ESP8266 - Traffic Light
This tutorial instructs you how to use an ESP8266 to control a traffic light module. Specifically, we will cover the following aspects:
- Establishing the connection between the traffic light module and ESP8266
- Programming ESP8266 to oversee the RGB traffic light module
- Implementing ESP8266 programming to manage the RGB traffic light module without relying on the delay() function
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
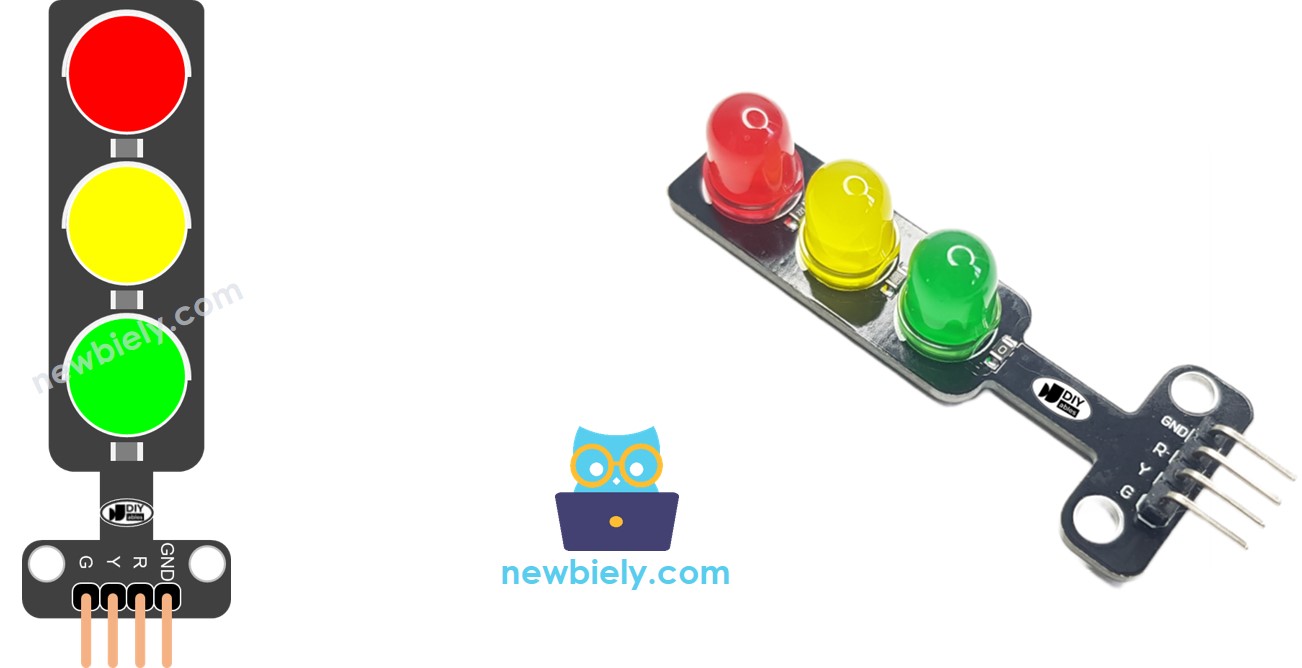
Overview of Traffic Light Module
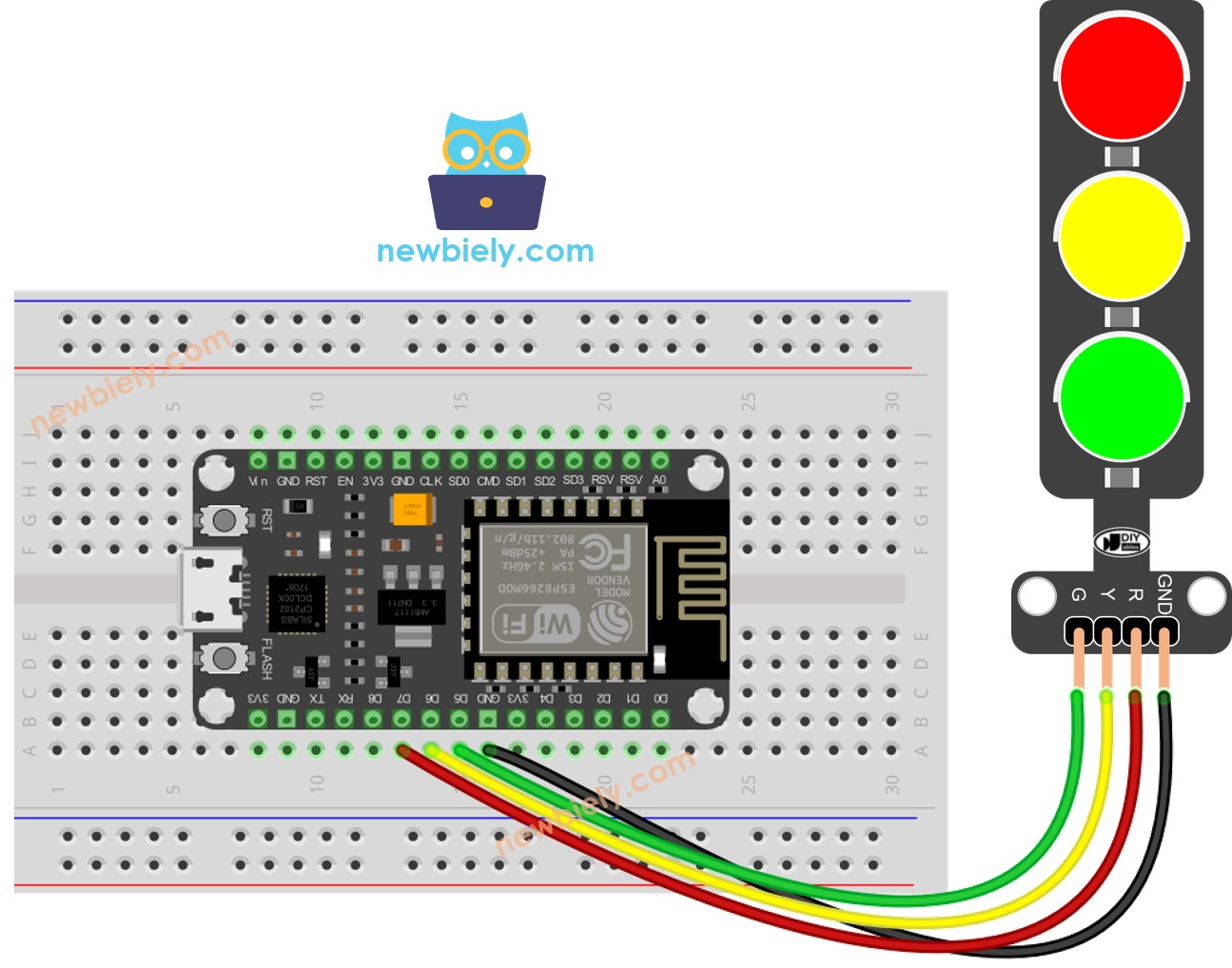
Pinout
A traffic light module is equipped with four pins:
- GND pin: Connect this pin to the GND of the ESP8266.
- R pin: Manages the red light; connect this pin to a digital output of the ESP8266.
- Y pin: Controls the yellow light; connect this pin to a digital output of the ESP8266.
- G pin: Governs the green light; connect this pin to a digital output of the ESP8266.

How It Works
Wiring Diagram
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
How To Program For Traffic Light module
- Configure an ESP8266's pins to the digital output mode by using pinMode() function
- Program to turn ON red light by using digitalWrite() function:
ESP8266 Code
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP8266
- Check out the traffic light module
It's important to note that the exact workings of a traffic light can vary depending on the specific design and technology used in different regions and intersections. The principles described above provide a general understanding of how traffic lights operate to manage traffic and enhance safety on the roads.
The code above demonstrates individual light control. Now, let's enhance the code for better optimization.
ESP8266 Code Optimization
- Let's improve the code by implementing a function for light control.
- Let's improve the code by using a for loop.
- Let's improve the code by using millis() function intead of delay().
