ESP8266 - Gas Sensor
This tutorial instructs you how to use ESP8266 and the MQ2 gas sensor to assess the quality of the air by measuring the levels of gases like LPG, smoke, alcohol, propane, hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide. In detail, we will learn:
- How to connect the MQ2 gas sensor to ESP8266
- How to program ESP8266 to read value from the MQ2 gas sensor
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of MQ2 Gas Sensor
The MQ2 gas sensor is a useful device that can detect the levels of various gases, including LPG, smoke, alcohol, propane, hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide, in the surrounding environment. It offers two output options: a digital output pin and an analog output pin.
It's important to note that the MQ2 gas sensor doesn't provide separate information about each gas. Instead, it gives us a general indication of the gas combination or the presence of gases as a whole.
By using the MQ2 sensor, we can determine if there is a gas leak or if the air quality is poor. This information is valuable as it allows us to take appropriate measures to ensure our safety, such as activating an alarm or turning on ventilation systems.
Pinout
The MQ2 gas sensor consists of four pins that serve different functions:
- VCC pin: It should be connected to the power supply's positive terminal (5V) to provide the necessary power to the sensor.
- GND pin: It should be connected to the power supply's negative terminal (0V) to complete the electrical circuit.
- DO pin: This is a digital output pin that indicates the presence of flammable gases. When the gas concentration is detected, the output is set to LOW, and when there is no gas detected, the output is set to HIGH. The threshold for gas concentration detection can be adjusted using a potentiometer that is built into the sensor.
- AO pin: This is an analog output pin that generates a voltage signal proportional to the gas concentration. When the gas concentration increases, the voltage output also increases, and when the gas concentration decreases, the voltage output decreases accordingly.

Additionally, the MQ2 gas sensor includes two LED indicators:
- PWR-LED indicator: This LED serves as a power indicator, indicating whether the sensor is receiving power. When the sensor is properly powered, the PWR-LED is turned on, providing visual confirmation of the sensor's operational state.
- DO-LED indicator: This LED is directly linked to the DO pin of the sensor. It indicates the presence of gas concentration based on the value received from the DO pin. When the gas concentration is detected and the DO pin is set to LOW, the DO-LED turns on. Conversely, when there is no gas concentration detected and the DO pin is set to HIGH, the DO-LED turns off.
How It Works
Regarding the DO pin:
- The MQ2 module includes a built-in potentiometer for adjusting the sensitivity or threshold of gas concentration.
- When the gas concentration in the surrounding environment exceeds the set threshold, the output pin of the sensor becomes LOW, and the DO-LED turns on.
- Conversely, when the gas concentration falls below the threshold, the output pin becomes HIGH, and the DO-LED turns off.
Regarding the AO pin:
- The voltage on the AO pin increases as the gas concentration rises.
- Conversely, as the gas concentration decreases, the voltage on the AO pin decreases accordingly.
It's important to note that the potentiometer adjustment does not affect the value on the AO pin.
The MQ2 Sensor Warm-up
The MQ2 gas sensor requires a warming-up period before it can be used effectively. Here's what you need to know:
- When using the sensor for the first time after a long period of storage (around a month or more), it is necessary to warm it up for 24-48 hours. This ensures that the sensor operates accurately.
- If the sensor has been recently used, the warming-up time is much shorter, typically taking only 5-10 minutes. During this warm-up period, it is normal for the sensor to initially provide higher readings. However, these readings will gradually decrease until the sensor stabilizes.
To warm up the MQ2 sensor, simply connect its VCC and GND pins to a power supply or to the VCC and GND pins of an ESP8266. Allow the sensor to remain connected for the specified warm-up period.
Wiring Diagram
Since the MQ2 gas sensor module has two outputs, you can choose to use one or both of them, depending on what you need.
- The wiring diagram between ESP8266 and the MQ2 gas sensor when using DO only.
