Arduino Nano - Read Config from SD Card
This tutorial instructs you how to use a config file on a Micro SD Card. Specifically, we will be looking at:
How to create a config.txt file on a Micro SD Card, containing key-value pairs
How to read the config from the Micro SD Card and save it into an int variable
How to read the config from the Micro SD Card and save it into a float variable
How to read the config from the Micro SD Card and save it into a String variable
Or you can buy the following kits:
Disclosure: Some of the links provided in this section are Amazon affiliate links. We may receive a commission for any purchases made through these links at no additional cost to you.
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand,
DIYables .
If you are unfamiliar with the Micro SD Card Module, including its pinout, how it works, and how to program it, check out the Arduino Nano - Micro SD Card tutorial.
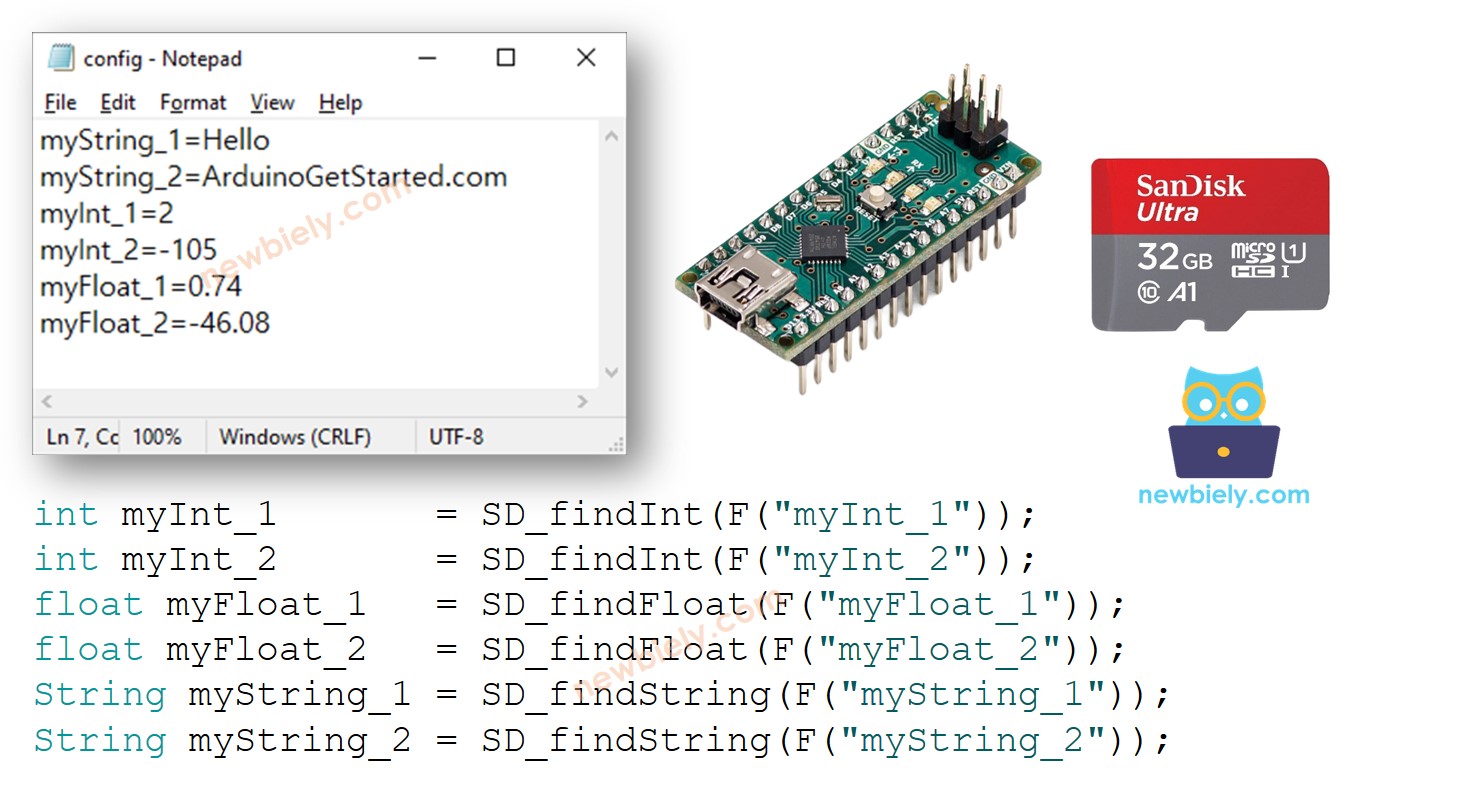
Each key-value pair is stored on the Micro SD Card in its own line. The key and value are divided by an = sign. A newline character separates each key-value pair from the others.
