ESP8266 - Potentiometer fade LED
In a previous tutorial, we discovered how a potentiometer can be used to trigger a LED. This tutorial instructs you how to use ESP8266 to adjust the brightness of the LED based on the output value of the potentiometer.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Buy Note: Use the LED Module for easier wiring. It includes an integrated resistor.
Overview of LED and Potentiometer
If you are unfamiliar with LED and potentiometer (including pinout, functioning, programming, etc.), the following tutorials can help you out:
Wiring Diagram
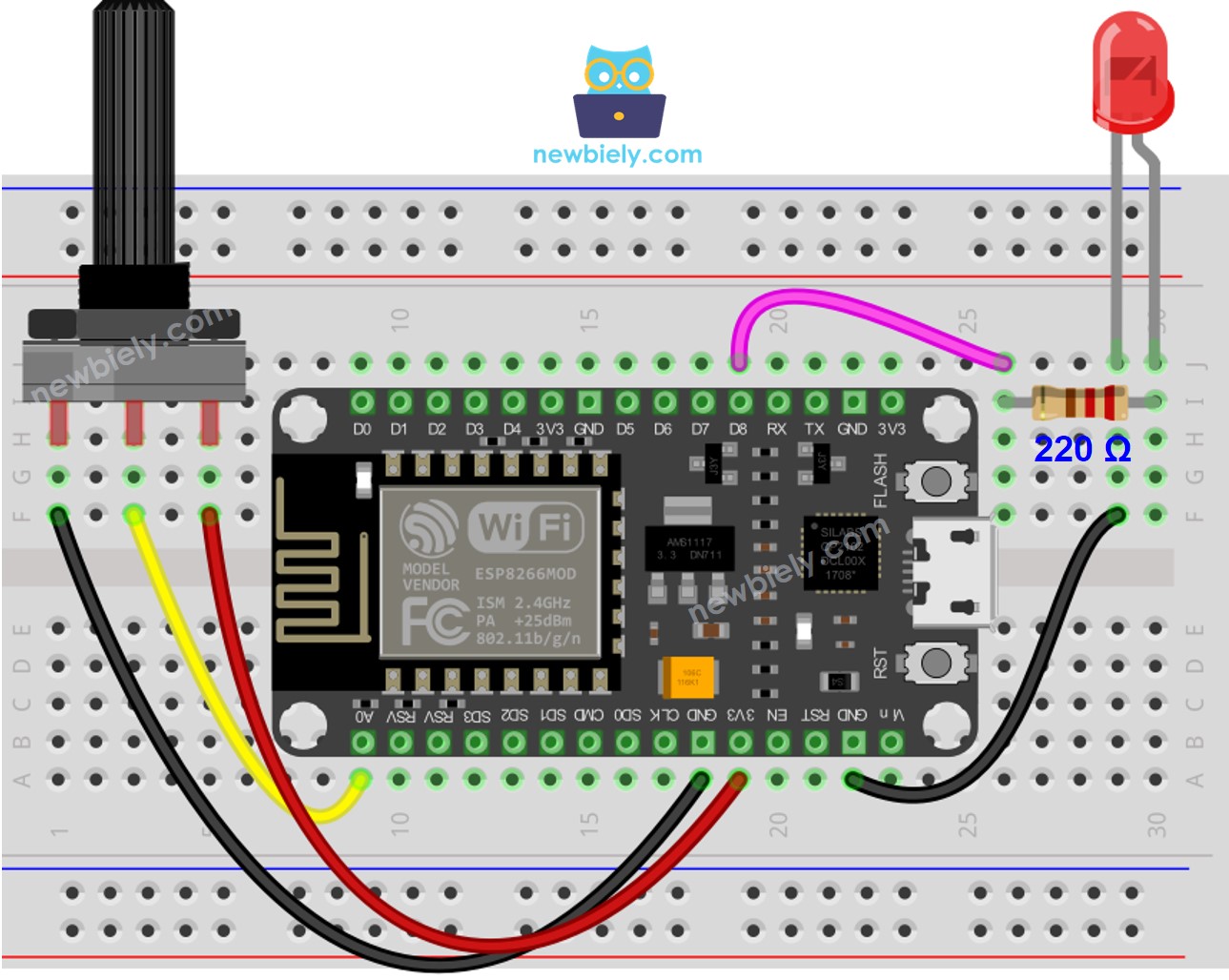
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
How To Program
- Gets the value from the analog pin A0, which is between 0 and 1023.
- Adjusts the brightness to a value between 0 and 255.
- Sets the brightness of the LED connected to pin 3.
ESP8266 Code
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Copy the code and open it with the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button in the IDE to transfer the code to the ESP8266.
- Open the Serial Monitor.
- Turn the potentiometer.
- Check out the LED.
- Check out the result on the Serial Monitor.
※ NOTE THAT:
This tutorial uses the analogRead() function to get data from an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) that's connected to a sensor or another part. The ESP8266's ADC works well for projects where you don't need very precise readings. But remember, the ESP8266's ADC isn't very accurate for detailed measurements. If your project needs to be very precise, you might want to use a separate ADC like the ADS1115 with the ESP8266, or use Arduino like the Arduino Uno R4 WiFi, which has a more reliable ADC.
