ESP8266 - Temperature Humidity Sensor - OLED
This tutorial instructs you how to use ESP8266 to read the temperature and humidity from DHT11/DHT22 sensor and displaying it on an OLED.
Hardware Preparation
You can use DHT22 sensor instead of DHT11 sensor.
| 1 | × | Recommended: Screw Terminal Expansion Board for ESP8266 | |
| 1 | × | Recommended: Power Splitter for ESP8266 Type-C |
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of OLED display, DHT11 and DHT22 Temperature Humidity Sensor
If you are unfamiliar with OLED display, DHT11 and DHT22 temperature humidity sensor (including pinout, functionality, programming, etc.), the following tutorials can help you:
- ESP8266 - OLED tutorial
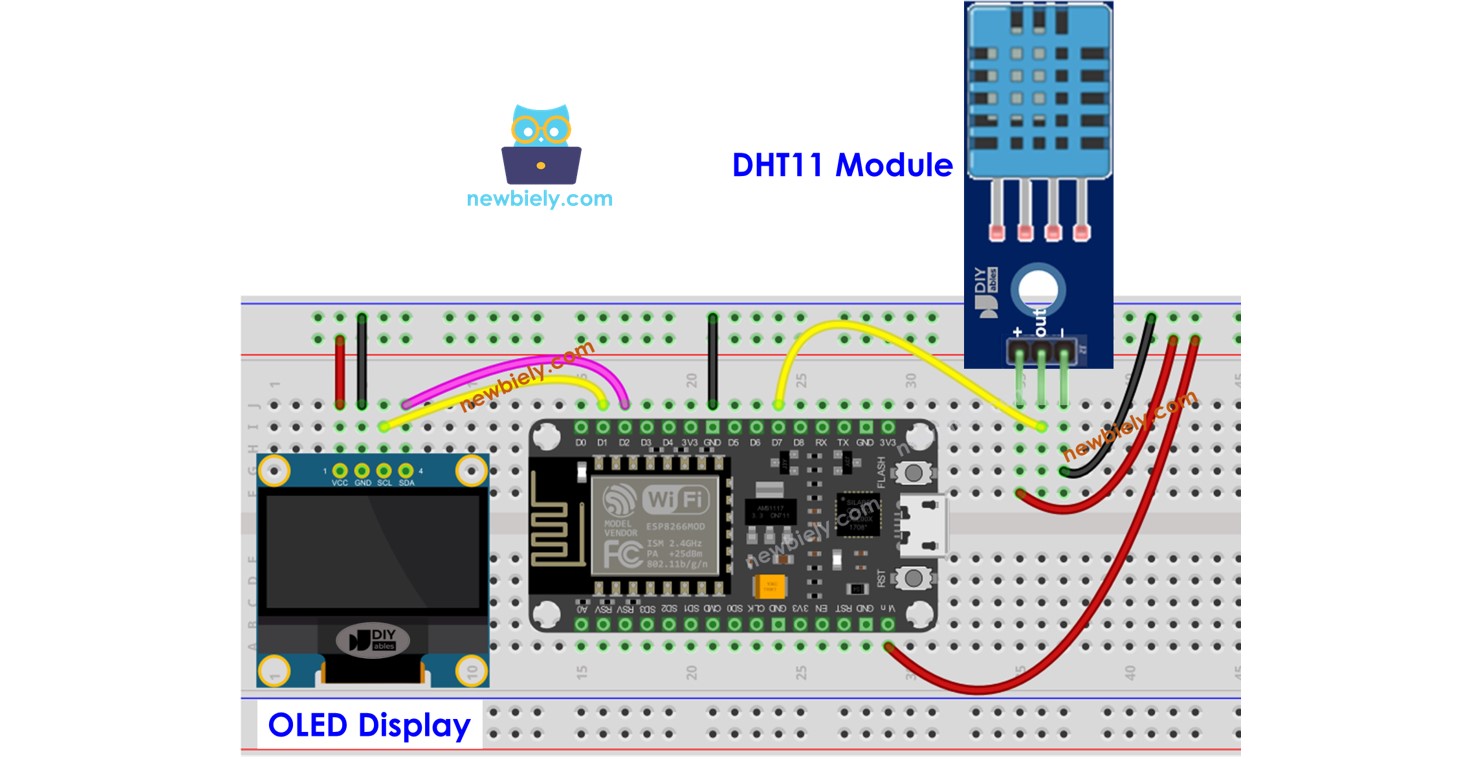
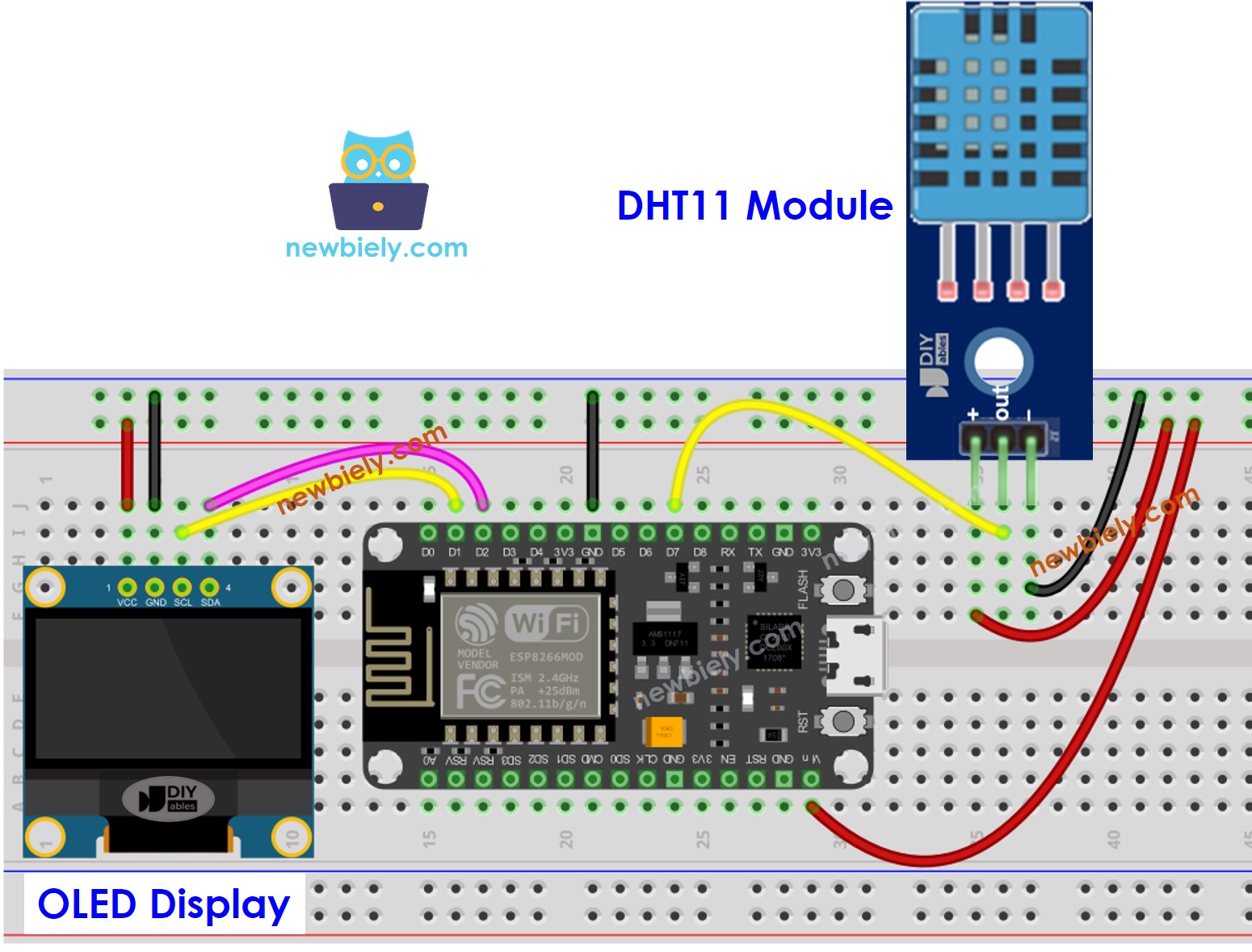
Wiring Diagram
ESP8266 - DHT11 Module LCD Wiring
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
ESP8266 - DHT22 Module LCD Wiring
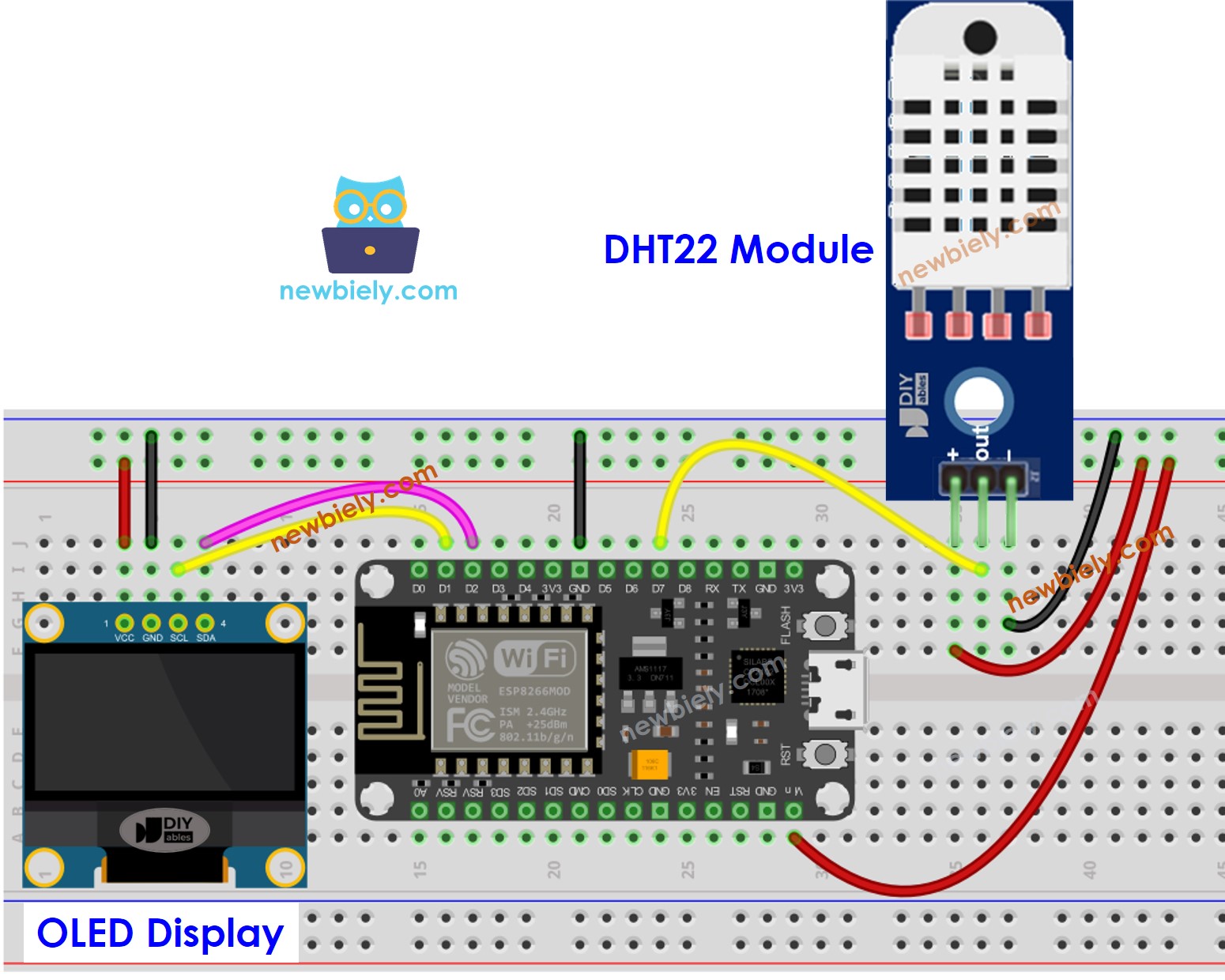
