ESP8266 - MQTT
In this tutorial, we will explore how to utilize ESP8266 for sending and receiving data with an MQTT broker using the MQTT protocol. Specifically, we will cover the following:
- Establishing a connection between ESP8266 and an MQTT broker.
- Programming ESP8266 to transmit data to an MQTT broker by publishing it to an MQTT topic.
- Programming ESP8266 to receive data by subscribing to an MQTT topic.
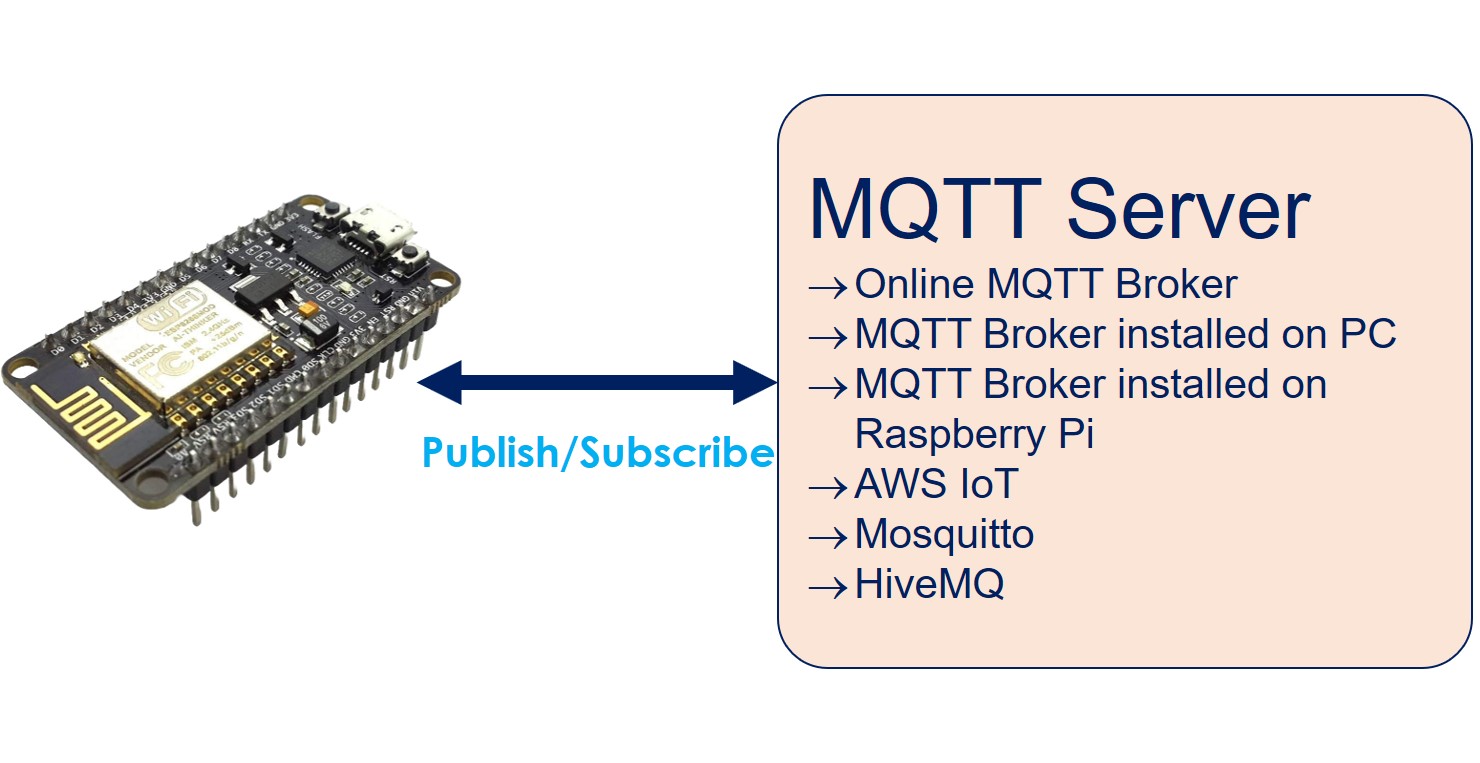
We will delve into two distinct scenarios:
- Utilizing ESP8266 with an online MQTT broker.
- Employing ESP8266 with an MQTT broker installed on your personal computer.
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of ESP8266 and MQTT
If you're not yet familiar with the MQTT protocol, you can find information about it online. This tutorial focuses on using ESP8266 for sending and receiving data through MQTT.
Here are some ways ESP8266 can be used with MQTT:
- You can connect ESP8266 to an online MQTT broker such as Mosquitto or AWS IoT.