The Arduino Nano code will search for the key and locate the associated value, storing it in a variable. The variable can be of type int, float, or String.
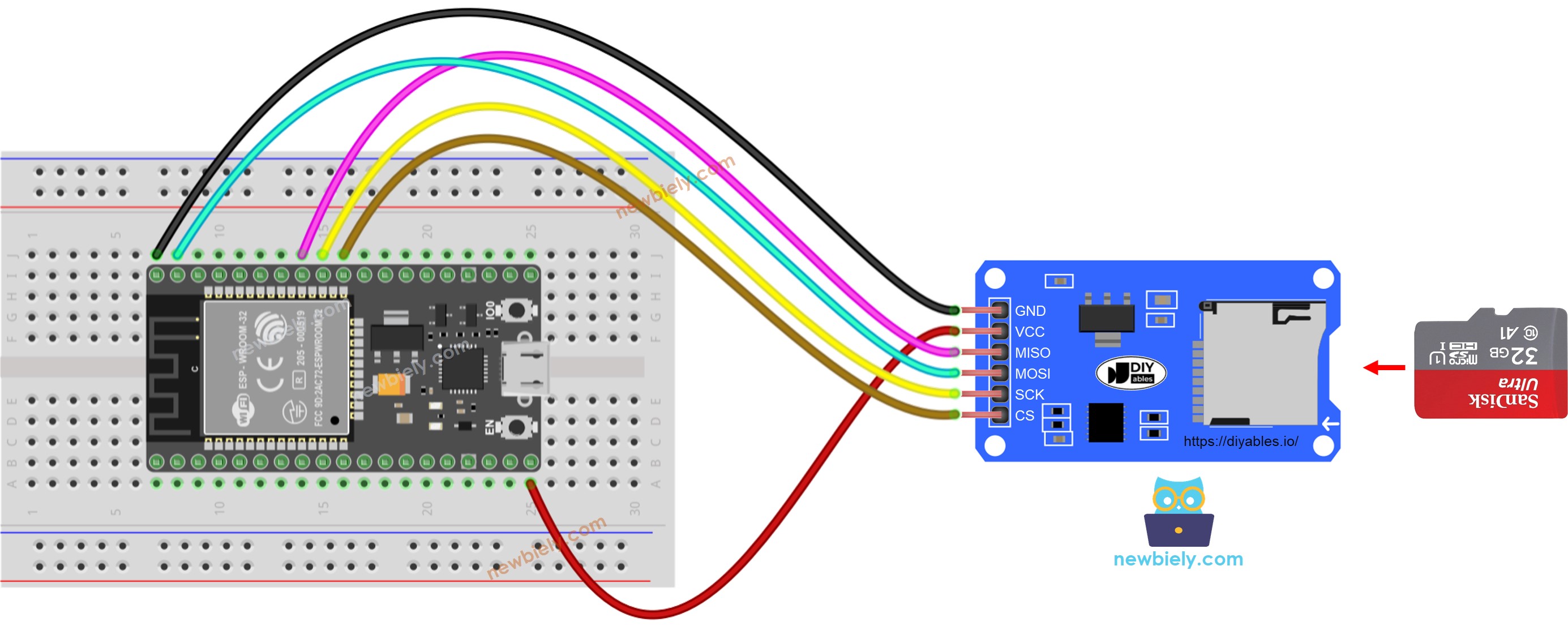
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
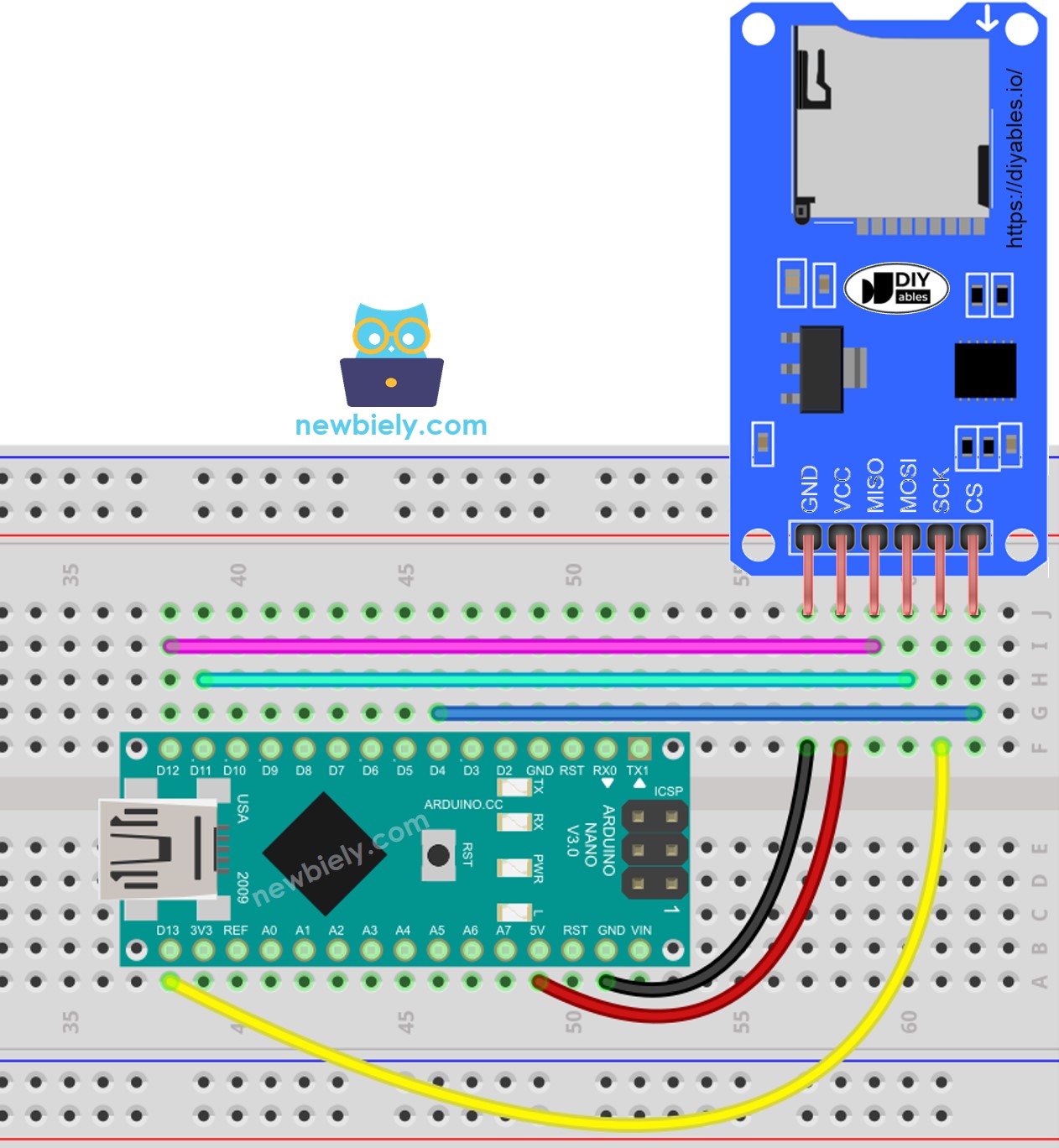
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See The best way to supply power to the Arduino Nano and other components.
myString_1=Hello
myString_2=ArduinoGetStarted.com
myInt_1=2
myInt_2=-105
myFloat_1=0.74
myFloat_2=-46.08
Attach the Micro SD Card to the PC with a USB 3.0 SD Card Reader.
Ensure that the Micro SD Card is formatted FAT16 or FAT32 (you can search online for instructions).
Place the config.txt file in the main folder of the Micro SD Card.
Detach the Micro SD Card from the PC.
Connect the Micro SD Card to the Arduino Nano using the Micro SD Card Module, following the wiring diagram.
Copy the code below and open it with the Arduino IDE.
