ESP8266 - Cooling System using DHT Sensor
This tutorial instructs you how to regulate temperature with the help of a fan and either a DHT11 or DHT22 sensor.
- ESP8266 reads temperature from sensor, if the temperature exceeds a threshold, it turns on the cooling fan.
- Otherwise, it turns off the cooling fan.
If you would prefer to use a DS18B20 sensor instead of a DHT sensor, please refer to ESP8266 - Cooling System using DS18B20 Sensor.
Hardware Preparation
You can use DHT22 sensor instead of DHT11 sensor.
| 1 | × | Recommended: Screw Terminal Expansion Board for ESP8266 | |
| 1 | × | Recommended: Power Splitter for ESP8266 Type-C |
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Cooling Fan and DHT Sensor
The fan in this tutorial requires a 12v power supply. If the power is supplied, the fan will turn on, and if not, it will stay off. To control the fan with an ESP8266, we must use a relay as an intermediary.
If you are unfamiliar with temperature sensor and fan (including pinout, how it works, and programming), the following tutorials can provide you with the necessary information:
Wiring Diagram
- A diagram showing the connections of a DHT11 module.
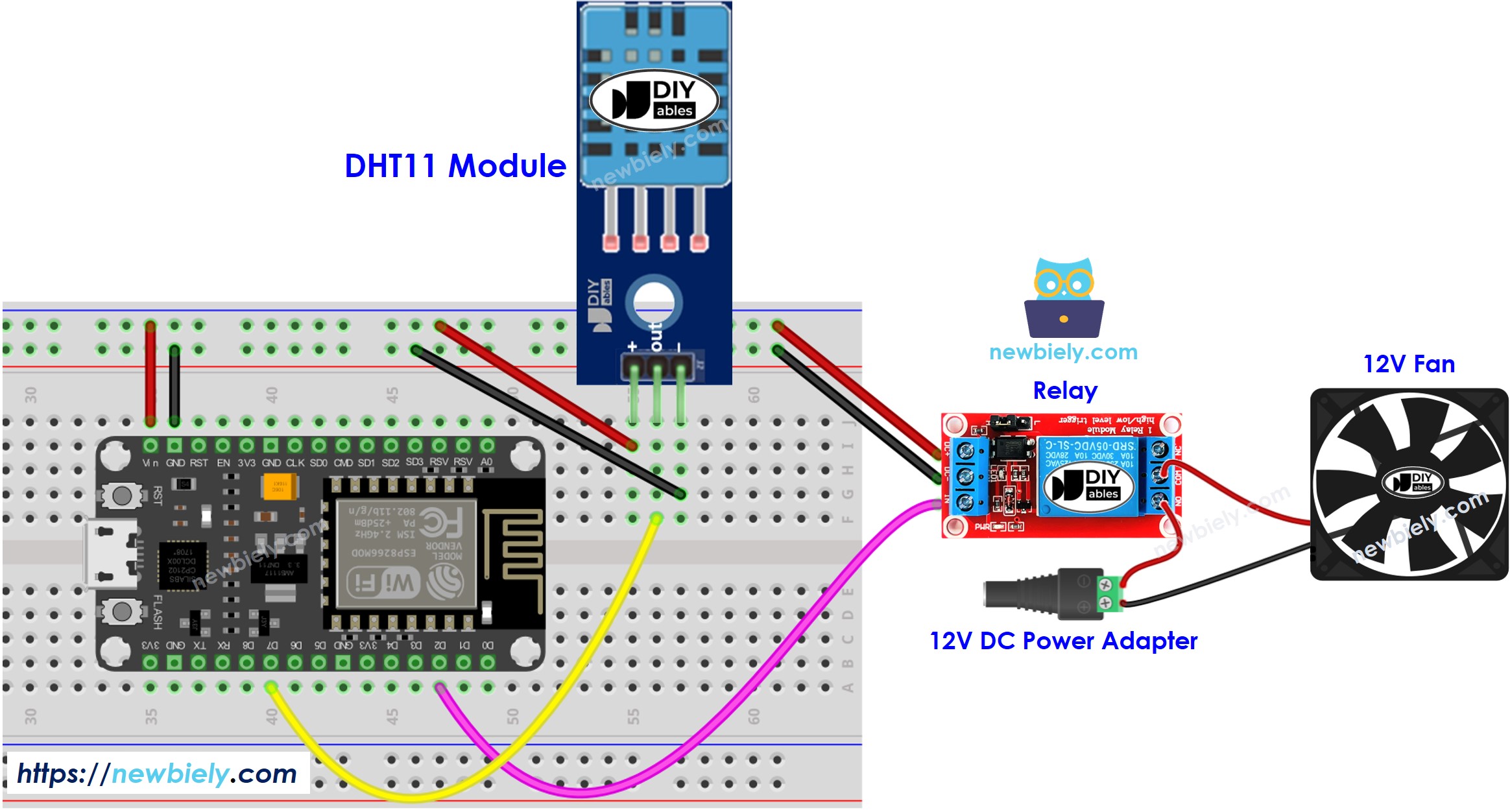
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
- A diagram showing the connections of a DHT22 module
- An illustration of the wiring for a DHT22 module
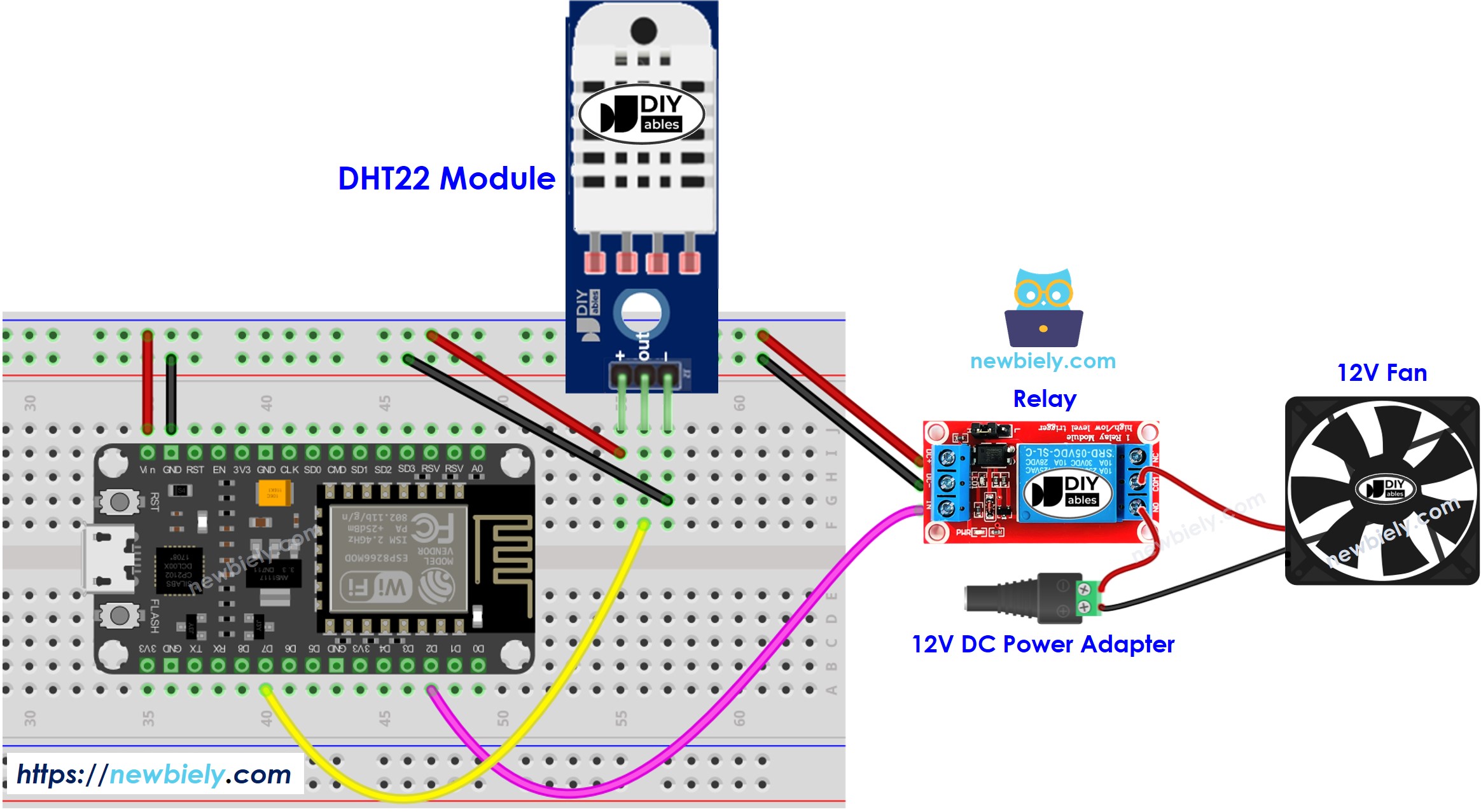
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
How System Works
- ESP8266 obtains the temperature from the temperature sensor.
