ESP8266 - Control Servo Motor via Web
This tutorial instructs you how to use the ESP8266 to control a servo motor via the web from a browser on your smartphone or PC. We'll use something called WebSocket to control the servo motor smoothly and dynamically through a graphical web user interface.
Now, why use WebSocket? Here's the idea:
- Without WebSocket, every time you want to change the angle of the servo, you have to reload the page. Not great!
- But with WebSocket, we set up a special connection between the webpage and the ESP8266. This means we can send the angle value to the ESP8266 in the background, without reloading the page. That makes the servo move smoothly and in real-time. Pretty cool, huh?
Let's start!
Hardware Preparation
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some of these links are for products from our own brand, DIYables .
Overview of Servo Motor and WebSocket
We have specific tutorials about servo motor and WebSocket. Each tutorial contains detailed information and step-by-step instructions about hardware pinout, working principle, wiring connection to ESP8266, ESP8266 code... Learn more about them at the following links:
- ESP8266 - Servo Motor tutorial
- ESP8266 - WebSocket tutorial
How It Works
The ESP8266 code creates both a web server and a WebSocket Server. Here's how it works:
- When you enter the ESP8266's IP address in a web browser, it requests the webpage (User Interface) from the ESP8266.
- The ESP8266's web server responds by sending the webpage's content (HTML, CSS, JavaScript).
- Your web browser then displays the webpage.
- The JavaScript code within the webpage establishes a WebSocket connection to the WebSocket server on the ESP8266.
- Once this WebSocket connection is established, if you turn the handle on the webpage, the JavaScript code quietly sends the angle value to the ESP8266 through this WebSocket connection in the background.
- The WebSocket server on the ESP8266, upon receiving the angle value, controls the servo motor accordingly.
In a nutshell, the WebSocket connection enables the smooth, real-time control of the servo motor angle.
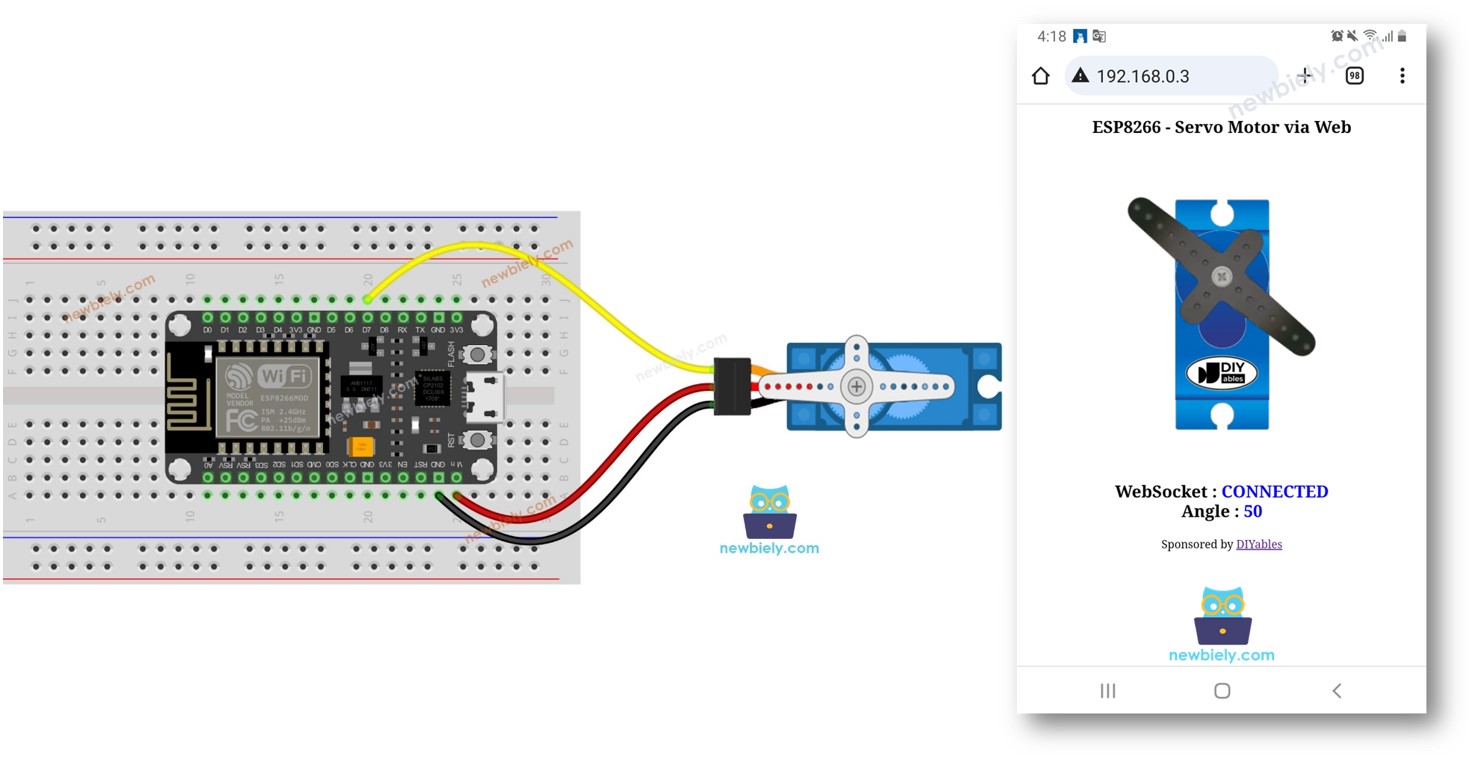
Wiring Diagram between Servo Motor and ESP8266
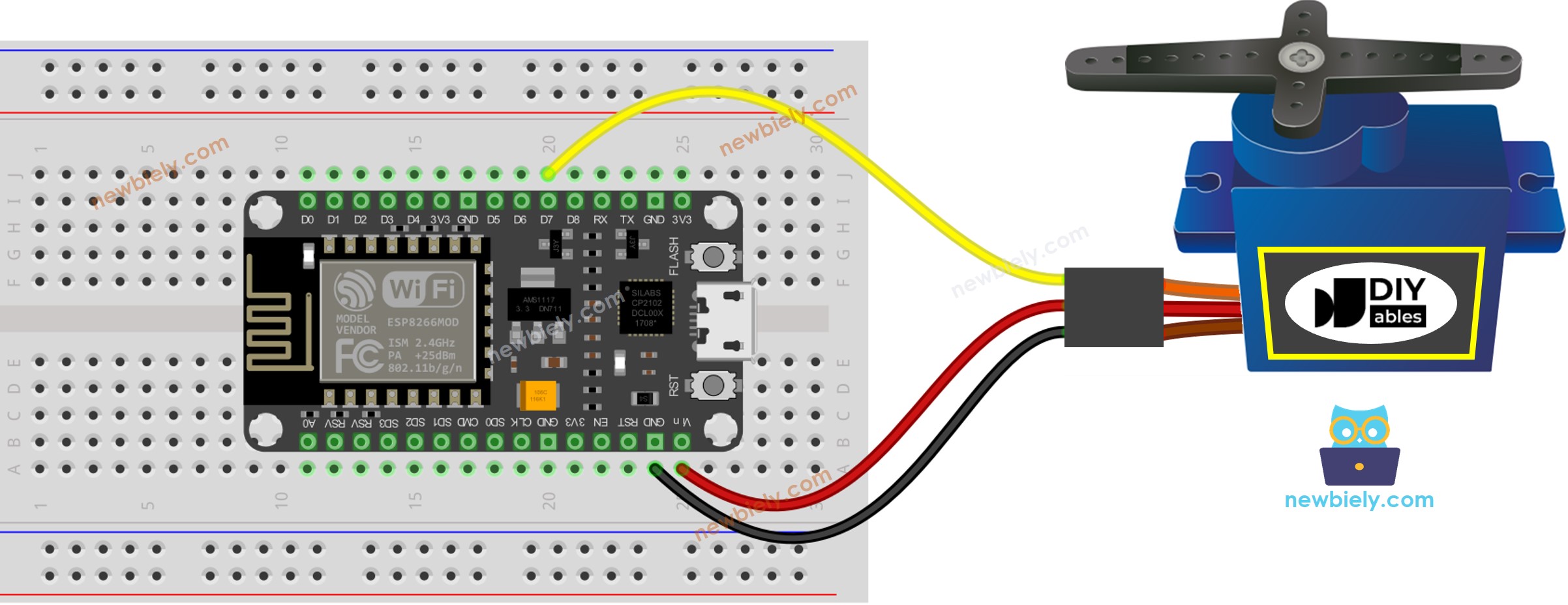
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
For the sake of simplicity, the above wiring diagram is used for the testing or learning purposes, and for small-torque servo motor. In practice, we highly recommend using the external power supply for the servo motor. The below wiring diagram shows how to connect servo motor to an external power source.
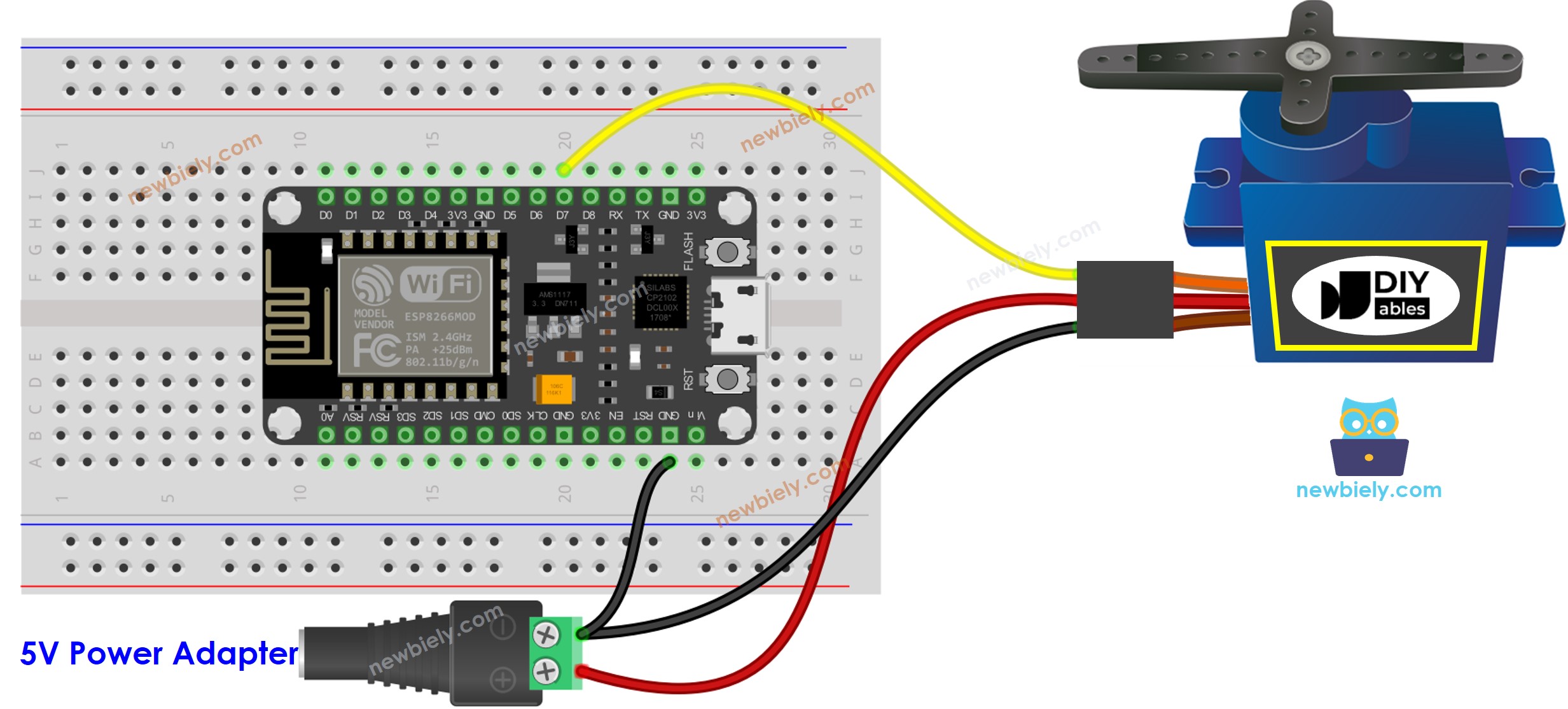
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
See more in ESP8266's pinout and how to supply power to the ESP8266 and other components.
ESP8266 Code
The webpage's content (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) are stored separately on an index.h file. So, we will have two code files on Arduino IDE:
- An .ino file that is ESP8266 code, which creates a web sever and WebSocket Server, and control servo motor
- An .h file, which contains the webpage's content.
Detailed Instructions
To get started with ESP8266 on Arduino IDE, follow these steps:
- Check out the how to setup environment for ESP8266 on Arduino IDE tutorial if this is your first time using ESP8266.
- Wire the components as shown in the diagram.
- Connect the ESP8266 board to your computer using a USB cable.
- Open Arduino IDE on your computer.
- Choose the correct ESP8266 board, such as (e.g. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), and its respective COM port.
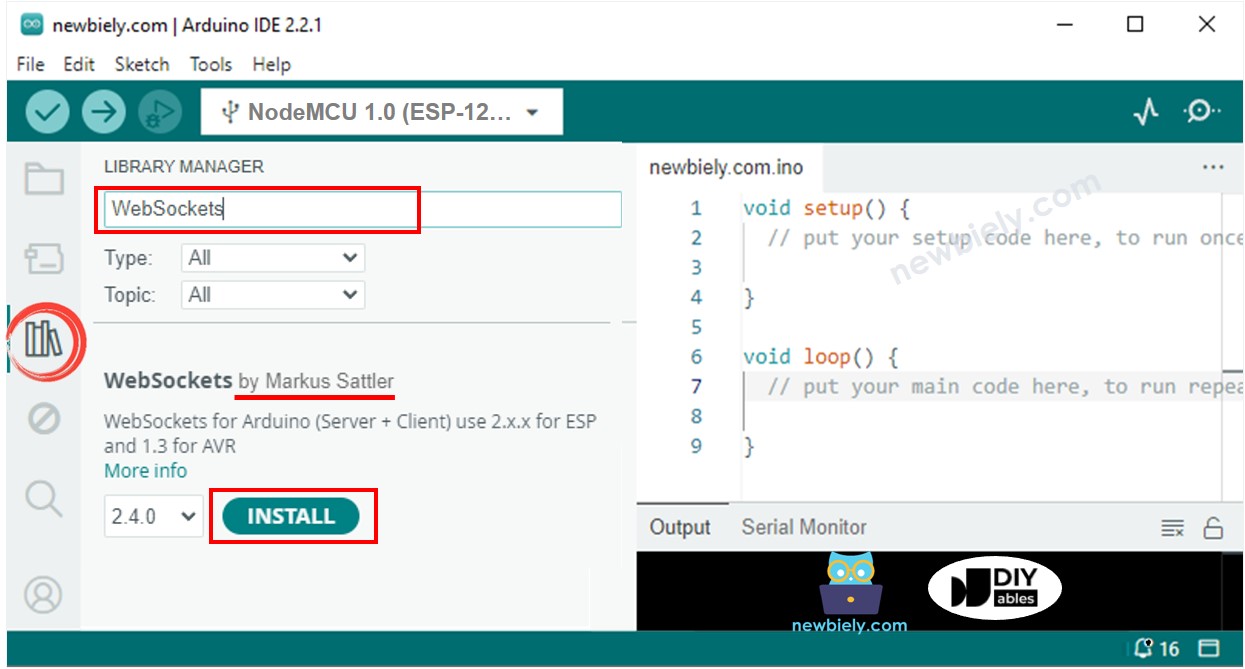
- Open the Library Manager by clicking on the Library Manager icon on the left navigation bar of Arduino IDE.