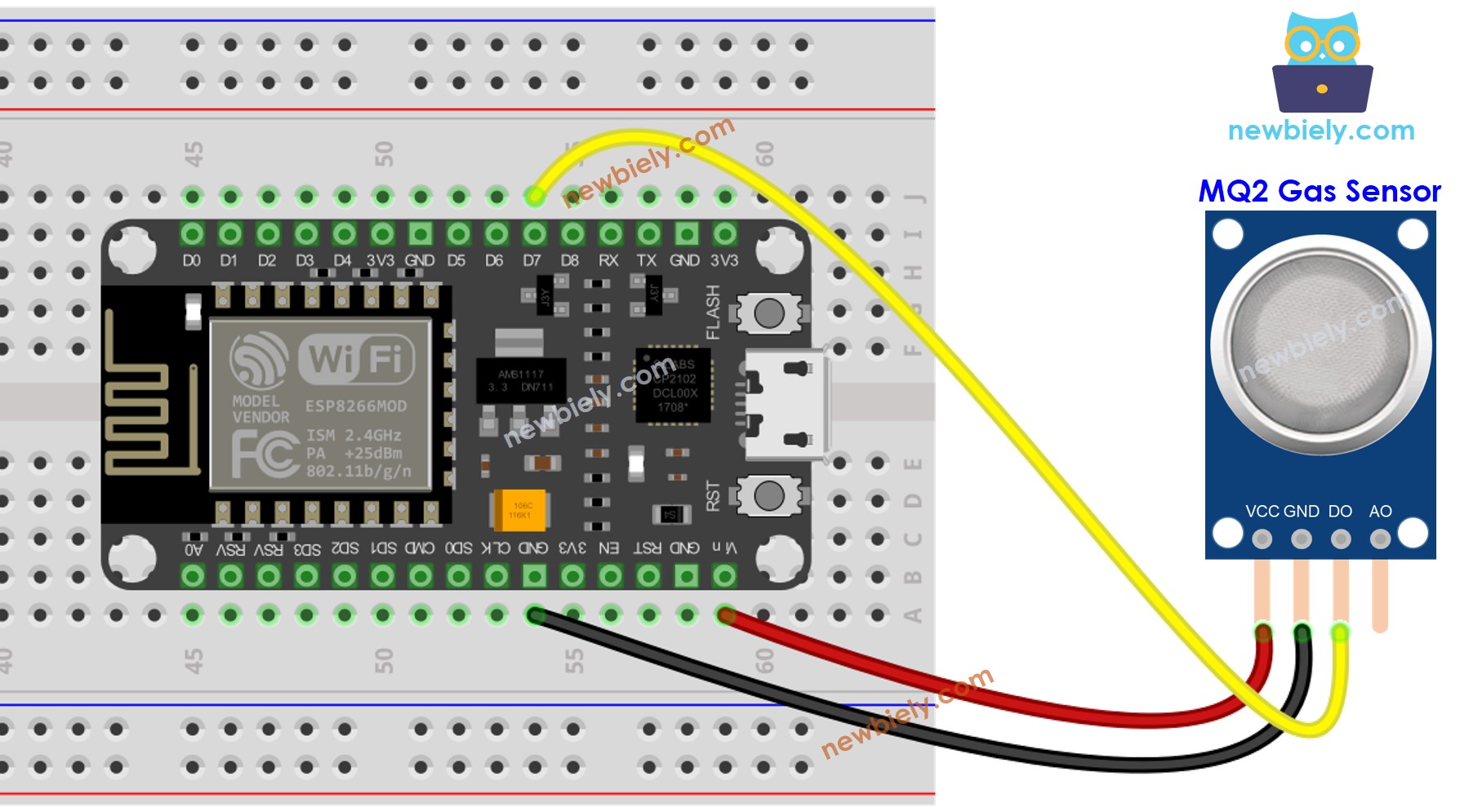
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
- The wiring diagram between ESP8266 and the MQ2 gas sensor when using AO only.
