ESP8266 - DIP Switch
DIP (Dual In-line Package) switches find widespread use in electronics for various configuration tasks, like device addresses, communication settings, security codes. This tutorial will delve into utilizing the DIP switch with ESP8266. Specifically, we'll cover:
- Understanding the DIP switch and how it works.
- Establishing connections between the DIP switch and ESP8266.
- Programming ESP8266 to read the ON/OFF status of the DIP switch.
- Programming ESP8266 to interpret the integer values configured by the DIP switch.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of DIP Switch
DIP switches are mainly used to configure devices, enabling users to adjust settings like device address, communication parameters, security codes, operation modes, and system preferences across various industries and applications.
A DIP switch consists of several small slide switches bundled together. Each of these slide switches is known as a "position." DIP switches are available in different types based on the number of positions they offer. For example, there are 2-position, 4-position, 5-position, 6-position, 8-position, and 10-position DIP switches.
A DIP switch can represent a configurable number. Each position on the switch corresponds to a bit of the number. By toggling the positions between ON and OFF, we can set the desired number we want.
Pinout
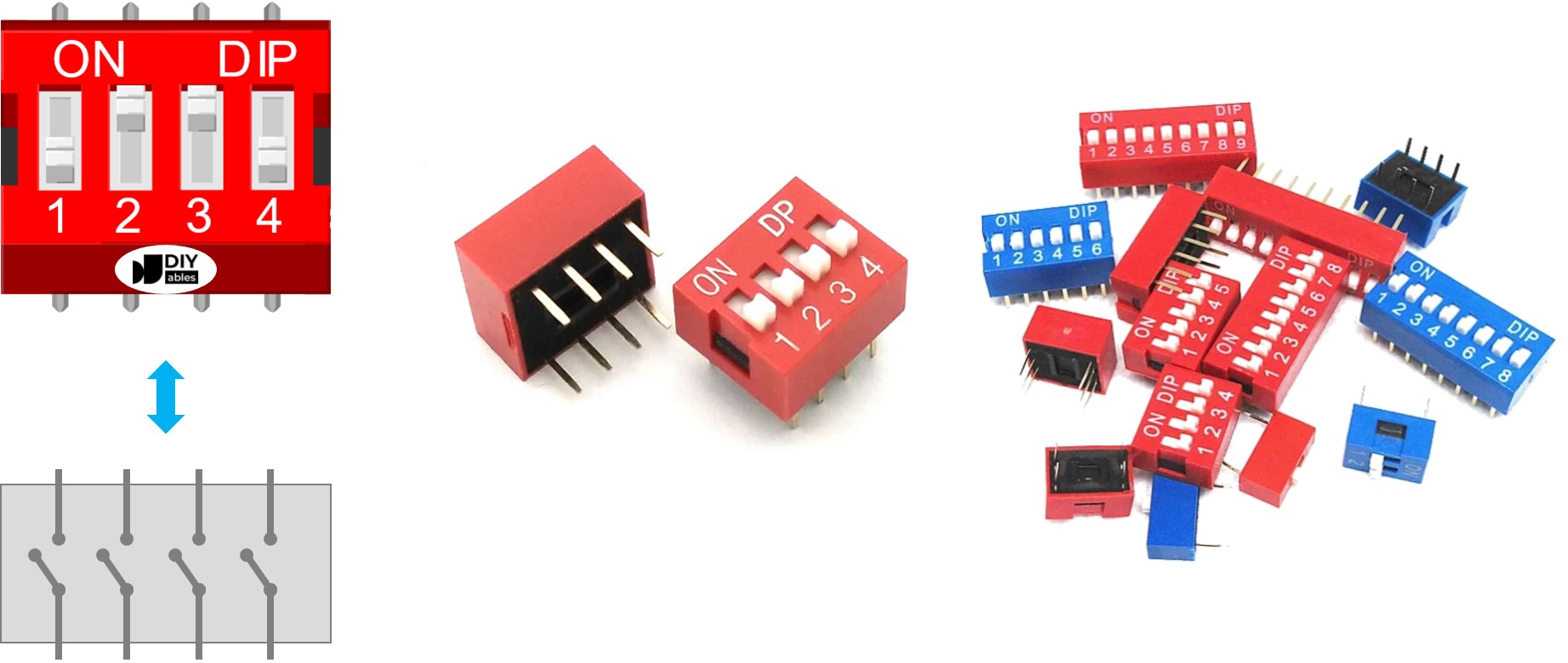
A DIP switch is composed of two rows of pins, with the number of pins in each row matching the available switch positions. For instance, a 4-position DIP switch includes a total of 8 pins, evenly distributed with 4 pins on each side. Within the DIP switch structure, each pair of opposing pins forms a slide switch. It's worth mentioning that differentiating between pins on the two sides isn't required as they can be used interchangeably.
