ESP8266 - Car
One of the coolest things to try if you're just starting with ESP8266 is making a robot car. In this guide, we'll learn how to use ESP8266 to build a robot car and control it with a IR remote control. We'll learn how to make a Bluetooth robot car in another tutorial.

Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Robot Car
In the ESP8266 context, the robot car is often called by different names like robot car, RC car, remote control car, smart car, or DIY car. It can be controlled from a distance without any wires. You can use either a special remote control that uses infrared light or a smartphone app through Bluetooth or WiFi. The robot car can go left or right and also go forward or backward.
A 2WD (Two-Wheel Drive) car for ESP8266 is a small robotic vehicle that you can build and control using an ESP8266 board. It typically consists of the following components:
- Chassis: The base or frame of the car,where all other components are mounted.
- Wheels: The two wheels that provide locomotion to the car. They are attached to two DC motor.
- Motors: Two DC motors are used to drive the two wheels.
- Motor Driver: The motor driver board is an essential component that interfaces between the ESP8266 and the motors. It takes signals from the ESP8266 and provides the necessary power and control to the motors.
- ESP8266 Board: The brain of the car. It reads inputs from sensors and user commands and controls the motors accordingly.
- Power Source: The 2WD car requires a power source, usually batteries and a battery holder, to power the motors and the ESP8266 board.
- Wireless receiver: an infrared, Bluetooth or WiFi module for wireless communication with a remote control or smartphone.