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
ESP8266 Code - DHT11 Sensor - OLED
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
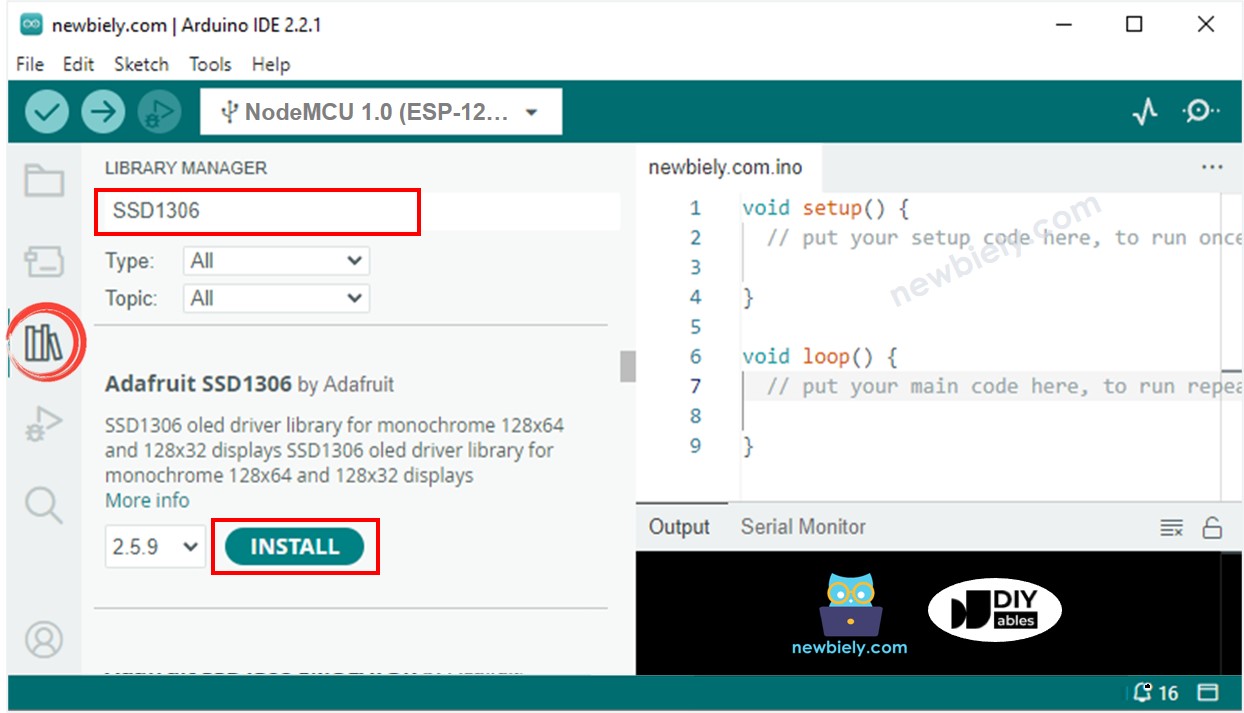
- Click to the Libraries icon on the left bar of the Arduino IDE.
- Search for “SSD1306” and locate the SSD1306 library from Adafruit.
