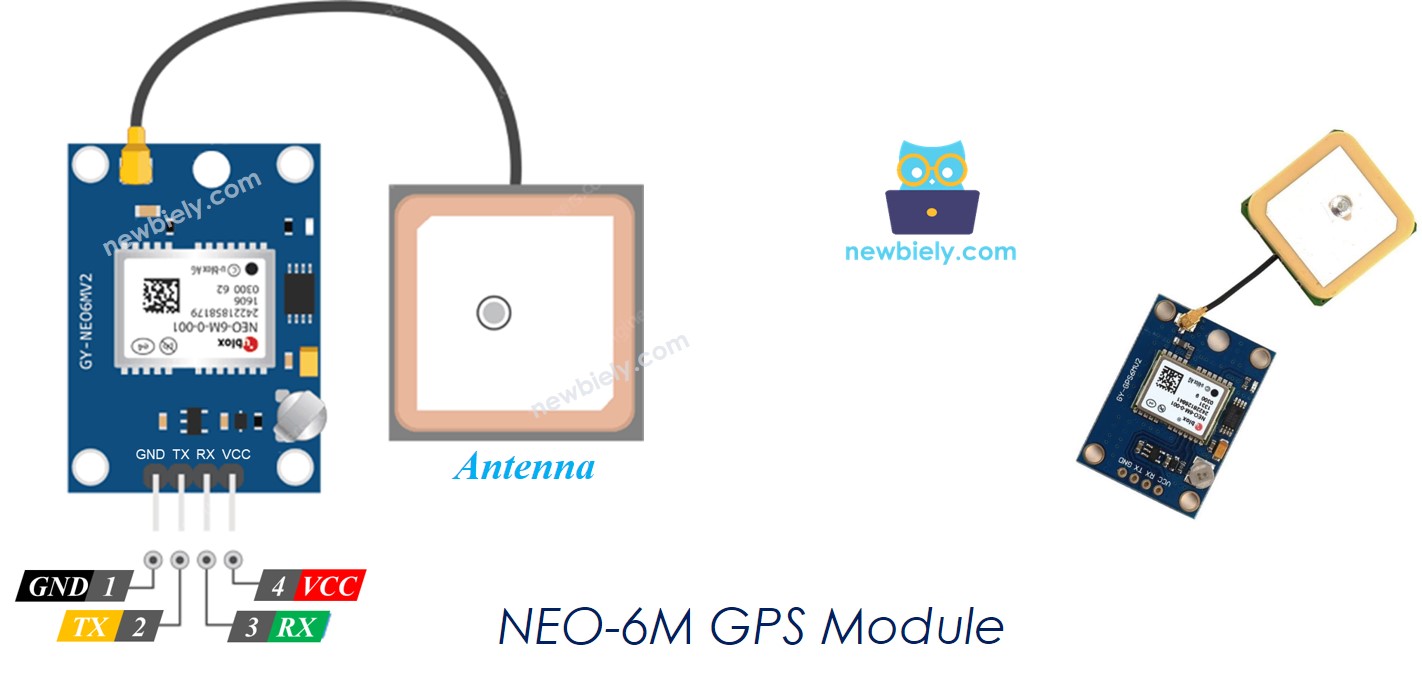
The NEO-6M GPS Module Pinout
The NEO-6M GPS module has four pins:
- The VCC pin: should be connected to the VCC (5V)
- The GND pin: should be connected to the GND (0V)
- The TX pin: is used for serial communication and should be connected to the Serial (or SoftwareSerial) RX pin on Arduino Nano.
- The RX pin: is used for serial communication and should be connected to the Serial (or SoftwareSerial) TX pin on Arduino Nano.