#include <SD.h>
#define PIN_SPI_CS 4
#define FILE_NAME "config.txt"
#define KEY_MAX_LENGTH 30
#define VALUE_MAX_LENGTH 30
int myInt_1;
int myInt_2;
float myFloat_1;
float myFloat_2;
String myString_1;
String myString_2;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (!SD.begin(PIN_SPI_CS)) {
Serial.println(F("SD Card failed, or not present"));
while (1);
}
Serial.println(F("SD Card initialized."));
myInt_1 = SD_findInt(F("myInt_1"));
myInt_2 = SD_findInt(F("myInt_2"));
myFloat_1 = SD_findFloat(F("myFloat_1"));
myFloat_2 = SD_findFloat(F("myFloat_2"));
myString_1 = SD_findString(F("myString_1"));
myString_2 = SD_findString(F("myString_2"));
Serial.print(F("myInt_1 = "));
Serial.println(myInt_1);
Serial.print(F("myInt_2 = "));
Serial.println(myInt_2);
Serial.print(F("myFloat_1 = "));
Serial.println(myFloat_1);
Serial.print(F("myFloat_2 = "));
Serial.println(myFloat_2);
Serial.print(F("myString_1 = "));
Serial.println(myString_1);
Serial.print(F("myString_2 = "));
Serial.println(myString_2);
}
void loop() {
}
bool SD_available(const __FlashStringHelper * key) {
char value_string[VALUE_MAX_LENGTH];
int value_length = SD_findKey(key, value_string);
return value_length > 0;
}
int SD_findInt(const __FlashStringHelper * key) {
char value_string[VALUE_MAX_LENGTH];
int value_length = SD_findKey(key, value_string);
return HELPER_ascii2Int(value_string, value_length);
}
float SD_findFloat(const __FlashStringHelper * key) {
char value_string[VALUE_MAX_LENGTH];
int value_length = SD_findKey(key, value_string);
return HELPER_ascii2Float(value_string, value_length);
}
String SD_findString(const __FlashStringHelper * key) {
char value_string[VALUE_MAX_LENGTH];
int value_length = SD_findKey(key, value_string);
return HELPER_ascii2String(value_string, value_length);
}
int SD_findKey(const __FlashStringHelper * key, char * value) {
File configFile = SD.open(FILE_NAME);
if (!configFile) {
Serial.print(F("SD Card: error on opening file "));
Serial.println(FILE_NAME);
return;
}
char key_string[KEY_MAX_LENGTH];
char SD_buffer[KEY_MAX_LENGTH + VALUE_MAX_LENGTH + 1];
int key_length = 0;
int value_length = 0;
PGM_P keyPoiter;
keyPoiter = reinterpret_cast<PGM_P>(key);
byte ch;
do {
ch = pgm_read_byte(keyPoiter++);
if (ch != 0)
key_string[key_length++] = ch;
} while (ch != 0);
while (configFile.available()) {
int buffer_length = configFile.readBytesUntil('\n', SD_buffer, 100);
if (SD_buffer[buffer_length - 1] == '\r')
buffer_length--;
if (buffer_length > (key_length + 1)) {
if (memcmp(SD_buffer, key_string, key_length) == 0) {
if (SD_buffer[key_length] == '=') {
value_length = buffer_length - key_length - 1;
memcpy(value, SD_buffer + key_length + 1, value_length);
break;
}
}
}
}
configFile.close();
return value_length;
}
int HELPER_ascii2Int(char *ascii, int length) {
int sign = 1;
int number = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = *(ascii + i);
if (i == 0 && c == '-')
sign = -1;
else {
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
number = number * 10 + (c - '0');
}
}
return number * sign;
}
float HELPER_ascii2Float(char *ascii, int length) {
int sign = 1;
int decimalPlace = 0;
float number = 0;
float decimal = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = *(ascii + i);
if (i == 0 && c == '-')
sign = -1;
else {
if (c == '.')
decimalPlace = 1;
else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
if (!decimalPlace)
number = number * 10 + (c - '0');
else {
decimal += ((float)(c - '0') / pow(10.0, decimalPlace));
decimalPlace++;
}
}
}
}
return (number + decimal) * sign;
}
String HELPER_ascii2String(char *ascii, int length) {
String str;
str.reserve(length);
str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = *(ascii + i);
str += String(c);
}
return str;
}
SD Card initialized.
myInt_1 = 2
myInt_2 = -105
myFloat_1 = 0.74
myFloat_2 = -46.08
myString_1 = Hello
myString_2 = ArduinoGetStarted.com
You can now alter the code in order to include additional variables.
※ NOTE THAT:
The code does not take into account the sequence of key-value pairs. It will search through the file from the start to the finish until the key is found.