ESP8266 - Gmail
This guide will show you how to set up an ESP8266 to send an email through your Gmail account. The email will be sent from a Gmail account and can be received by any email account.

Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Disclosure: Some of the links provided in this section are Amazon affiliate links. We may receive a commission for any purchases made through these links at no additional cost to you.
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Pre-Preparation
To use the code, you need a Gmail account and a special app password. Here are the key details to remember:
- Create a new Gmail account specifically for testing instead of using your regular one, to avoid any issues.
- The password used in the ESP8266 code is not the same as your Gmail account password. You need to obtain an "App Password" from your Google Account by following certain instructions.
Here are the steps, one by one:
- Create a new Gmail account.
- Log into the account you created.
- Go to your Google Account.
- Click on the "Security" section.
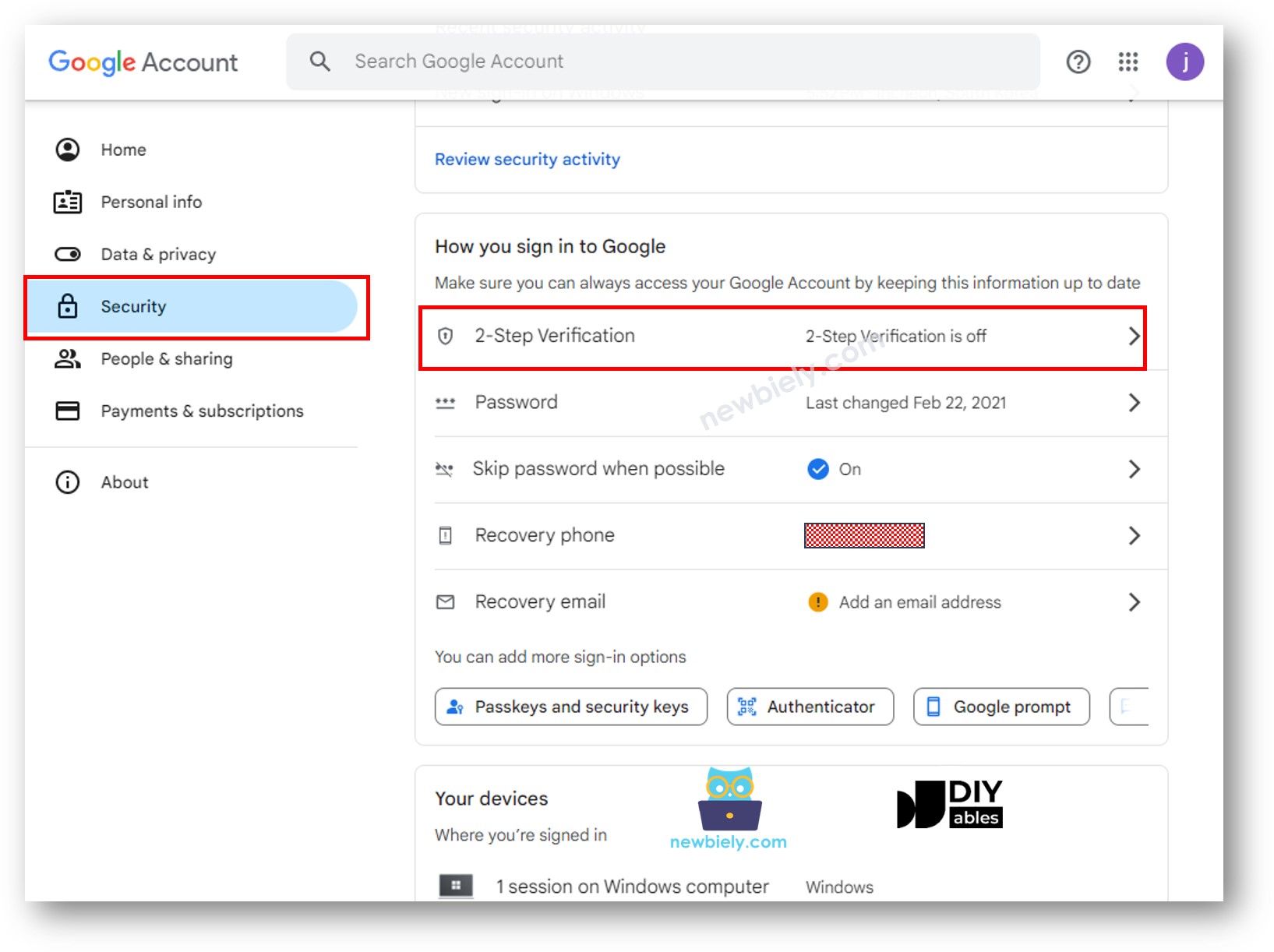
- Activate 2-Step Verification (This is essential before you can use app passwords).
- Visit the Google App Passwords website and create an app password. You can name it whatever you like.
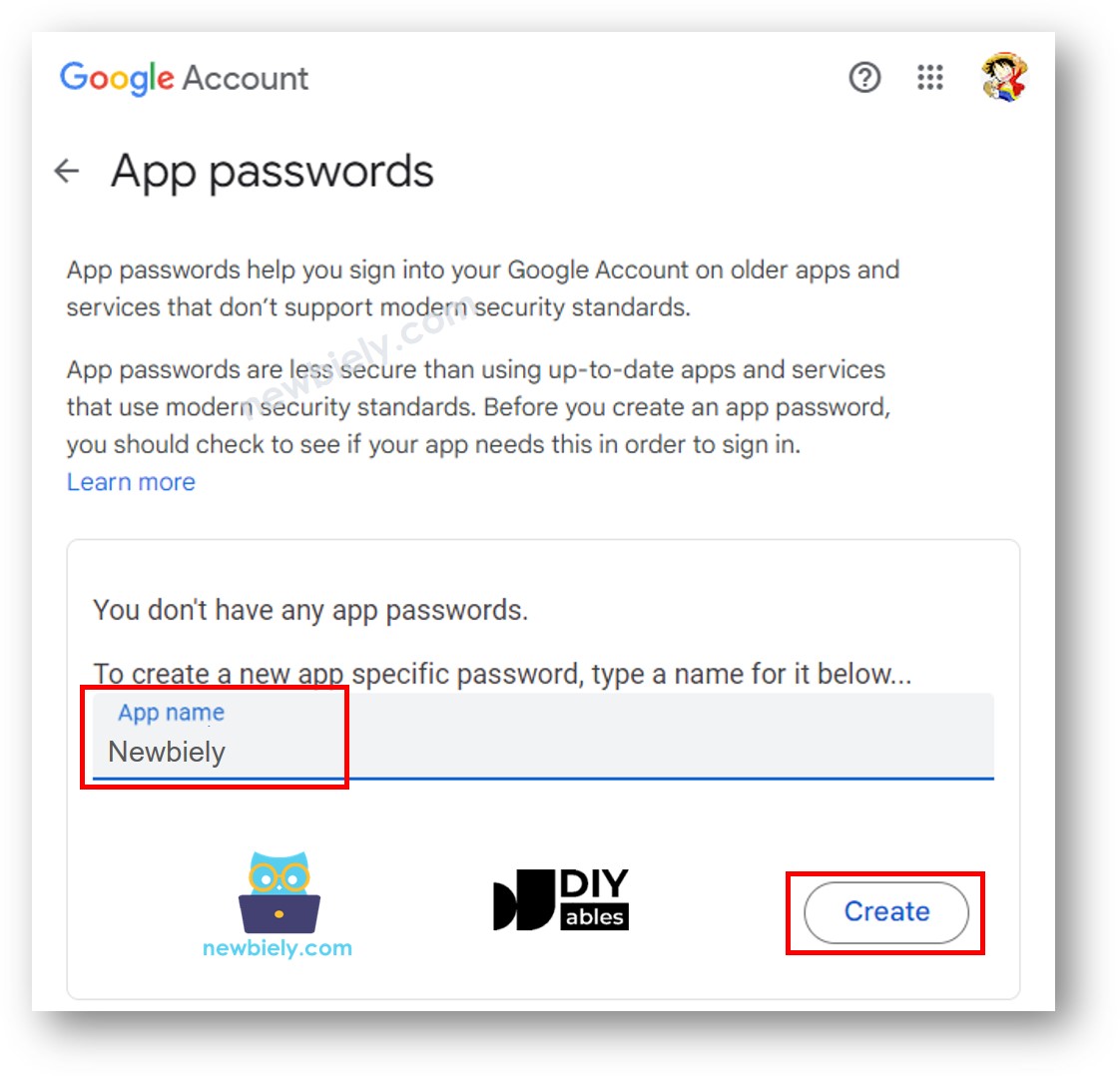
- Click the Create button and a 16-digit password will be displayed for you.