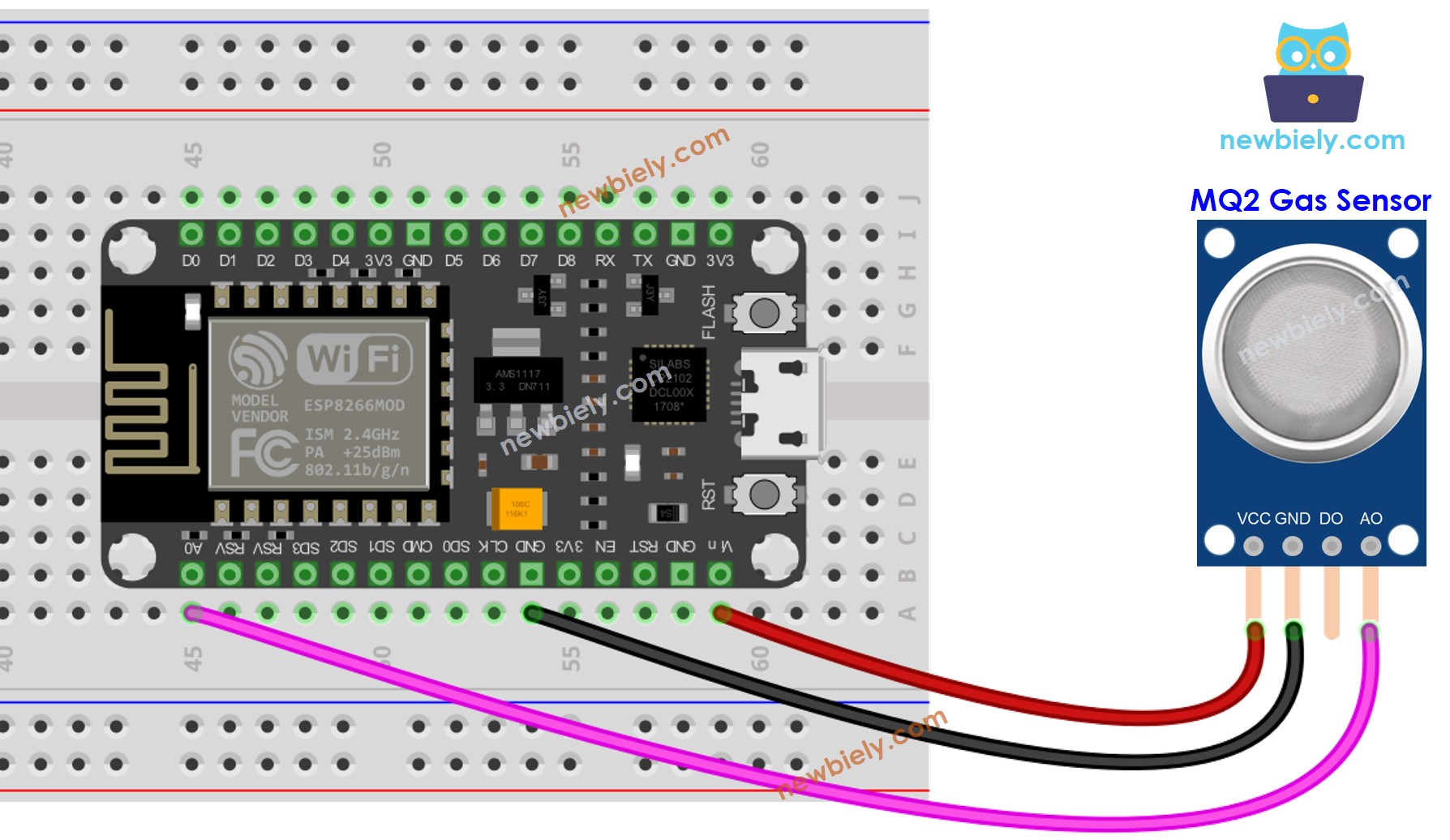
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
- The wiring diagram between ESP8266 and the MQ2 gas sensor when using both AO an DO.