- Search “WebSockets”, then find the WebSockets created by Markus Sattler.
- Click Install button to install WebSockets library.
- On Arduino IDE, create new sketch, Give it a name, for example, newbiely.com.ino
- Copy the below code and open with Arduino IDE
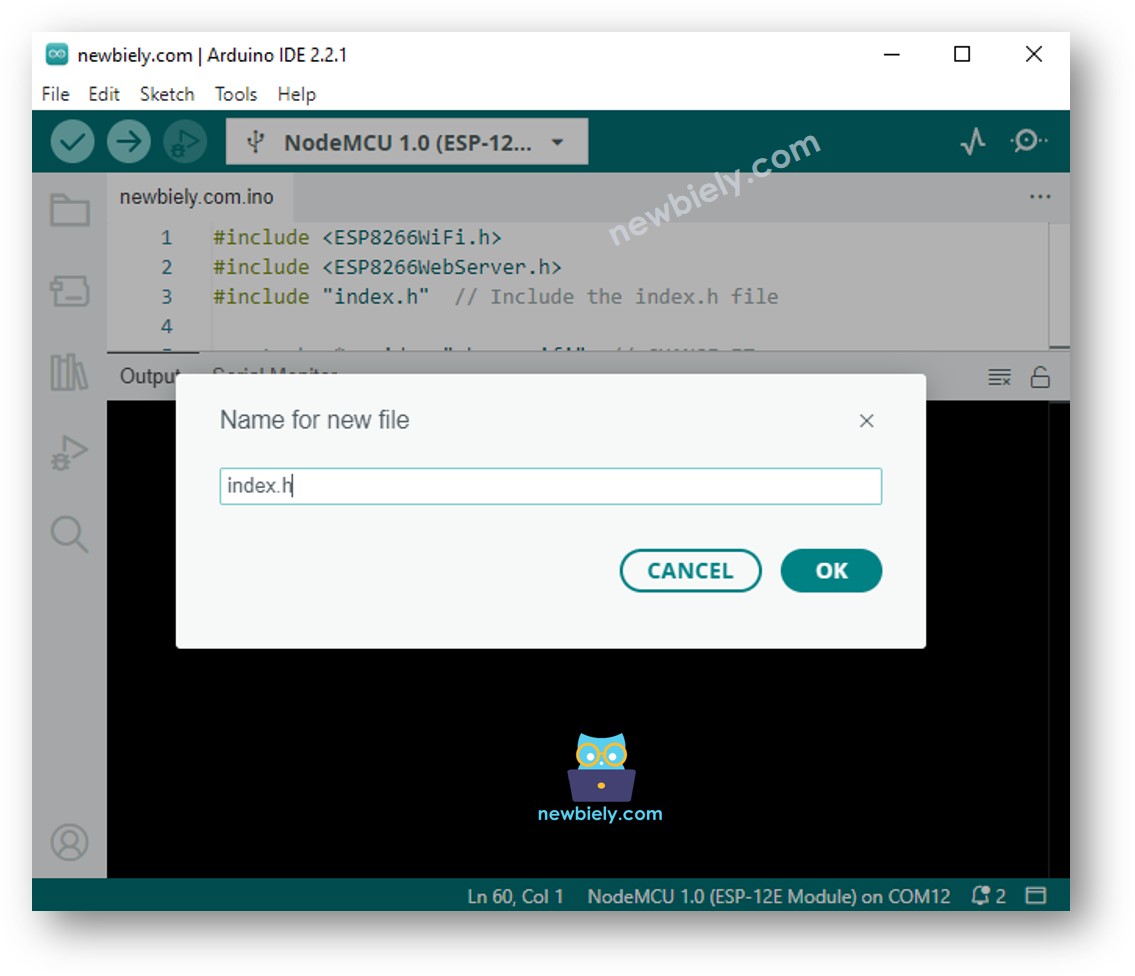
- Create the index.h file On Arduino IDE by:
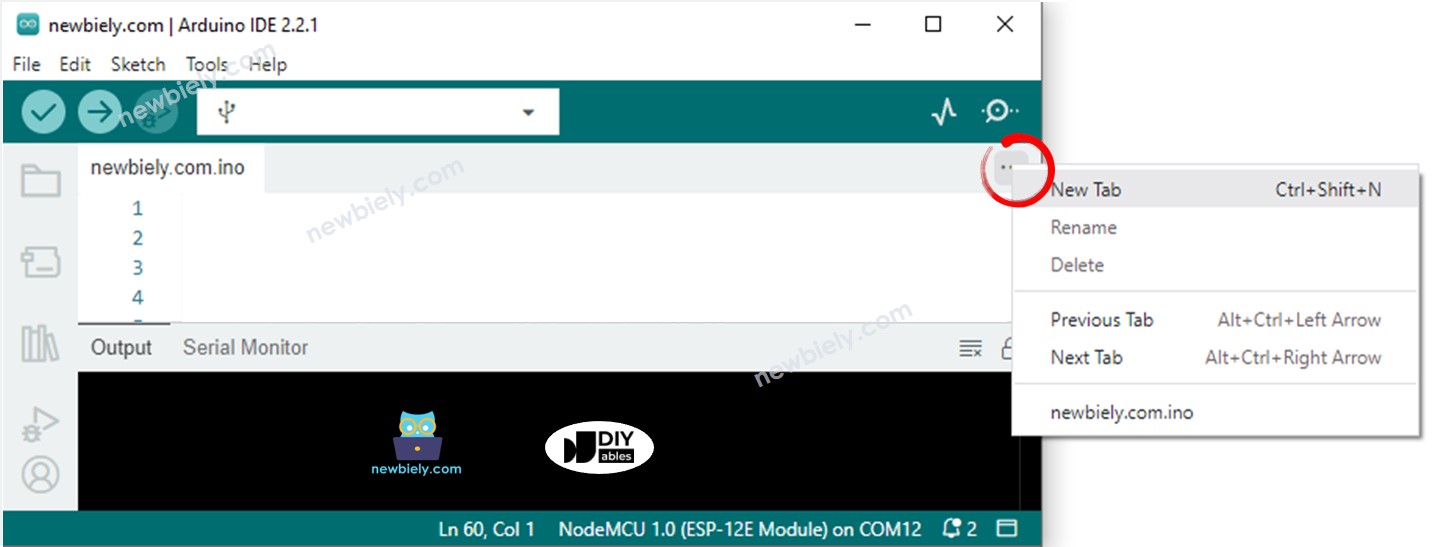
- Either click on the button just below the serial monitor icon and choose New Tab, or use Ctrl+Shift+N keys.
- Give the file's name index.h and click OK button
- Copy the below code and paste it to the index.h.
- Now you have the code in two files: newbiely.com.ino and index.h
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to ESP8266
- Open the Serial Monitor
- Check out the result on Serial Monitor.
- Take note of the IP address displayed, and enter this address into the address bar of a web browser on your smartphone or PC.
- You will see the webpage it as below:
- The JavaScript code of the webpage automatically creates the WebSocket connection to ESP8266.
- Now you can control the servo motor's angle via the web interface.
- If you modify the HTML content in the index.h and does not touch anything in newbiely.com.ino file, when you compile and upload code to ESP8266, Arduino IDE will not update the HTML content.
- To make Arduino IDE update the HTML content in this case, make a change in the newbiely.com.ino file (e.g. adding empty line, add a comment....)

To save the memory of ESP8266, the images of servo motor are NOT stored on ESP8266. Instead, they are stored on the internet, so, your phone or PC need to have internet connection to load images for the web control page.
※ NOTE THAT:
Line-by-line Code Explanation
The above ESP8266 code contains line-by-line explanation. Please read the comments in the code!