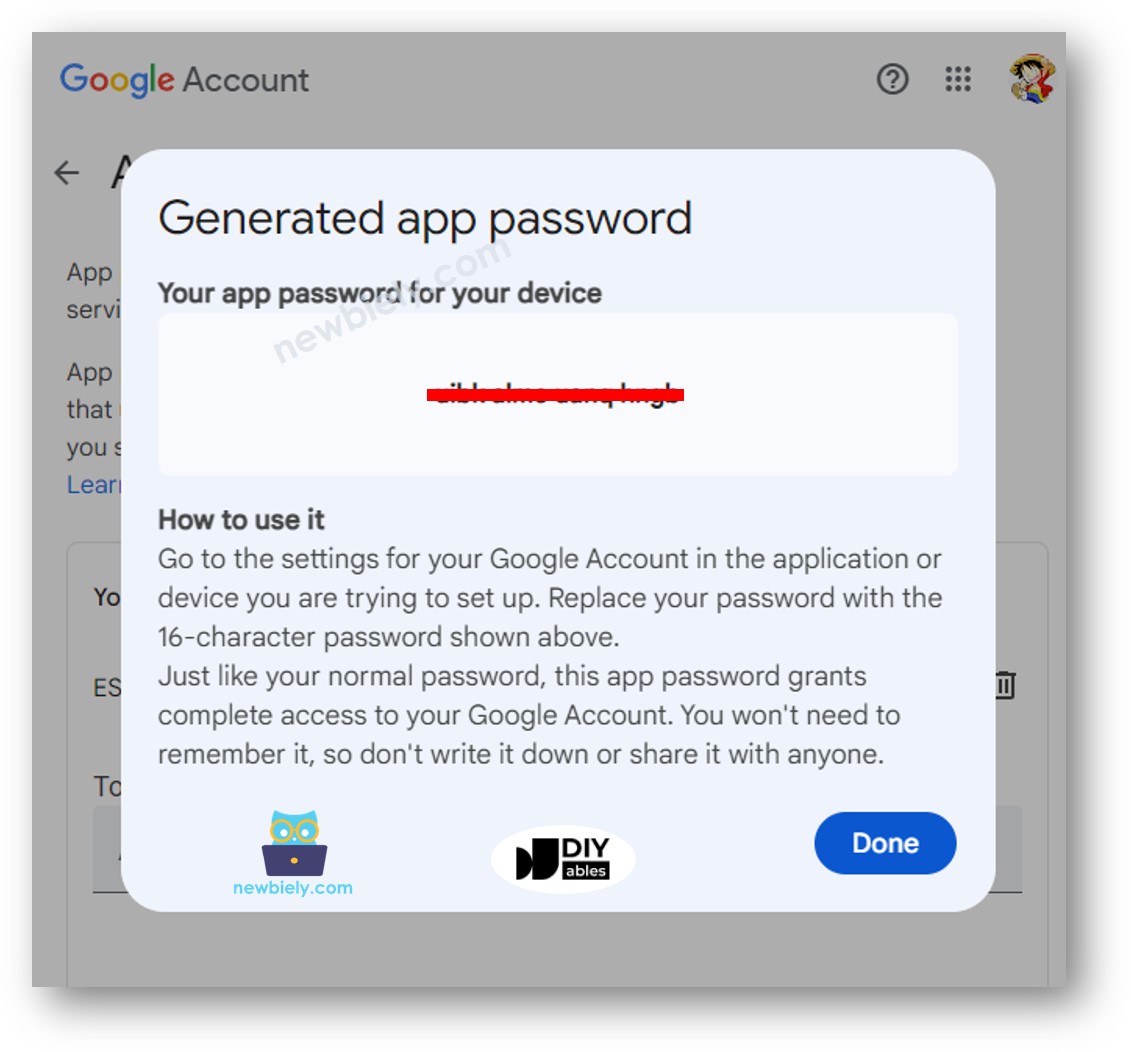
- Save this 16-digit number. You will need it for the ESP8266 code in the next step.