Wiring Diagram
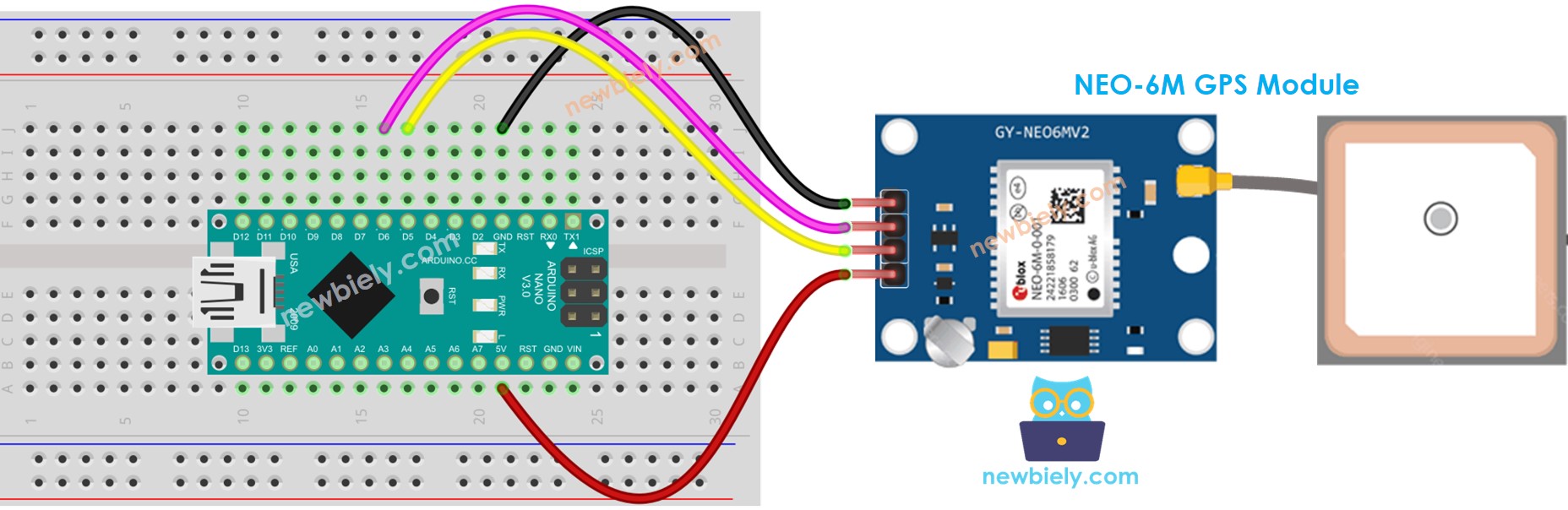
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See The best way to supply power to the Arduino Nano and other components.
Arduino Nano Code
Reading GPS coordinates, speed (km/h), and date time
/*
* This Arduino Nano code was developed by newbiely.com
*
* This Arduino Nano code is made available for public use without any restriction
*
* For comprehensive instructions and wiring diagrams, please visit:
* https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-nano/arduino-nano-gps
*/
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
const int RX_PIN = 6, TX_PIN = 5;
const uint32_t GPS_BAUD = 9600; //Default baud of NEO-6M is 9600
TinyGPSPlus gps; // The TinyGPS++ object
SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(RX_PIN, TX_PIN); // The serial interface to the GPS device
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
gpsSerial.begin(GPS_BAUD);
Serial.println(F("Arduino - GPS module"));
}
void loop() {
if (gpsSerial.available() > 0) {
if (gps.encode(gpsSerial.read())) {
if (gps.location.isValid()) {
Serial.print(F("- latitude: "));
Serial.println(gps.location.lat());
Serial.print(F("- longitude: "));
Serial.println(gps.location.lng());
Serial.print(F("- altitude: "));
if (gps.altitude.isValid())
Serial.println(gps.altitude.meters());
else
Serial.println(F("INVALID"));
} else {
Serial.println(F("- location: INVALID"));
}
Serial.print(F("- speed: "));
if (gps.speed.isValid()) {
Serial.print(gps.speed.kmph());
Serial.println(F(" km/h"));
} else {
Serial.println(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.print(F("- GPS date&time: "));
if (gps.date.isValid() && gps.time.isValid()) {
Serial.print(gps.date.year());
Serial.print(F("-"));
Serial.print(gps.date.month());
Serial.print(F("-"));
Serial.print(gps.date.day());
Serial.print(F(" "));
Serial.print(gps.time.hour());
Serial.print(F(":"));
Serial.print(gps.time.minute());
Serial.print(F(":"));
Serial.println(gps.time.second());
} else {
Serial.println(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.println();
}
}
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
Serial.println(F("No GPS data received: check wiring"));
}
Detailed Instructions
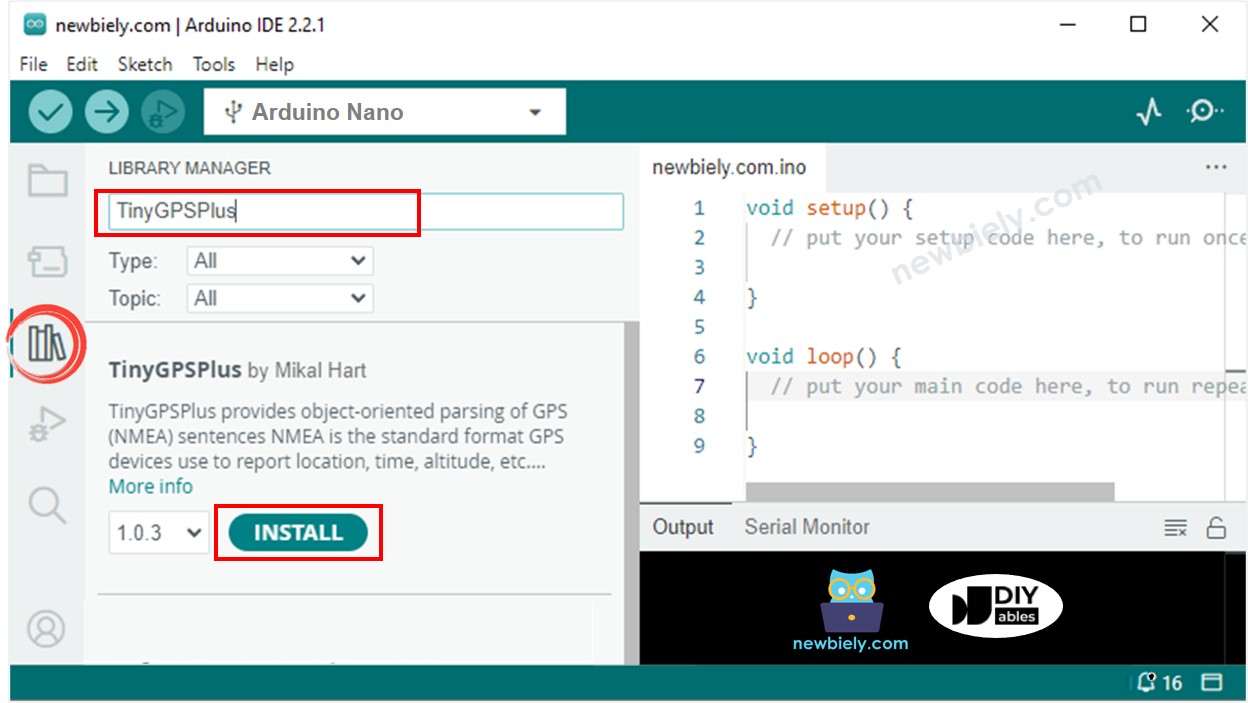
- Click to the Libraries icon on the left bar of the Arduino IDE.