- If the temperature is higher than the upper threshold, ESP8266 activates the fan.
- If the temperature is lower than the lower threshold, ESP8266 shuts off the fan.
This loop is repeated without end.
ESP8266 Code
ESP8266 Code for Cooling System with DHT11 sensor
ESP8266 Code for Cooling System with DHT22 sensor
In the codes above, the ESP8266 will activate the fan when the temperature is greater than 25°C and will keep it running until the temperature drops below 20°C.
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Connect an ESP8266 to a PC using a USB cable
- Open the Arduino IDE, select the correct board and port
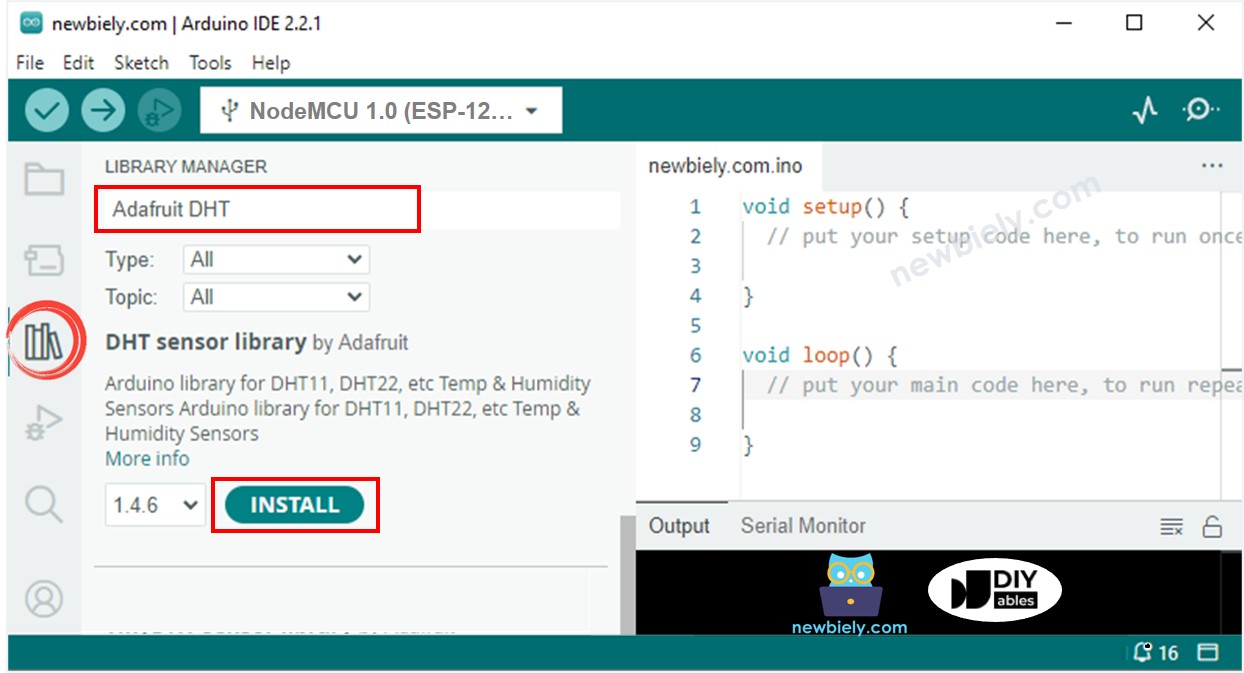
- Click to the Libraries icon on the left bar of the Arduino IDE.
- Look up “DHT” and locate the DHT sensor library from Adafruit.
- Hit the Install button to add the library.