※ NOTE THAT:
Google's user interface may change. If you do not see "App Passwords" after following the steps above, search for "How to get Google App Passwords" to find updated instructions.
ESP8266 Code
/*
* This ESP8266 NodeMCU code was developed by newbiely.com
*
* This ESP8266 NodeMCU code is made available for public use without any restriction
*
* For comprehensive instructions and wiring diagrams, please visit:
* https://newbiely.com/tutorials/esp8266/esp8266-gmail
*/
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <ESP_Mail_Client.h>
#define WIFI_SSID "YOUR_WIFI_SSID" // CHANGE IT
#define WIFI_PASSWORD "YOUR_WIFI_PASSWORD" // CHANGE IT
// the sender email credentials
#define SENDER_EMAIL "xxxxxx@gmail.com" // CHANGE IT
#define SENDER_PASSWORD "xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx" // CHANGE IT to your Google App password
#define RECIPIENT_EMAIL "xxxxxx@gmail.com" // CHANGE IT
#define SMTP_HOST "smtp.gmail.com"
#define SMTP_PORT 587
SMTPSession smtp;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
WiFi.begin(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASSWORD);
Serial.print("Connecting to Wi-Fi");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(300);
}
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connected with IP: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.println();
String subject = "Email Notification from ESP8266";
String textMsg = "This is an email sent from ESP8266.\n";
textMsg += "Sensor value: ";
textMsg += "15"; // OR replace this value read from a sensor
gmail_send(subject, textMsg);
}
void loop() {
// YOUR OTHER CODE HERE
}
void gmail_send(String subject, String textMsg) {
// set the network reconnection option
MailClient.networkReconnect(true);
smtp.debug(1);
smtp.callback(smtpCallback);
Session_Config config;
// set the session config
config.server.host_name = SMTP_HOST;
config.server.port = SMTP_PORT;
config.login.email = SENDER_EMAIL;
config.login.password = SENDER_PASSWORD;
config.login.user_domain = F("127.0.0.1");
config.time.ntp_server = F("pool.ntp.org,time.nist.gov");
config.time.gmt_offset = 3;
config.time.day_light_offset = 0;
// declare the message class
SMTP_Message message;
// set the message headers