- Optional Components: Depending on your project's complexity, you may add various optional components like sensors (e.g., ultrasonic sensors for obstacle avoidance, line-following sensors), and more.
In this tutorial, to make it simple, we will use:
- 2WD Car kit (including Chassis, wheels, motors, battery holder)
- L298N Motor Driver
- IR infrared kit (including IR controller and IR receiver)
Check the hardware list at the top of this page.
How It Works
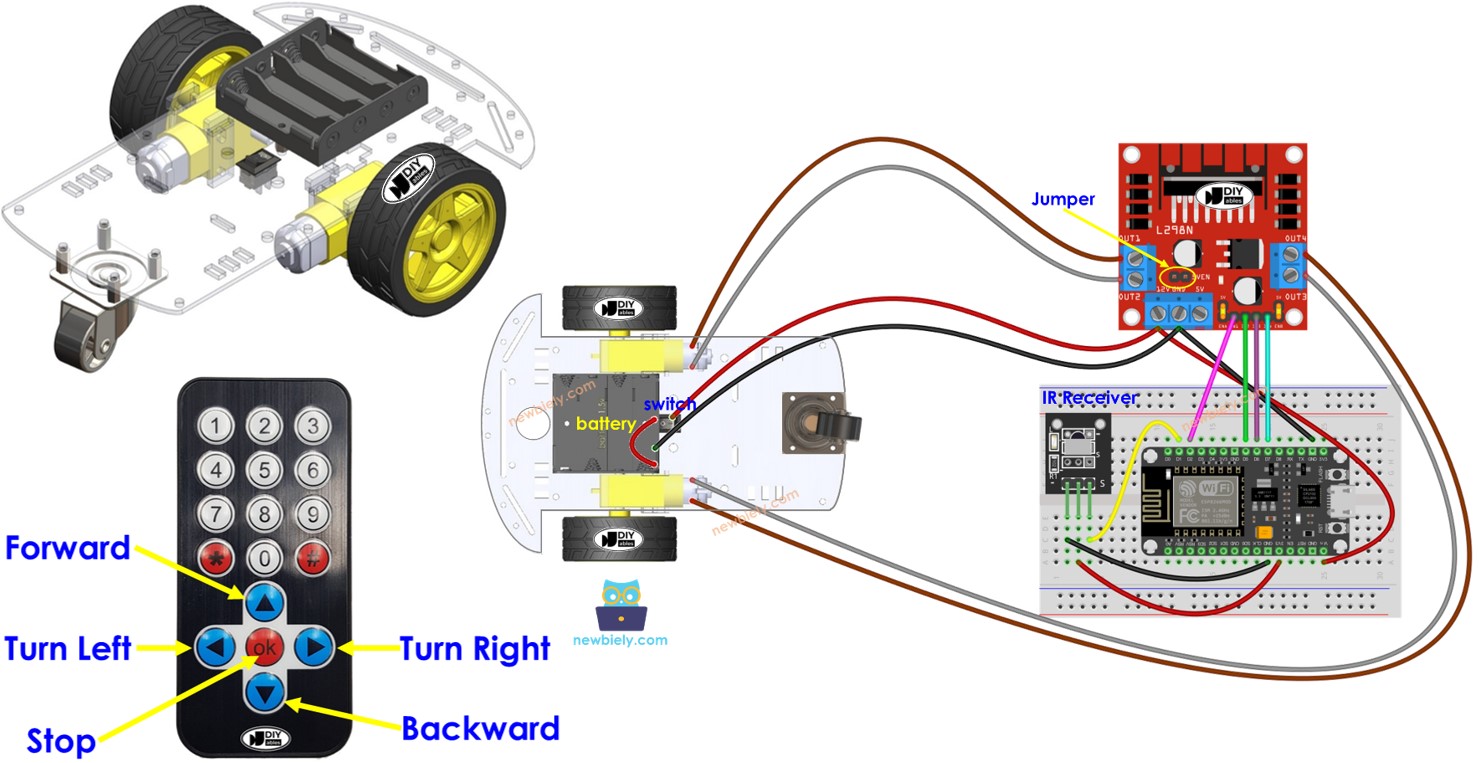
- ESP8266 connects to the DC motors of the robot car through L298N motor driver module.
- ESP8266 connects to an IR receiver.
- The battery powers ESP8266, DC motors, motor driver, and IR receiver.
- Users press the UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT/OK keys on the IR remote controller.
- ESP8266 receives the UP/DOWN/LEFT/RIGHT/OK commands through the IR receiver.
- ESP8266 controls the car to move FORWARD/BACKWARD/LEFT/RIGHT/STOP by controlling the DC motor via the motor driver.
Wiring Diagram
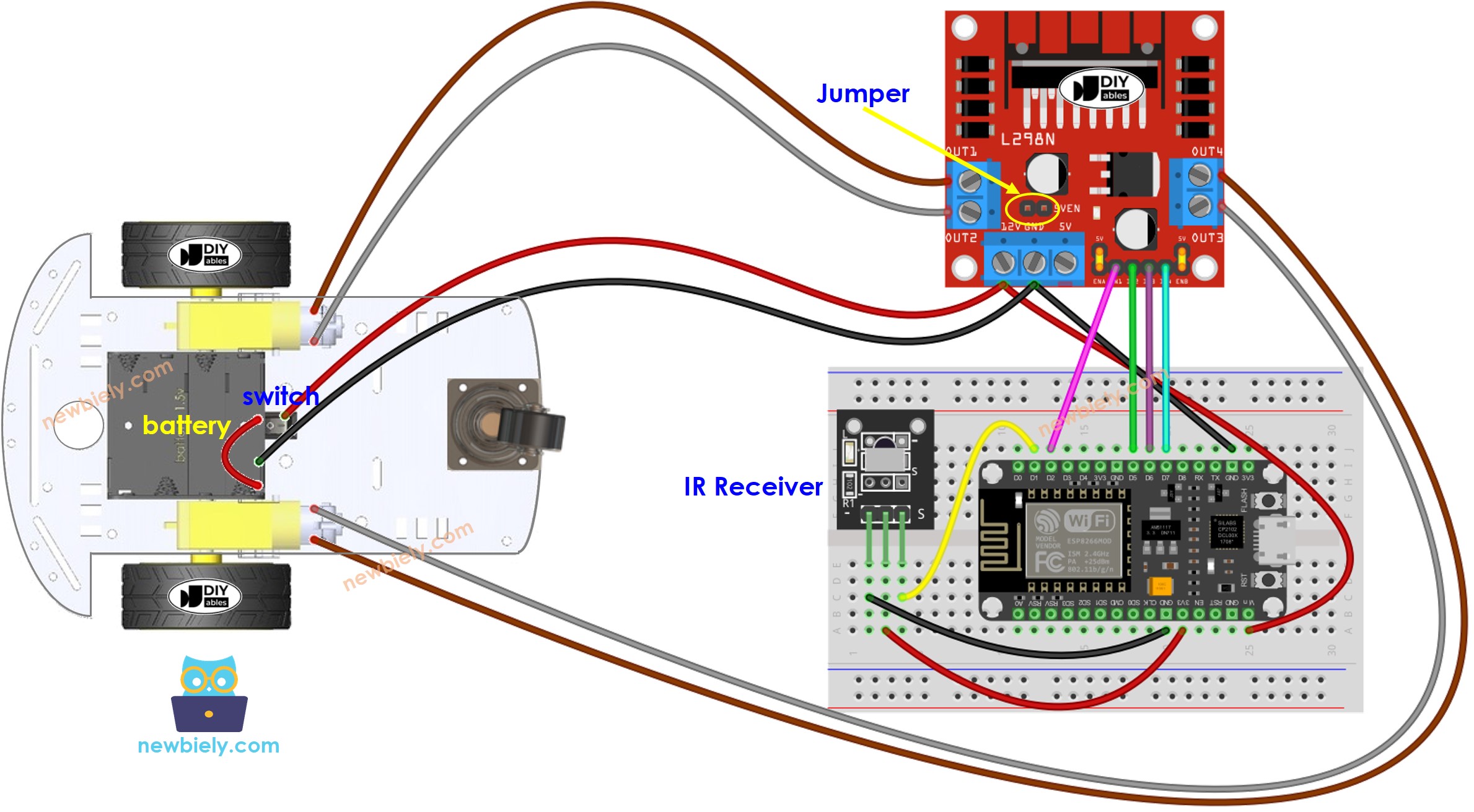
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
Usually, It requires two sources of power:
- One for the motor (indirectly through the L298N module).
- Another for the ESP8266 board, the L298N module, and the IR receiver.
However, there's a method to simplify this by using only one power source for everything. You can achieve this by using four 1.5V batteries (totaling 6V). Here's how you can do it:
- Connect the batteries to the L298N module as shown in the diagram.
- Place two jumpers that connect the ENA and ENB pins to 5 volts on the L298N module.