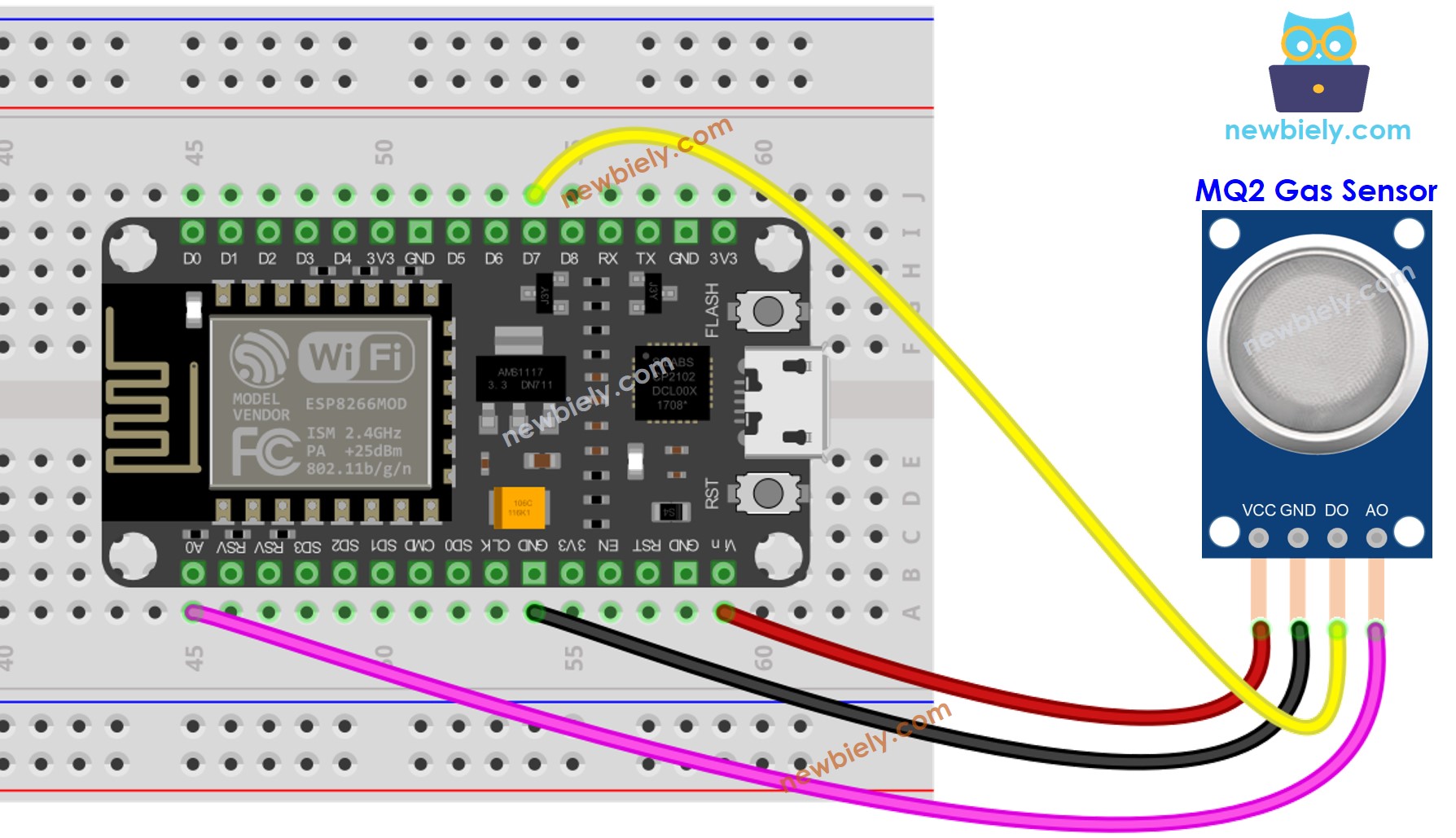
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
ESP8266 Code - Read value from DO pin
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP8266
- Place the MQ2 gas sensor near the smoke/gas you want to detect
- Check out the result on the Serial Monitor.
Please keep in mind that if you notice the LED status remaining on constantly or off, you can adjust the potentiometer to fine-tune the sensitivity of the sensor.
ESP8266 Code - Read value from AO pin
Detailed Instructions
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP8266
- Place the MQ2 gas sensor near the smoke/gas you want to detect
- Check out the result on the Serial Monitor.
From values read from DO or AO, you can infer the air quality based on your standard, or trigger an alarm or turn on ventilation systems.
※ NOTE THAT:
This tutorial uses the analogRead() function to get data from an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) that's connected to a sensor or another part. The ESP8266's ADC works well for projects where you don't need very precise readings. But remember, the ESP8266's ADC isn't very accurate for detailed measurements. If your project needs to be very precise, you might want to use a separate ADC like the ADS1115 with the ESP8266, or use Arduino like the Arduino Uno R4 WiFi, which has a more reliable ADC.