- Then, press the Install button to complete the installation.
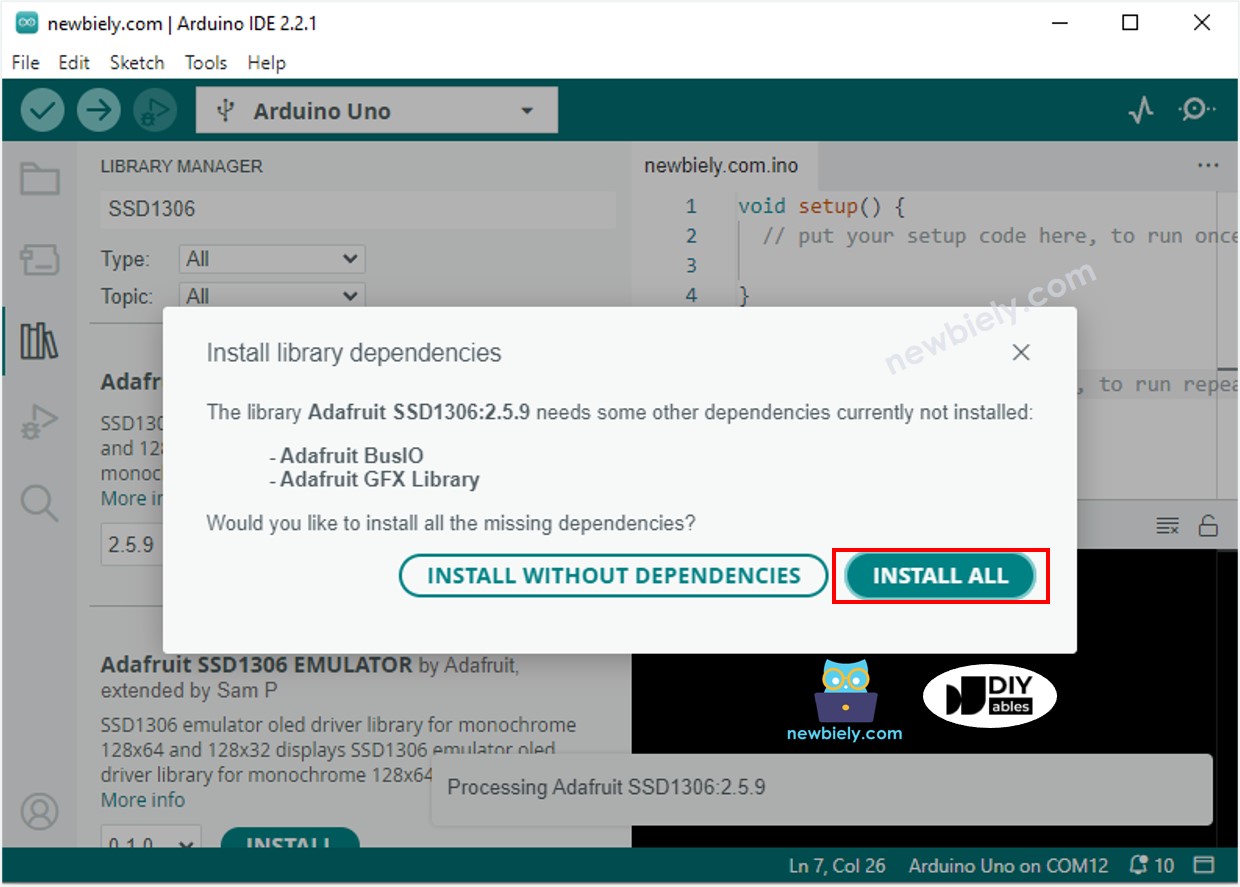
- You will be prompted to install additional library dependencies.
- To install all of them, click the Install All button.
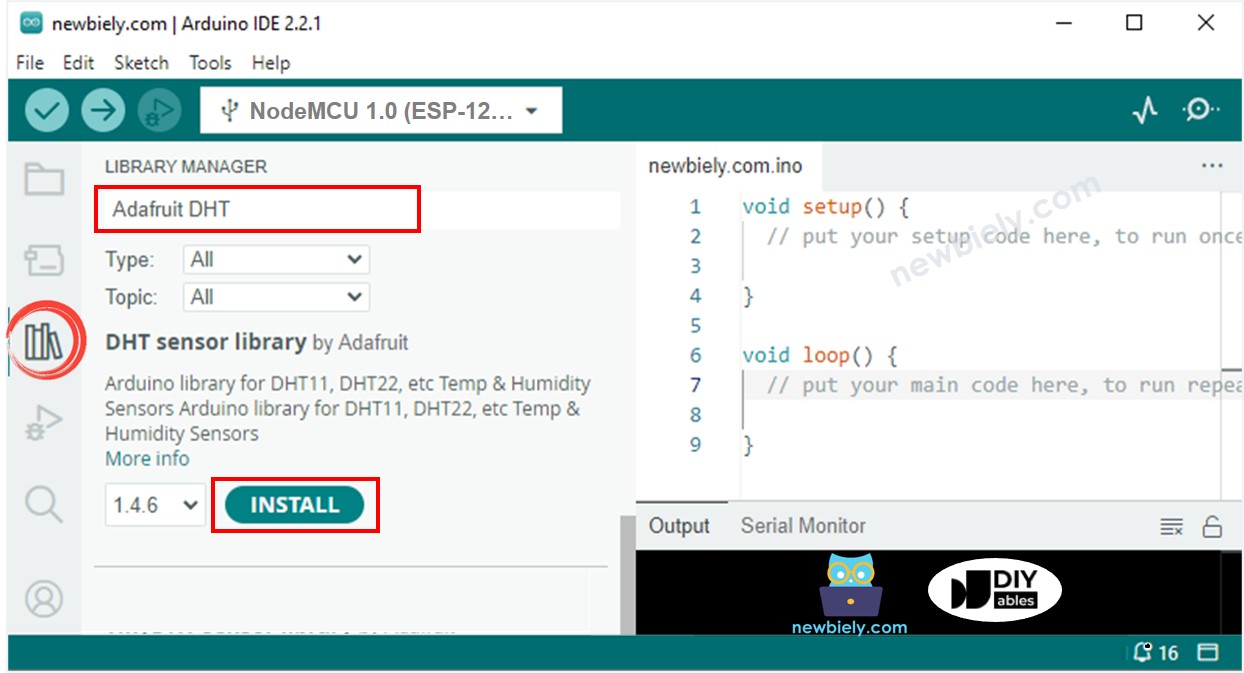
- Search for “DHT” and locate the DHT sensor library by Adafruit.