message.sender.name = F("ESP8266");
message.sender.email = SENDER_EMAIL;
message.subject = subject;
message.addRecipient(F("To Whom It May Concern"), RECIPIENT_EMAIL);
message.text.content = textMsg;
message.text.transfer_encoding = "base64";
message.text.charSet = F("utf-8");
message.priority = esp_mail_smtp_priority::esp_mail_smtp_priority_low;
// set the custom message header
message.addHeader(F("Message-ID: <abcde.fghij@gmail.com>"));
// connect to the server
if (!smtp.connect(&config)) {
Serial.printf("Connection error, Status Code: %d, Error Code: %d, Reason: %s\n", smtp.statusCode(), smtp.errorCode(), smtp.errorReason().c_str());
return;
}
if (!smtp.isLoggedIn()) {
Serial.println("Not yet logged in.");
} else {
if (smtp.isAuthenticated())
Serial.println("Successfully logged in.");
else
Serial.println("Connected with no Auth.");
}
// start sending Email and close the session
if (!MailClient.sendMail(&smtp, &message))
Serial.printf("Error, Status Code: %d, Error Code: %d, Reason: %s\n", smtp.statusCode(), smtp.errorCode(), smtp.errorReason().c_str());
}
// callback function to get the Email sending status
void smtpCallback(SMTP_Status status) {
// print the current status
Serial.println(status.info());
// print the sending result
if (status.success()) {
Serial.println("----------------");
Serial.printf("Message sent success: %d\n", status.completedCount());
Serial.printf("Message sent failed: %d\n", status.failedCount());
Serial.println("----------------\n");
for (size_t i = 0; i < smtp.sendingResult.size(); i++) {
// get the result item
SMTP_Result result = smtp.sendingResult.getItem(i);
Serial.printf("Message No: %d\n", i + 1);
Serial.printf("Status: %s\n", result.completed ? "success" : "failed");
Serial.printf("Date/Time: %s\n", MailClient.Time.getDateTimeString(result.timestamp, "%B %d, %Y %H:%M:%S").c_str());
Serial.printf("Recipient: %s\n", result.recipients.c_str());
Serial.printf("Subject: %s\n", result.subject.c_str());
}
Serial.println("----------------\n");
// free the memory
smtp.sendingResult.clear();
}
}
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
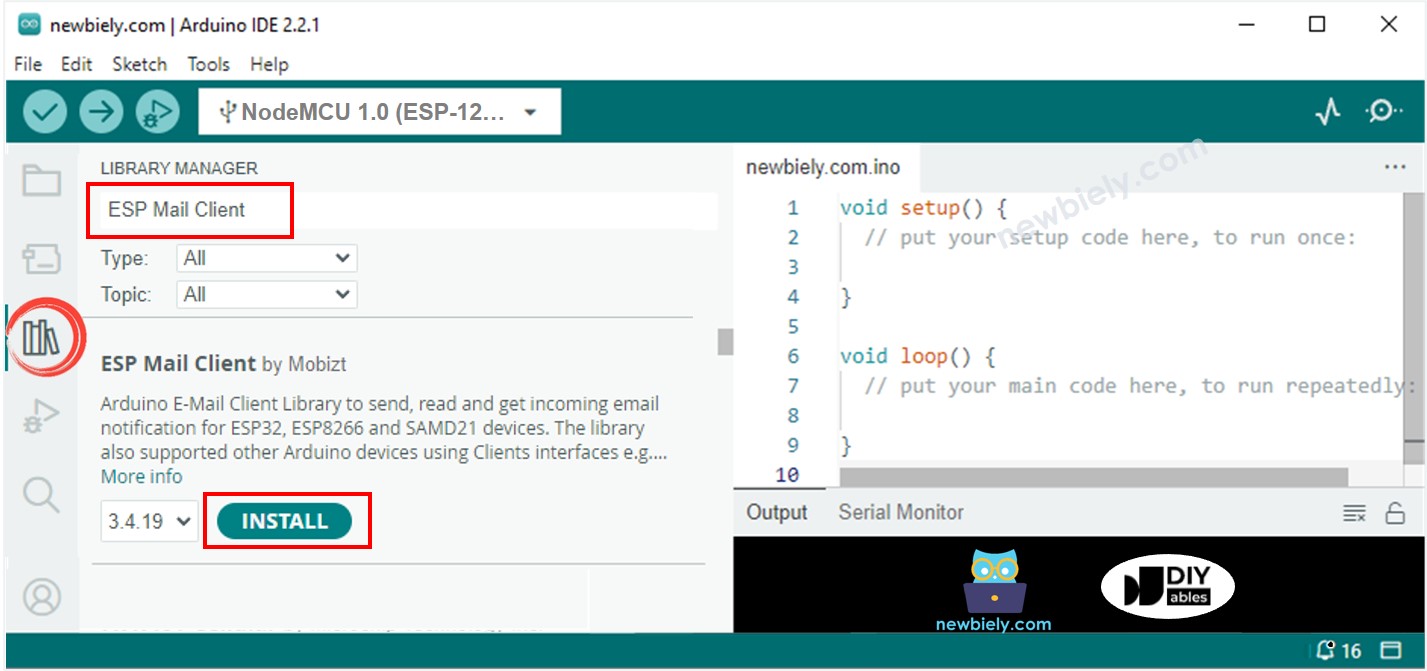
- Click on the Library Manager icon on the left in the Arduino IDE.