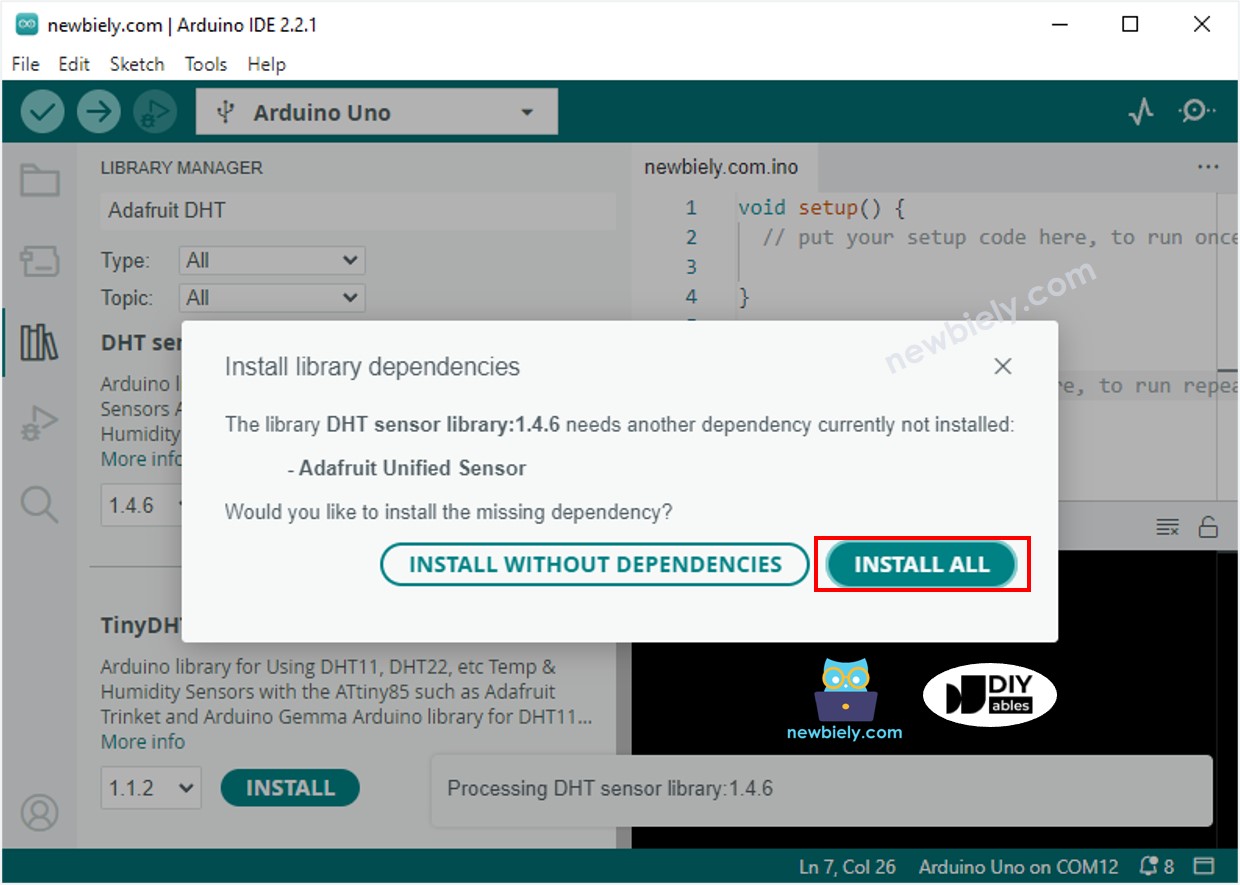
- You will be asked to install some other library dependancies.
- Click the Install All button to install all library dependancies.
- On serial monitor
- Copy the code that is associated with the sensor you have and open it in the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to compile and upload the code to the ESP8266.
- Change the temperature of the area around the sensor.
- Check out the status of the fan on the serial monitor.
Advanced Knowledge
The above method of control is referred to as an on-off controller, which is also known as a signaller or "bang-bang" controller. This approach is very easy to set up.
An alternative approach is the PID controller. This method makes temperature regulation more stable, however it is complex and challenging to comprehend and apply. As a result, the PID controller is not widely used for temperature control.