- Search “TinyGPSPlus”, then find the TinyGPSPlus library by Mikal Hart
- Click Install button to install TinyGPSPlus library.
- Copy the code mentioned above and open it in the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button on the Arduino IDE to send the code to the Arduino Nano.
- Check the Serial Monitor to observe the outcome.
COM6
Autoscroll
Clear output
9600 baud
Newline
Calculating the distance from current location to a predefined location
The code below computes the distance between the current location and London (lat:51.508131 , long: -0.128002).
/*
* This Arduino Nano code was developed by newbiely.com
*
* This Arduino Nano code is made available for public use without any restriction
*
* For comprehensive instructions and wiring diagrams, please visit:
* https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-nano/arduino-nano-gps
*/
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
const int RX_PIN = 6, TX_PIN = 5;
const uint32_t GPS_BAUD = 9600; //Default baud of NEO-6M is 9600
TinyGPSPlus gps; // The TinyGPS++ object
SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(RX_PIN, TX_PIN); // The serial interface to the GPS device
const double LONDON_LAT = 51.508131;
const double LONDON_LON = -0.128002;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
gpsSerial.begin(GPS_BAUD);
Serial.println(F("Arduino - GPS module"));
}
void loop() {
if (gpsSerial.available() > 0) {
if (gps.encode(gpsSerial.read())) {
if (gps.location.isValid()) {
double latitude = gps.location.lat();
double longitude = gps.location.lng();
unsigned long distanceKm = TinyGPSPlus::distanceBetween(latitude, longitude, LONDON_LAT, LONDON_LON) / 1000;
Serial.print(F("- latitude: "));
Serial.println(latitude);
Serial.print(F("- longitude: "));
Serial.println(longitude);
Serial.print(F("- distance to London: "));
Serial.println(distanceKm);
} else {
Serial.println(F("- location: INVALID"));
}
Serial.println();
}
}
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
Serial.println(F("No GPS data received: check wiring"));
}
Detailed Instructions
- Copy the code and open it with the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button on the Arduino IDE to compile and upload the code to the Arduino Nano.
- View the outcome on the Serial Monitor.
COM6
Autoscroll
Clear output
9600 baud
Newline