- Press the Install button to install the library.
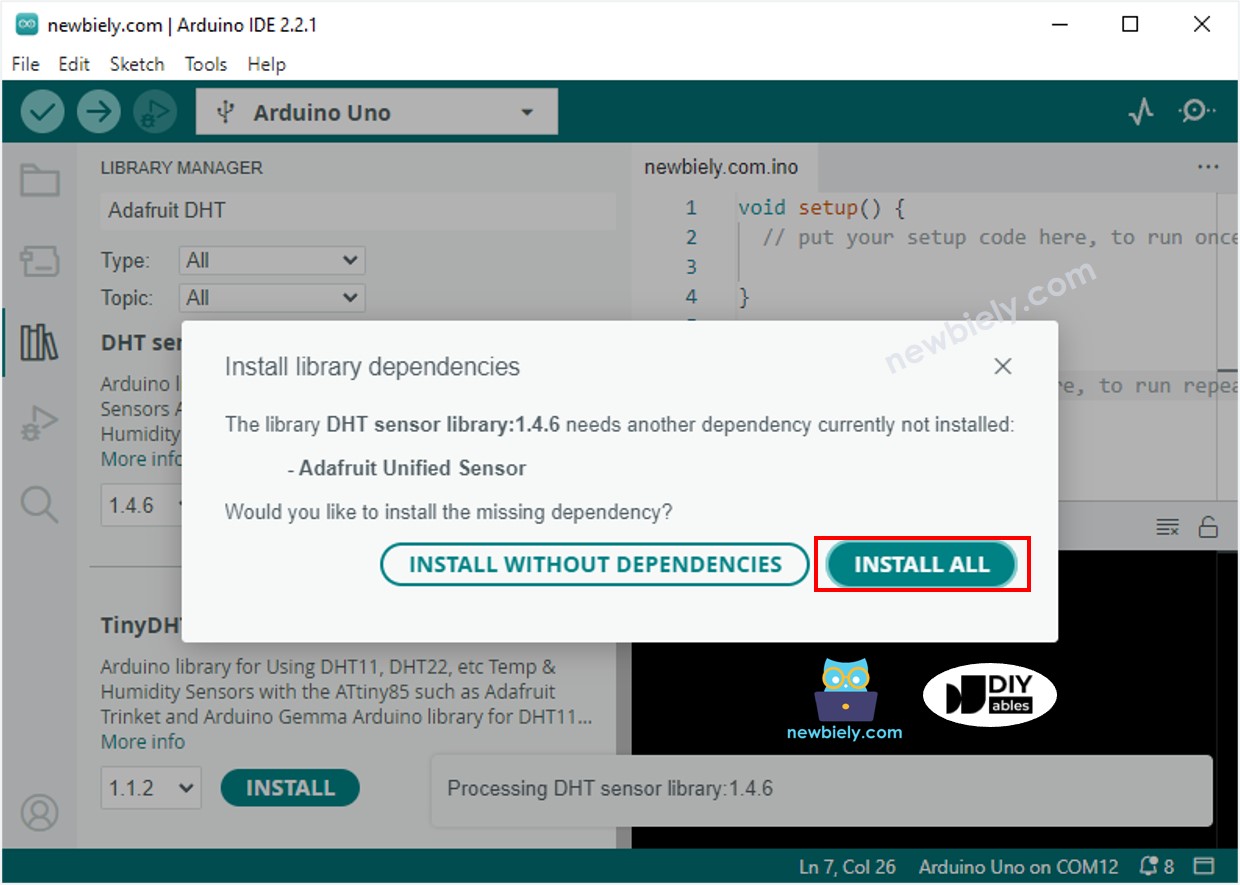
- You will be requested to install some other library dependencies.
- Click the Install All button to install all of the library dependencies.
- Copy the code and open it with the Arduino IDE.
- Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to compile and upload the code to the ESP8266.
- Place the sensor in hot and cold water, or hold it in your hand.
- Check out the result on the OLED display and in the Serial Monitor.
※ NOTE THAT:
The code in question will center the text both horizontally and vertically on an OLED display.
ESP8266 Code - DHT22 Sensor - OLED
※ NOTE THAT:
The code for the DHT11 and DHT22 is the same, apart from a single line. The library for both of these is the same too.