How It Works
IIn DIP switches, when a switch is in the ON position, it signifies that the switch is closed. This indicates that the electrical connection is established, permitting current to pass through the switch.
Conversely, when a switch is in the OFF position, it implies that the switch is open. In this state, the electrical connection is interrupted, and current cannot flow through the switch.
So, to summarize:
- ON position: Closed circuit, allowing current flow.
- OFF position: Open circuit, obstructing current flow.
When we connect one side of a switch to GND and the other to an ESP8266 pin, then configure the ESP8266 pin as a pull-up digital input, the table below illustrates the relationship between switch positions and the values read from the ESP8266:
| DIP switch position | Binary representation | Circuit state | ESP8266 pin state |
|---|---|---|---|
| ON | 1 | CLOSED | LOW |
| OFF | 0 | OPEN | HIGH |
In the next parts, we will use 4-position DIP switch for example. You can easily to adapt for 2-position DIP switches, 3-position DIP switches, 5-position DIP switches, 6-position DIP switches, 8-position DIP switches, and 10-position DIP switches...
Wiring Diagram
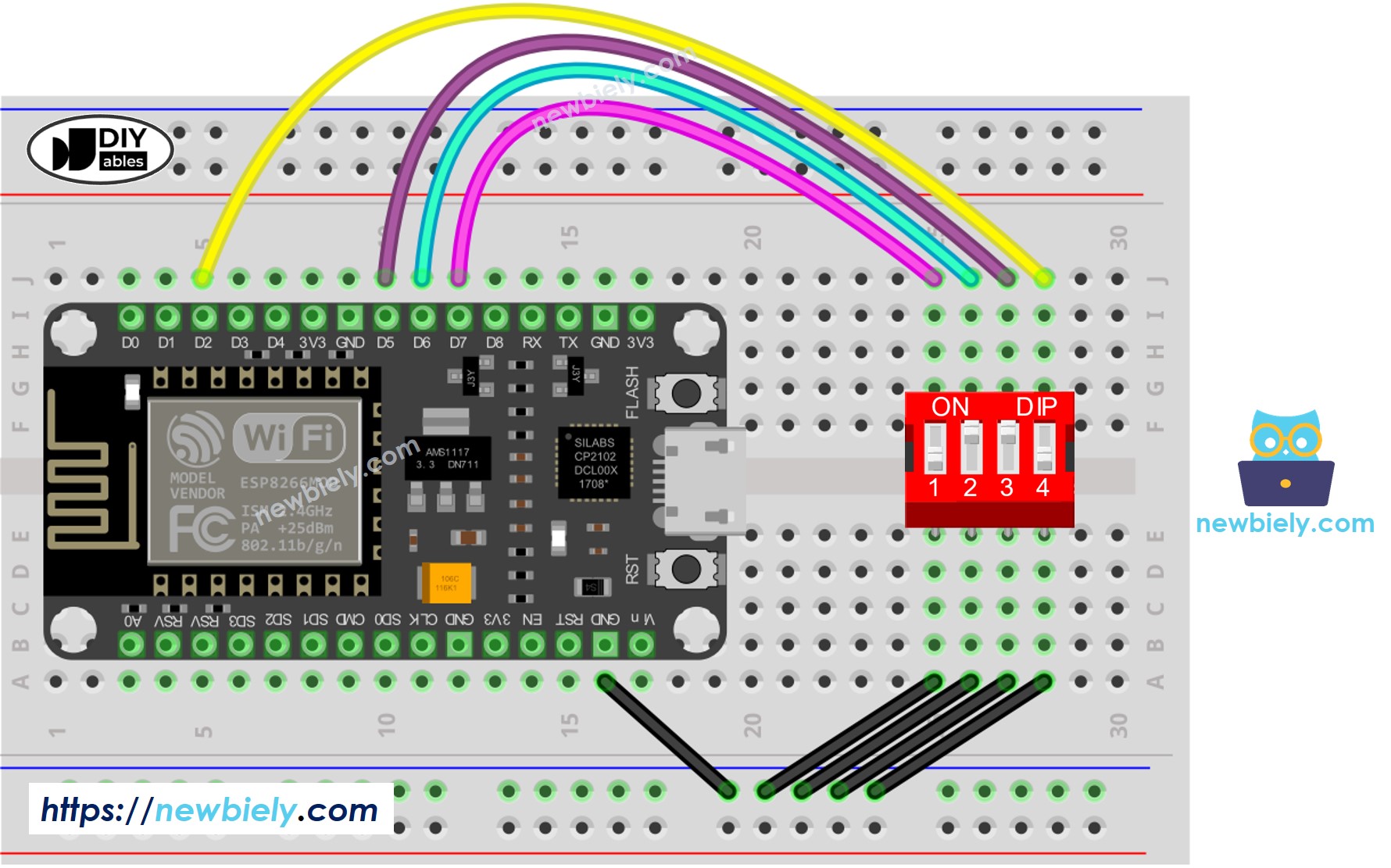
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
ESP8266 Code - DIP Switch
We will learn through two pieces of code:
- Reading the ON/OFF state of individual position on the DIP switch.
- Encoding the positions into a number.
ESP8266 code - Reading the ON/OFF state of the DIP switch
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Do wiring as above wiring diagram
- Connect ESP8266 to PC via USB cable
- Open Arduino IDE
- Select the right board and port
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP8266
- Switch each position on the DIP Switch to ON one by one.
- See the result on Serial Monitor.
ESP8266 code - Encoding the states of DIP switch into a number
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Upload the above code to ESP8266
- Switch each position on the DIP switch to ON one by one.
- See the result on Serial Monitor, it look like below.
Please note that the value depends on positions of each slide switches. The below table shows the mapping between ON/OFF position and the integer value for 4-position DIP switch:
| Position-1 | Position-2 | Position-3 | Position-4 | Binary Value | Decimal Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | 0000 | 0 |
| OFF | OFF | OFF | ON | 0001 | 1 |
| OFF | OFF | ON | OFF | 0010 | 2 |
| OFF | OFF | ON | ON | 0011 | 3 |
| OFF | ON | OFF | OFF | 0100 | 4 |
| OFF | ON | OFF | ON | 0101 | 5 |
| OFF | ON | ON | OFF | 0110 | 6 |
| OFF | ON | ON | ON | 0111 | 7 |
| ON | OFF | OFF | OFF | 1000 | 8 |
| ON | OFF | OFF | ON | 1001 | 9 |
| ON | OFF | ON | OFF | 1010 | 10 |
| ON | OFF | ON | ON | 1011 | 11 |
| ON | ON | OFF | OFF | 1100 | 12 |
| ON | ON | OFF | ON | 1101 | 13 |
| ON | ON | ON | OFF | 1110 | 14 |
| ON | ON | ON | ON | 1111 | 15 |