- Remove a jumper labeled 5VEN, which is marked with a yellow circle on the diagram.
- Do the remaining wiring as above diagram.
ESP8266 Code
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Install DIYables_IRcontroller library on Arduino IDE by following this instruction
- Do the wiring as the diagram shown above.
- Disconnect the wire from the Vin on the ESP8266 because we will power ESP8266 via USB cable when uploading code.
- Flip the car upside down so that the wheels are on top.
- Copy the provided code and open it in the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to transfer the code to the ESP8266.
- Use the IR remote controller to make the car go forward, backward, left, right, or stop.
- Check if the wheels move correctly according to your commands.
- If the wheels move the wrong way, swap the wires of the DC motor on the L298N module.
- You can also see the results on the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE.
- If everything is going well, unplug the USB cable from the ESP8266, and then connect the wire back into the Vin 5V pin. This will give power to the ESP8266 from the battery.
- Flip the car back to its normal position with the wheels on the ground.
- Have fun controlling the car!
Code Explanation
Read the line-by-line explanation in comment lines of code!
You can learn more about the code by checking the following tutorials:
- ESP8266 - Infrared Remote Control tutorial
- ESP8266 - DC motor tutorial
You can extend this project by:
- Adding obstacle avoidance sensors to immidilately stop the car if an obstacle is detected.
- Adding function to control the speed of car (see ESP8266 - DC motor tutorial). The provided code controls car with full speed.