- Search for ESP Mail Client and choose the one by Mobizt.
- Press the Install button to add the ESP Mail Client library.
- Copy the above code and open it using the Arduino IDE.
- Update your WiFi information by changing WIFI_SSID and WIFI_PASSWORD to your WiFi network's SSID and password.
- Enter your email and password in the code under SENDER_EMAIL and SENDER_PASSWORD.
- Update the receiver's email address in RECIPIENT_EMAIL to your own email, if needed. It can be the same as the sender's email.
※ NOTE THAT:
- The sender's email should be a Gmail account.
- The sender's password is the App password given in the previous step.
- The recipient's email can be any kind.
- Click on the Upload button in Arduino IDE to send the code to ESP8266.
- Open the Serial Monitor.
- Check the results on the Serial Monitor.
COM6
#### Message sent successfully
> C: message sent successfully
----------------
Message sent success: 1
Message sent failed: 0
----------------
Message No: 1
Status: success
Date/Time: May 27, 2024 04:42:50
Recipient: xxxxxx@gmail.com
Subject: Email Notification from ESP8266
----------------
Autoscroll
Clear output
9600 baud
Newline
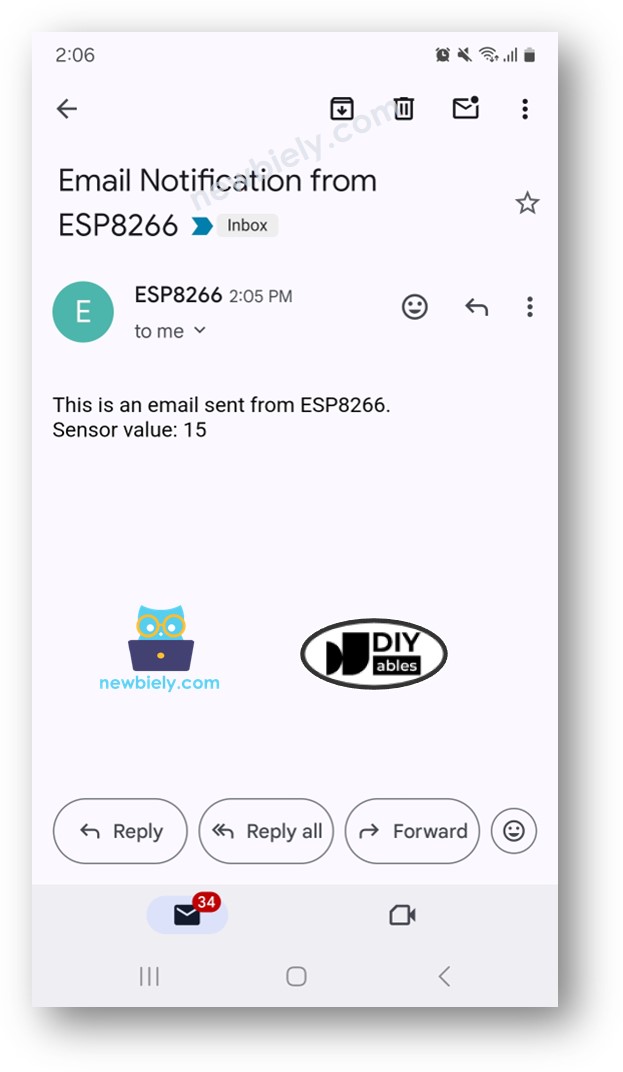
- Look in the email inbox of the person you sent the email to. You will find an email similar to this: