ESP8266 - Touch Sensor - Solenoid Lock
This tutorial instructs you how to use the ESP8266 and touch sensor to control the solenoid lock. By connecting the solenoid lock to a soleniod lock, light bulb, LED strip, motor, or actuator..., we can use a touch sensor to control the them. We will learn two different applications:
Application 1 - The solenoid lock state is synchronized with the touch sensor state. In detail:
- ESP8266 turns on the solenoid lock when the touch sensor is being touched.
- ESP8266 turns off the solenoid lock when the touch sensor is NOT being touched.
Application 2 - The solenoid lock state is toggled each time the touch sensor is touched. More specifically:
- If ESP8266 detects that the touch sensor has been touched (changing from a HIGH state to a LOW state), it will turn ON the solenoid lock if it's currently OFF, or turn OFF the solenoid lock if it's currently ON.
- Releasing the touch sensor does not affect to the solenoid lock state.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Solenoid Lock and Touch Sensor
If you are unfamiliar with solenoid lock and touch sensor (including pinout, operation, and programming), the following tutorials can help:
Wiring Diagram
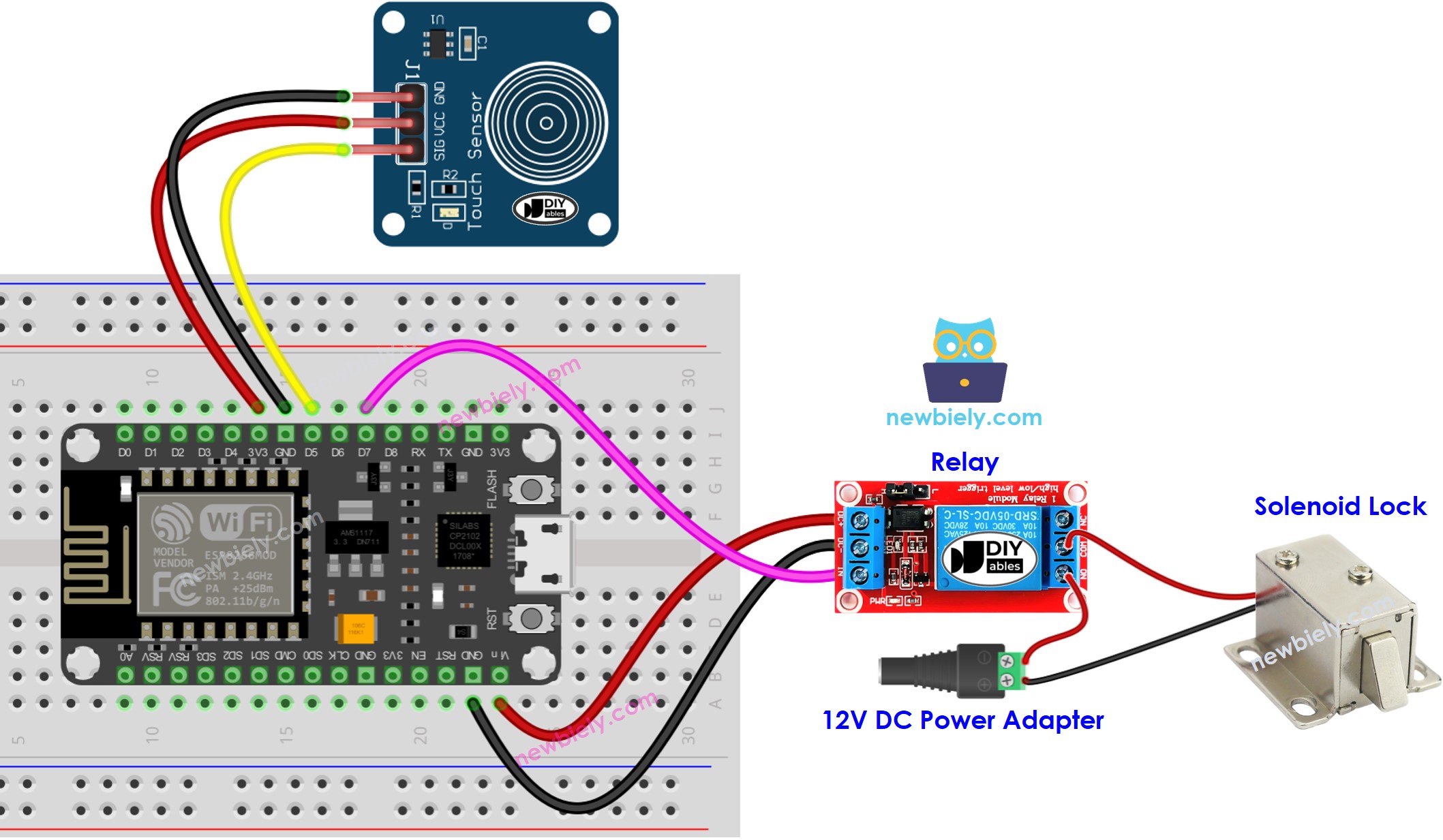
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
Application 1 - The solenoid lock state is in sync with the touch sensor state
ESP8266 Code
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Connect an ESP8266 to your computer with a USB cable.
- Launch the Arduino IDE, and select the correct board and port.
- Copy the code and open it in the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button on the Arduino IDE to compile and upload the code to the ESP8266.
- Touch the touch sensor and hold it for a few seconds.
- Check out the change in the solenoid lock's condition.
You will see that the solenoid lock state is in sync with the touch sensor state.
Code Explanation
Check out the line-by-line explanation contained in the comments of the source code!
Application 2 - Touch Sensor toggles Solenoid Lock
ESP8266 Code - Touch Sensor toggles Solenoid Lock
Code Explanation
You can locate the explanation in the comment lines of the ESP8266 code above.
In the code, the expression solenoidLockState = !solenoidLockState is equivalent to the following code:
Detailed Instructions
- Copy the code and open it in the Arduino IDE.
- Upload the code to the ESP8266.
- Touch and release the touch sensor several times.
- Check out the change in the solenoid lock's state.
You'll notice that the solenoid lock will switch on or off one time whenever you Touch the touch sensor.