- Alternatively, you can link ESP8266 to an MQTT broker installed on your computer, like Mosquitto or HiveMQ.
- If you have a Raspberry Pi, ESP8266 can connect to an MQTT broker running on it, for instance, Mosquitto.
- Additionally, ESP8266 can be connected to a cloud-based MQTT broker, such as Mosquitto or HiveMQ on AWS EC2.
In this tutorial, we'll begin by testing whether ESP8266 can connect to an online Mosquitto broker. We'll demonstrate ESP8266's ability to send and receive data through this broker over the internet.
Next, we'll guide you through setting up the Mosquitto broker on your computer. ESP8266 will then connect to this local broker, allowing you to continue sending and receiving data.
Once you've completed this tutorial, you can delve deeper by exploring these additional tutorials:
These resources will provide further insight into related topics.
Connect ESP8266 to an online MQTT broker
In this part, we will learn how to connect ESP8266 to test.mosquitto.org, an online MQTT broker created by Mosquitto. Please note that this broker should be used for the testing purpose only.
ESP8266 Code
The below ESP8266 code does:
- Connect to the MQTT broker
- Subscribe to a topic
- Periodically publish messages to the same topic that it subscribes
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
- Open the Library Manager by clicking on the Library Manager icon on the left navigation bar of Arduino IDE
- Type MQTT on the search box, then look for the MQTT library by Joel Gaehwiler.
- Click Install button to install MQTT library.
- Type ArduinoJson on the search box, then look for the ArduinoJson library by Benoit Blanchon.
- Click Install button to install ArduinoJson library.
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Replace the WiFi information (SSID and password) in the code with your own.
- In the code, you will see the word 'YOUR-NAME' three times. Replace this word with your name or random characters (alphabet characters only, no spaces). This is necessary because if you do not make the change, there may be multiple people running this code at the same time, which could lead to conflicts because the MQTT client IDs and topics are the same for everyone.
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP8266
- Open the Serial Monitor
- See the result on Serial Monitor.
As you can see, ESP8266 publishes messages to the MQTT broker, then receives back the same message. That is because the above code subscribes to the same topic that it publishes data to. If you do not want ESP8266 to receive the message that it publishes, simply make the SUBSCRIBE topic different from the PUBLISH topic.
Connect ESP8266 to the MQTT broker installed on your PC
Installing Mosquitto MQTT Broker
- Download the Mosquitto MQTT Broker
- Install it on the D: drive instead of the C: drive. Avoid installing the Mosquitto broker on the C: drive to prevent potential issues.
Run Mosquitto MQTT broker
Now, let's check if the MQTT broker is functioning properly by following these steps:
- Go to the directory where Mosquitto was installed. For instance: D:\mqtt\mosquitto>
- Make a new file named test.conf, copy the content below, and save it in that directory:
- Run a Command Prompt as Administrator on your PC. Let's call it Broker Window. Do not close it until the end of the tutorial.
- Run the below commands one by one:
- You will see:
- Open another Command Prompt as Administrator on your PC.
- Find the IP address of your PC by running the below command:
- Write down the IP address for later use. In the above example: 192.168.0.26
Test if the Mosquitto Broker works
- Open another Command Prompt as Administrator on your PC. Let's call it Subscriber Window
- Subscribe to a topic by running the below commands one by one (replace by your IP address):
- Open another Command Prompt as Administrator on your PC. Let's call it Publisher Window
- Publish a message to the same topic by running the below commands one by one (replace by your IP address):
- You will see:
You will see that message is forwarded to the Subscriber Window as follows:
Now, you installed successfully the Mosquitto MQTT broker on your PC. Please do NOT close three windows: Broker Window, Subscriber Window, and Publisher Window. We will use them next.
ESP8266 Code
The below ESP8266 code does:
- Connect to the MQTT broker
- Subscribe to a topic
- Periodically publish messages to another topic
Detailed Instructions
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Replace the WiFi information (SSID and password) in the code with your own.
- Replace the MQTT broker address in the code (domain name or IP address).
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP8266
Send message from ESP8266 to PC via MQTT
ESP8266 codes publishes data to the MQTT topic esp8266-001/send, Subscriber Window on PC subscribe that topic to receive the data.
- Open the Serial Monitor, you will see ESP8266 periodically publish a message to a topic.
- Check the Subscriber Window, you will see that it receives the message published by ESP8266 as below:
Send message from PC to ESP8266 via MQTT
ESP8266 subscribes to the topic esp8266-001/receive, Publisher Window on PC publish a message to that topic to send it to the ESP8266.
- Publish a message to the topic that ESP8266 subscribed by running the following command on Publisher Window:
- You will see this message is received by ESP8266 on Serial Monitor as below:
