ESP8266 - Electromagnetic Lock
This tutorial instructs you how to use ESP8266 to control the electromagnetic lock, which is also known as EM lock, magnetic lock, or maglock.
An alternative to the electromagnetic lock is the solenoid lock. Please refer to the ESP8266 - Solenoid Lock tutorial for more information.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Electromagnetic Lock
The electromagnetic lock is commonly used to secure a door. It is typically operated with a switch, fingerprint reader, RFID/NFC reader, keypad, or application on a PC/mobile device to control access to a door, building gate, etc.
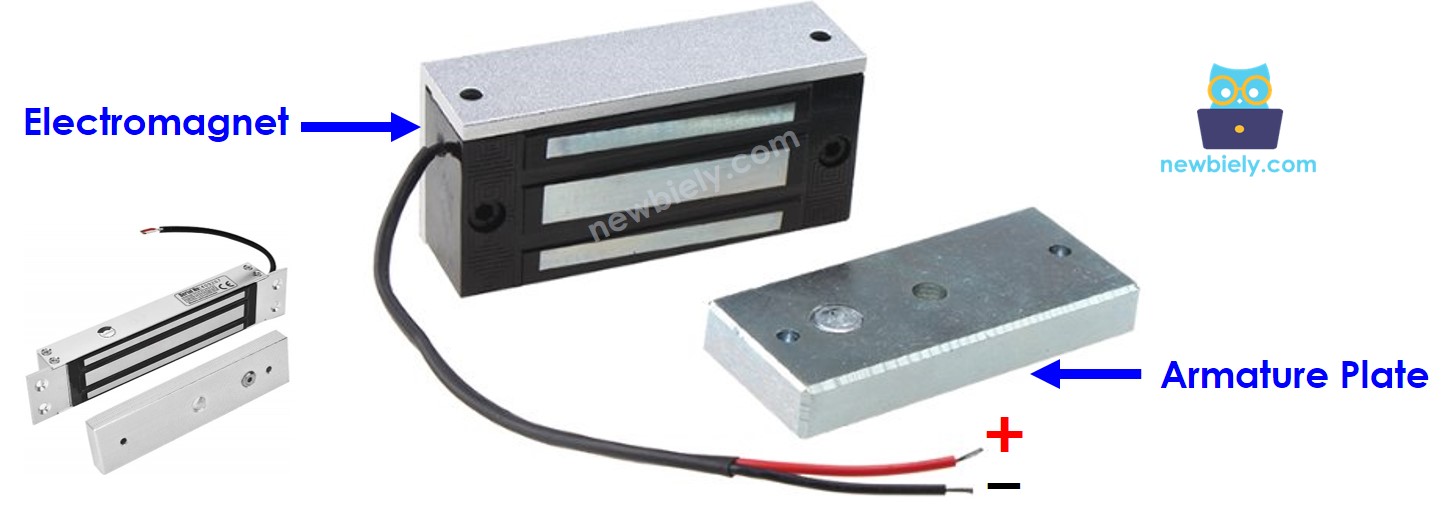
The Electromagnetic Lock Pinout
An electromagnetic lock consists of two parts:
- An electromagnet, which has two pins
- An armature plate
How It Works
- When the electromagnet is powered, a current passing through it generates a magnetic flux that causes the armature plate to be attracted to the electromagnet, resulting in a locking action.
- Conversely, when the electromagnet is NOT powered, there is no magnetic flux and the armature plate does NOT attract to the electromagnet, thus creating an unlocking action.
※ NOTE THAT:
The electromagnetic lock typically requires 12V, 24V or 48V power supply. Consequently, it CANNOT be connected directly to an ESP8266 pin. A relay must be used for this purpose.
If we link the electromagnetic lock to a relay (in normally open mode):
- When the relay is not activated, the door is unlocked
- When the relay is triggered, the door is locked
Connecting ESP8266 to a relay enables us to program it to control the electromagnetic lock. To find out more about relays, please refer to ESP8266 - Relay tutorial.
For installation, the armature plate should be affixed to the door/window (the part that moves), and the electromagnet should be attached to the door frame (the stationary part). When the door is shut, the two components are in contact.
Wiring Diagram
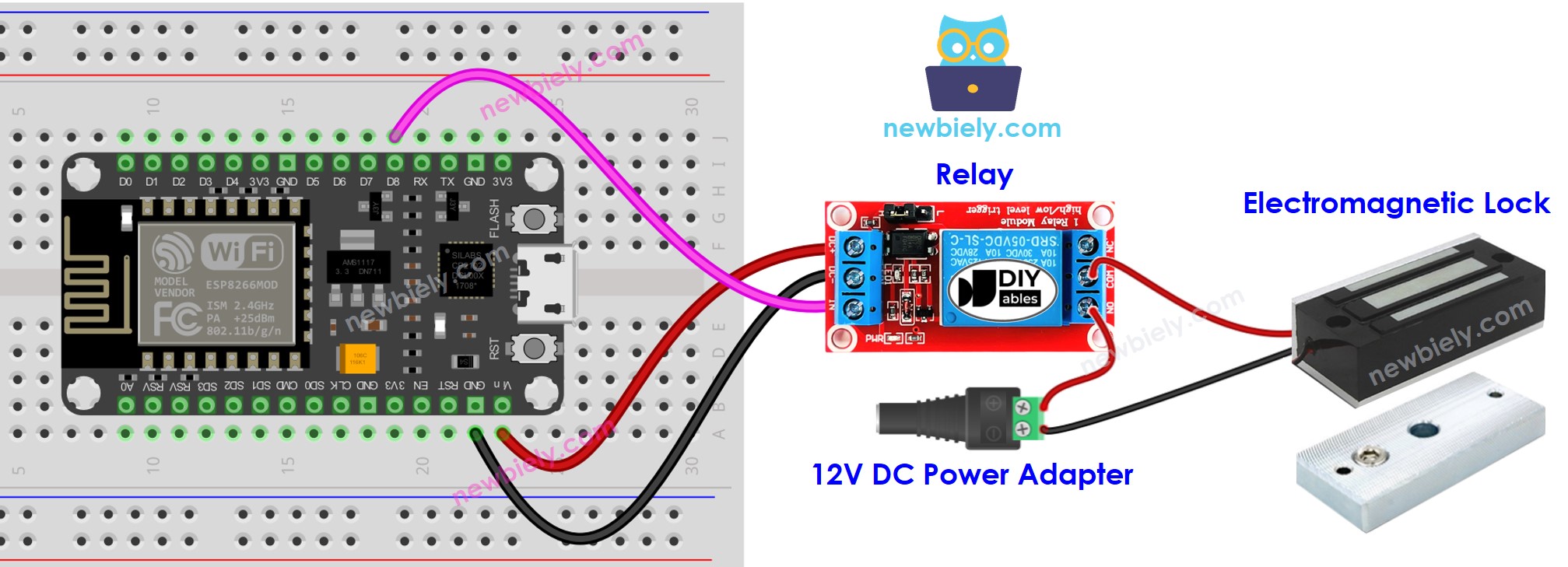
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
ESP8266 Code for Controlling EM Lock
The code below will cause the door to be locked and unlocked every 5 seconds.
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Copy the code and open it with the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button on the Arduino IDE to compile and upload the code to the ESP8266.
- Bring the armature plate close to the electromagnet.
- Check out the attraction between the armature plate and the electromagnet.
